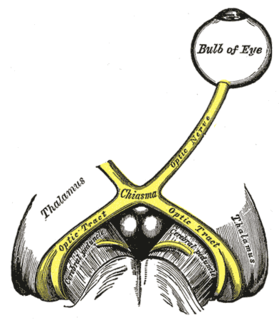
Septo-optic dysplasia (SOD), known also as de Morsier syndrome, is a rare congenital malformation syndrome that features a combination of the underdevelopment of the optic nerve, pituitary gland dysfunction, and absence of the septum pellucidum . Two or more of these features need to be present for a clinical diagnosis — only 30% of patients have all three. French-Swiss doctor Georges de Morsier first recognized the relation of a rudimentary or absent septum pellucidum with hypoplasia of the optic nerves and chiasm in 1956.
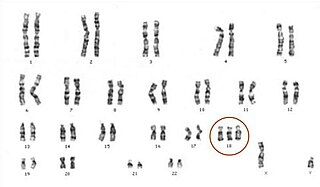
Edwards syndrome, also known as trisomy 18, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of a third copy of all or part of chromosome 18. Many parts of the body are affected. Babies are often born small and have heart defects. Other features include a small head, small jaw, clenched fists with overlapping fingers, and severe intellectual disability.

Cardiofaciocutaneous (CFC) syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder, and is one of the RASopathies. It was first described in 1986.

Primrose syndrome is a rare, slowly progressive genetic disorder that can vary symptomatically between individual cases, but is generally characterised by ossification of the external ears, learning difficulties, and facial abnormalities. It was first described in 1982 in Scotland's Royal National Larbert Institution by Dr D.A.A. Primrose.

Jacobsen syndrome is a rare chromosomal disorder resulting from deletion of genes from chromosome 11 that includes band 11q24.1. It is a congenital disorder. Since the deletion takes place on the q arm of chromosome 11, it is also called 11q terminal deletion disorder. The deletion may range from 5 million to 16 million deleted DNA base pairs. The severity of symptoms depends on the number of deletions; the more deletions there are, the more severe the symptoms are likely to be.

Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome is a disorder that affects development of the limbs, head, and face. The features of this syndrome are highly variable, ranging from very mild to severe. People with this condition typically have one or more extra fingers or toes (polydactyly) or an abnormally wide thumb or big toe (hallux).
Abruzzo–Erickson syndrome is an extremely rare disorder characterized by deafness, protruding ears, coloboma, a cleft palate or palatal rugosity, radial synostosis, and short stature. It was first characterized by Abruzzo and Erickson in 1977 as a CHARGE like syndrome as variably expressed among a family of two brothers, their mother, and their maternal uncle. Members of this family exhibited many of the CHARGE symptoms, but notably did not have choanal atresia and the brothers experienced typical genital development. Due to the recent discovery of this disorder, its etiology is not fully known but it is understood that it arises from mutations on the TBX22 gene on the X-chromosome. The disorder is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. There is currently no known cure but its symptoms can be treated.
49,XXXXY syndrome is an extremely rare aneuploidic sex chromosomal abnormality. It occurs in approximately 1 out of 85,000 to 100,000 males. This syndrome is the result of maternal non-disjunction during both meiosis I and II. It was first diagnosed in 1960 and was coined Fraccaro syndrome after the researcher.
1p36 deletion syndrome is a congenital genetic disorder characterized by moderate to severe intellectual disability, delayed growth, hypotonia, seizures, limited speech ability, malformations, hearing and vision impairment, and distinct facial features. The symptoms may vary, depending on the exact location of the chromosomal deletion.

Cat eye syndrome (CES) or Schmid–Fraccaro syndrome is a rare condition caused by an abnormal extra chromosome, i.e. a small supernumerary marker chromosome. This chromosome consists of the entire short arm and a small section of the long arm of chromosome 22. In consequence, individuals with the cat eye syndrome have three (trisomic) or four (tetrasomic) copies of the genetic material contained in the abnormal chromosome instead of the normal two copies. The prognosis for patients with CES varies depending on the severity of the condition and their associated signs and symptoms, especially when heart or kidney abnormalities are seen.

Young–Simpson syndrome (YSS) is a rare congenital disorder with symptoms including hypothyroidism, heart defects, facial dysmorphism, cryptorchidism in males, hypotonia, mental retardation, and postnatal growth retardation.
Potocki–Shaffer syndrome (PSS), also known as DEFECT11 syndrome or chromosome 11p11.2 deletion syndrome, is a rare contiguous gene syndrome that results from the microdeletion of section 11.2 on the short arm of chromosome 11 (11p11.2). The syndrome has its name from Dr. Lorraine (Lori) Potocki and Dr. Lisa Shaffer who discovered the deletion on the 11th chromosome and studied the impacts.

Microcephaly deafness syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder which consists of microcephaly, congenital hearing loss, mild intellectual disability, speech delay, low height, and facial dysmorphisms. Only 2 cases of this disorder have been recorded in medical literature; a mother and her son. The researchers who discovered this disorder later suggested that this disorder was inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, although the genetic cause of it has never been found. It's estimated to affect less than 1 in a million people worldwide.
Ichthyosis-intellectual disability-dwarfism-renal impairment is a very rare autosomal recessive ichthyotic genetic disorder which consists of congenital ichthyosis, intellectual disabilities, dwarfism/short stature and renal impairment. This condition has been described only in four members of an Iranian family and was discovered in the summer of 1975.
Cleft palate short stature vertebral anomalies, also known as Mathieu-De Broca-Bony syndrome, is a very rare multi-systemic genetic disorder which is characterized by congenital cleft palate, facial dysmorphisms, short stature and neck, vertebral abnormalities and intellectual disabilities. It is thought to be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.
Aortic arch anomaly - peculiar facies - intellectual disability is a rare, genetic, congenital developmental anomaly which is characterized by heart abnormalities, cranio-facial dysmorphia, and intellectual disabilities. No new cases have been reported since 1968.

Cataract-ataxia-deafness syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by mild intellectual disabilities, congenital cataracts, progressive hearing loss, ataxia, peripheral neuropathy, and short height. Only two cases have been reported in medical literature.
Blepharophimosis intellectual disability syndromes are a group of rare genetic disorders which are characterized by blepharophimosis, ptosis and intellectual disabilities. These disorders usually follow one of the following inheritance patterns: autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, x-linked recessive, and mitochondrial.
Osteopathia striata with cranial sclerosis (OSCS) is a rare genetic entity characterized by osseous abnormalities.

Mandibulofacial dysostosis with microcephaly syndrome, also known as growth delay-intellectual disability-mandibulofacial dysostosis-microcephaly-cleft palate syndrome, mandibulofacial dysostosis, guion-almeida type, or simply as MFDM syndrome is a rare genetic disorder which is characterized by developmental delays, intellectual disabilities, and craniofacial dysmorphisms.









