This article provides insufficient context for those unfamiliar with the subject.(February 2022) |
Feed-through null follows the duplexer and is commonly used with continuous-wave radar to improve performance.
This article provides insufficient context for those unfamiliar with the subject.(February 2022) |
Feed-through null follows the duplexer and is commonly used with continuous-wave radar to improve performance.
The transmitter is constantly issuing high power RF with continuous wave radar. Some of the transmit signal will leak into the receiver when the receive antenna is near the transmit antenna.
The signal that leaks from the transmitter to the receiver is called bleed-through. Electronic circuits have limited dynamic range, and this reduces receiver sensitivity.
Feed-through nulling significantly reduces the bleed-through signal, which can be used to increase receiver sensitivity in continuous wave radar. [1]
There are two kinds of feed-through nuller.
A sample of the transmit signal is fed to an attenuator.
The feed-through nuller samples the bleed-through signal arriving at the receiver. This bleed-through sample is amplified, filtered (low-pass), and this is used to drive the attenuator.
Attenuator output is phase shifted 180 degrees added to the receive signal. This cancels the bleed-through signal.
Total gain determines the amount of cancellation.
A passive feed-through nuller uses a band-stop filter to reduce low-frequency signals before digital signal sampling, and this includes the bleed-through signal.
The band-pass filter used with a microwave receiver is typically 1 MHz. The band-stop filter used as a feed-through nuller is typically 1kHz, which attenuates signals in the center of the band-pass filter.
The band-stop filter is generally wide enough to reduce clutter, in addition to the bleed-through signal.
Passive feed-through nulling is not used with CW radar altimeters because this eliminates the ground-bounce signal.

Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (ranging), angle, or velocity of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the object(s). Radio waves from the transmitter reflect off the object and return to the receiver, giving information about the object's location and speed.
A duplexer is an electronic device that allows bi-directional (duplex) communication over a single path. In radar and radio communications systems, it isolates the receiver from the transmitter while permitting them to share a common antenna. Most radio repeater systems include a duplexer. Duplexers can be based on frequency, polarization, or timing.

In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas.

A Doppler radar is a specialized radar that uses the Doppler effect to produce velocity data about objects at a distance. It does this by bouncing a microwave signal off a desired target and analyzing how the object's motion has altered the frequency of the returned signal. This variation gives direct and highly accurate measurements of the radial component of a target's velocity relative to the radar.

Very low frequency or VLF is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3–30 kHz, corresponding to wavelengths from 100 to 10 km, respectively. The band is also known as the myriameter band or myriameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten myriameters. Due to its limited bandwidth, audio (voice) transmission is highly impractical in this band, and therefore only low data rate coded signals are used. The VLF band is used for a few radio navigation services, government time radio stations and for secure military communication. Since VLF waves can penetrate at least 40 meters (131 ft) into saltwater, they are used for military communication with submarines.

A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects (attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
A continuous wave or continuous waveform (CW) is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency, typically a sine wave, that for mathematical analysis is considered to be of infinite duration. Continuous wave is also the name given to an early method of radio transmission, in which a sinusoidal carrier wave is switched on and off. Information is carried in the varying duration of the on and off periods of the signal, for example by Morse code in early radio. In early wireless telegraphy radio transmission, CW waves were also known as "undamped waves", to distinguish this method from damped wave signals produced by earlier spark gap type transmitters.

In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation.

A diplexer is a passive device that implements frequency-domain multiplexing. Two ports are multiplexed onto a third port. The signals on ports L and H occupy disjoint frequency bands. Consequently, the signals on L and H can coexist on port S without interfering with each other.
Beamforming or spatial filtering is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in an antenna array in such a way that signals at particular angles experience constructive interference while others experience destructive interference. Beamforming can be used at both the transmitting and receiving ends in order to achieve spatial selectivity. The improvement compared with omnidirectional reception/transmission is known as the directivity of the array.
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics.

Continuous-wave radar is a type of radar system where a known stable frequency continuous wave radio energy is transmitted and then received from any reflecting objects. Individual objects can be detected using the Doppler effect, which causes the received signal to have a different frequency from the transmitted signal, allowing it to be detected by filtering out the transmitted frequency.
Passive radar systems encompass a class of radar systems that detect and track objects by processing reflections from non-cooperative sources of illumination in the environment, such as commercial broadcast and communications signals. It is a specific case of bistatic radar, the latter also including the exploitation of cooperative and non-cooperative radar transmitters.
A radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies between about 30 Hz and 300 GHz. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary parts of all systems that use radio: radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, wireless networks, radar, two way radios like walkie talkies, radio navigation systems like GPS, remote entry systems, among numerous other uses.
A radio transmitter or receiver is connected to an antenna which emits or receives the radio waves. The antenna feed system or antenna feed is the cable or conductor, and other associated equipment, which connects the transmitter or receiver with the antenna and makes the two devices compatible. In a radio transmitter, the transmitter generates an alternating current of radio frequency, and the feed system feeds the current to the antenna, which converts the power in the current to radio waves. In a radio receiver, the incoming radio waves excite tiny alternating currents in the antenna, and the feed system delivers this current to the receiver, which processes the signal.

A radio repeater is a combination of a radio receiver and a radio transmitter that receives a signal and retransmits it, so that two-way radio signals can cover longer distances. A repeater sited at a high elevation can allow two mobile stations, otherwise out of line-of-sight propagation range of each other, to communicate. Repeaters are found in professional, commercial, and government mobile radio systems and also in amateur radio.
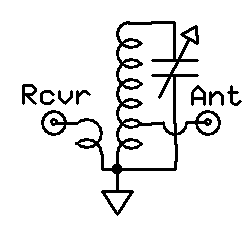
A preselector is a name for an electronic device that connects between a radio antenna and a radio receiver. The preselector is a band-pass filter that blocks troublesome out-of-tune frequencies from passing through from the antenna into the radio receiver that otherwise would be directly connected to the antenna.

Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications.
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes some unwanted components or features from a signal. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal. Most often, this means removing some frequencies or frequency bands. However, filters do not exclusively act in the frequency domain; especially in the field of image processing many other targets for filtering exist. Correlations can be removed for certain frequency components and not for others without having to act in the frequency domain. Filters are widely used in electronics and telecommunication, in radio, television, audio recording, radar, control systems, music synthesis, image processing, and computer graphics.

Two-tone testing is a means of testing electronic components and systems, particularly radio systems, for intermodulation distortion. It consists of simultaneously injecting two sinusoidal signals of different frequencies (tones) into the component or system. Intermodulation distortion usually occurs in active components like amplifiers, but can also occur in some circumstances in passive items such as cable connectors, especially at high power.