
The aspS RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. aspS motifs are found in a specific lineage of Actinomycetota.
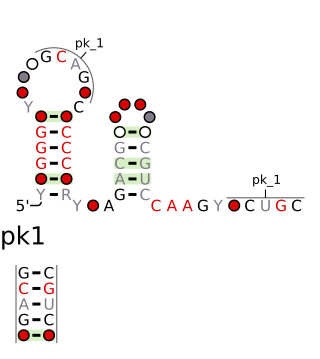
The chrB-a RNA motif and chrB-b RNA motif refer to a related, conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The structures of these motifs are similar, and some genomic locations are predicted to exhibit both motifs. The chrB-b motif has an extra pseudoknot that is not consistently found in chrB-a examples. It was proposed that the two motifs could be unified into one common structure, with additional information.

The COG3943 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. COG3943 motifs are found in unknown bacteria whose genomic DNA was isolated from cow rumen. As of 2018, there is no specific, classified organism that is known to contain a COG3943 motif RNA.

The dinG RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. dinG motifs are found in Clostridiales.
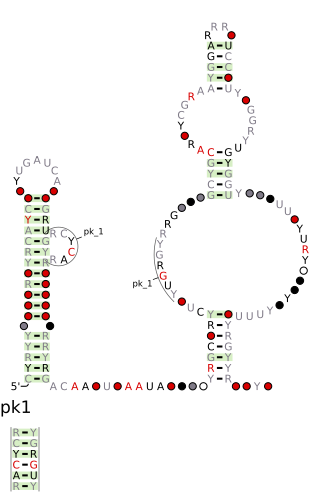
The DUF2800 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF2800 motif RNAs are found in Bacillota. DUF2800 RNAs are also predicted in the phyla Actinomycetota and Synergistota, although these RNAs are likely the result of recent horizontal gene transfer or conceivably sequence contamination.

The DUF3577 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF3577 motifs are found in the organism Cardiobacterium valvarum and metagenomic sequences from unknown organisms.

The folE RNA motif, now known as the THF-II riboswitch, is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. folE motifs are found in Alphaproteobacteria.
The freshwater-2 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Freshwater-2 motif RNAs are found in metagenomic sequences that are isolated from aquatic and especially freshwater environments. As of 2018, no freshwater-2 RNA has been identified in a classified organism.

The GA-cis RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. GA-cis motif RNAs are found in one species classified within the phylum Bacillota: specifically, there are 9 predicted copies in Coprocuccus eutactus ATCC 27759.

The ilvH RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. ilvH motifs are found in Betaproteobacteria.
lysM RNA motifs are conserved RNA structures that were discovered by bioinformatics. Such bacterial motifs are defined by consistently being upstream of 'lysM' genes, which encode lysin protein domains, a conserved domain that participates in cell wall degradation. lysM motif RNAs likely function as cis-regulatory elements, in view of their positions upstream of protein-coding genes, although this hypothesis is not certain.
malK RNA motifs are conserved RNA structures that were discovered by bioinformatics. They are defined by being consistently located upstream of malK genes, which encode an ATPase that is used by transporters whose ligand is likely a kind of sugar. Most of these genes are annotated either as transporting maltose or glycerol-3-phosphate, however the substrate of the transporters associated with malK motif RNAs has not been experimentally determined. All known types of malK RNA motif are generally located nearby to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence of the downstream gene.

The nhaA-I RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. nhaA-I motif RNAs are found in Acidobacteriota, alpha-, beta- and Gammaproteobacteria, Verrucomicrobiota and the tentative phylum NC10.
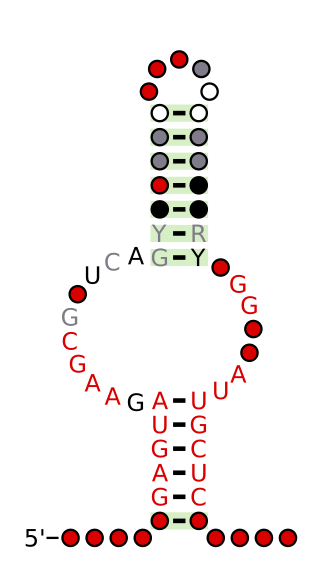
The NMT1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. NMT1 motif RNAs are found in Pseudomonadota. There is also one NMT1 RNA in each of Bacteroidota and Actinomycetota, but these appear to be the result of recent horizontal gene transfer or sequence contamination before or during genome sequencing

The osmY RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. osmY motif RNAs are found in Enterobacteriaceae organisms, although it is not predicted to reside in Escherichia coli.
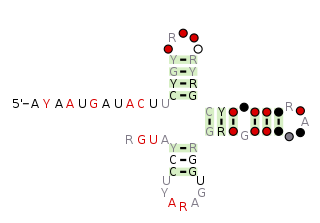
The pemK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. pemK motif RNAs are found in organisms within the phylum Bacillota, and is very widespread in this phylum.

The PGK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. PGK motif RNAs are found in metagenomic sequences isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals. PGK RNAs have not yet been detected in a classified organism.
A Streptomyces-metKH RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Such motifs are found in the genus Streptomyces, and are present upstream of either metK genes, which encode the S-adenosylmethionine synthetase enzyme or metH genes, which encodes the adenosylcobalamin-dependent form of methionine synthase. The RNA structures upstream of metK and metH genes are distinct from each other, but exhibit overall similar sequence and secondary structure features, suggesting that they are related to one another. Their presence upstream of protein-coding genes, and the fact that the genes perform related steps in metabolism, suggests that the RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.

The xerDC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. xerDC motif RNAs are found in Clostridia.
















