Related Research Articles

The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Siberia is accordingly called the Northeast Passage (NEP). The various islands of the archipelago are separated from one another and from Mainland Canada by a series of Arctic waterways collectively known as the Northwest Passages, Northwestern Passages or the Canadian Internal Waters.

The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, Canada, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon. The lower half of the river continues westward through the U.S. state of Alaska. The river is 3,190 kilometres (1,980 mi) long and empties into the Bering Sea at the Yukon–Kuskokwim Delta. The average flow is 6,400–7,000 m3/s (230,000–250,000 cu ft/s). The total drainage area is 833,000 km2 (321,500 sq mi), of which 323,800 km2 (125,000 sq mi) lies in Canada. The total area is more than 25% larger than Texas or Alberta.

The Beaufort Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores.

Nares Strait is a waterway between Ellesmere Island and Greenland that connects the northern part of Baffin Bay in the Atlantic Ocean with the Lincoln Sea in the Arctic Ocean. From south to north, the strait includes Smith Sound, Kane Basin, Kennedy Channel, Hall Basin and Robeson Channel. Nares Strait has a nearly permanent current from the north, powered by the Beaufort Gyre, making it harder to traverse for ships coming from the south.

Lincoln Sea is a body of water in the Arctic Ocean, stretching from Cape Columbia, Canada, in the west to Cape Morris Jesup, Greenland, in the east. The northern limit is defined as the great circle line between those two headlands. It is covered with sea ice throughout the year, the thickest sea ice in the Arctic Ocean, which can be up to 15 m (49 ft) thick. Water depths range from 100 m (330 ft) to 300 m (980 ft). Water and ice from Lincoln Sea empty into Robeson Channel, the northernmost part of Nares Strait, most of the time.
Edward C. Carmack is a Senior Research Scientist Emeritus for the Department of Fisheries and Oceans in Sidney, British Columbia. He formally worked with the Institute of Ocean Sciences in Sidney, British Columbia and as an Adjunct professor at the University of British Columbia.

The Arctic sea ice covers less area in the summer than in the winter. The multi-year sea ice covers nearly all of the central deep basins. The Arctic sea ice and its related biota are unique, and the year-round persistence of the ice has allowed the development of ice endemic species, meaning species not found anywhere else.

The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately 14,060,000 km2 (5,430,000 sq mi) and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been also been described as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.

The bowhead whale is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and is the only living representative of the genus Balaena. It is the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, and is named after its characteristic massive triangular skull, which it uses to break through Arctic ice. Other common names of the species included the Greenland right whale, Arctic whale, steeple-top, and polar whale.

The Beaufort Gyre is one of the two major ocean currents in the Arctic Ocean. It is roughly located north of the Alaskan and Canadian coast. In the past, Arctic sea-ice would circulate in the Beaufort gyre up to several years, leading to the formation of very thick multi-year sea-ice. Due to warming temperatures in the Arctic, the gyre has lost an extensive amount of ice, practically turning what used to be a nursery for sea-ice to mature and grow into the thickest and oldest ice of the Arctic Ocean into a "graveyard" for older ice.
Undersaturation is a state of a solution that contains less of a dissolved material than could be dissolved by that quantity of solvent under normal circumstances. It can also refer to a vapor of a compound that has a lower (partial) pressure than the compound's vapor pressure. Undersaturation is often followed by ingassing of the solvate until saturation is reached. Most states of solution involve undersaturation.

Katharine Anne Giles was a British climate scientist. Her research considered sea ice cover, ocean circulation and wind patterns. She was a passionate science communicator, and since 2015, the Association of British Science Writers has held a science communication award in her honour.
Cecilia M. Bitz is an American climatologist known for her research on sea ice and high-latitude climate change. She is a professor and chair in the Atmospheric Sciences Department, as well as the director of the Program on Climate Change at the University of Washington. She was featured on NPR's All Things Considered segment to speak about factors that lead to sea ice loss in 2007, and testified before the United States Senate committee of Energy and Natural Resources on arctic opportunities in 2015.
William Li is a Canadian biological oceanographer who did research on marine picoplankton, marine macroecology, ocean surveys of plankton from measurements of flow cytometry, and detection of multi-annual ecological change in marine phytoplankton.
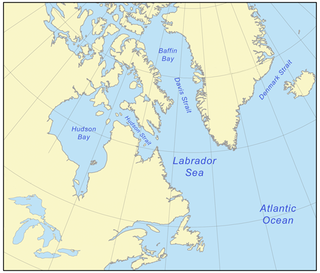
The Canadian Arctic Rift System is a major North American geological structure extending from the Labrador Sea in the southeast through Davis Strait, Baffin Bay and the Arctic Archipelago in the northwest. It consists of a series of interconnected rifts that formed during the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Extensional stresses along the entire length of the rift system have resulted in a variety of tectonic features, including grabens, half-grabens, basins and faults.
The Eurekan orogeny was a Phanerozoic mountain building event that affected the eastern portion of the Arctic Archipelago and, to a lesser extent, northern Greenland. Deformation initiated in the Late Cretaceous, during which time the Sverdrup Basin began to fragment and fold in response to the counterclockwise rotation of Greenland, caused by seafloor spreading in the Canadian Arctic Rift System. Isostatic uplift was most pronounced in the Grantland Mountains and Victoria and Albert Mountains on Ellesmere Island and in the Princess Margaret Range on Axel Heiberg Island, as evidenced by the current physiography. Compression in a broad zone on Ellesmere Island resulted in the formation of the Eurekan Fold Belt.
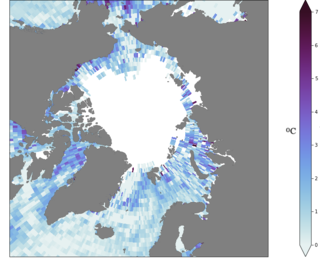
Atlantification is the increasing influence of Atlantic water in the Arctic. Warmer and saltier Atlantic water is extending its reach northward into the Arctic Ocean. The Arctic Ocean is becoming warmer and saltier and sea-ice is disappearing as a result. The process can be seen on the figure on the far right, where the sea surface temperature change in the past 50 years is shown, which is up to 5 degrees in some places. This change in the Arctic climate is most prominent in the Barents Sea, a shallow shelf sea north of Scandinavia, where sea-ice is disappearing faster than in any other Arctic region, impacting the local and global ecosystem.
Marika Holland is a scientist at the National Center for Atmospheric Research known for her work on modeling sea ice and its role in the global climate.
Mary-Louise Elizabeth Timmermans is a marine scientist known for her work on the Arctic Ocean. She is the Damon Wells Professor of Earth and Planetary Sciences at Yale University.
Rebecca Woodgate is a professor at the University of Washington known for her work on ocean circulation in polar regions.
References
- 1 2 "Fiona A. McLaughlin: Research Scientist". Department of Fisheries and Oceans. 11 December 2008. Archived from the original on 2010-07-25.
- ↑ Jennifer Holland (January 2004). "Northern Exposure". National Geographic . Archived from the original on 2010-01-16.
- ↑ Ed Struzik (2007). "Swirling Sea of Vast Surprises" (PDF). The 2006 Atkinson Fellowship in Public Policy. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-06.
Fiona McLaughlin was one of a handful of scientists back then who tracked a stream of relatively cold, freshwater water from the Beaufort migrating all the way to the Labrador Sea. This was right around the time the cod fishery was collapsing.
- ↑ McLaughlin, Fiona Ann (1996). Geochemical and physical water mass properties and halocarbon ventilation in the Southern Canadian Basin of the Arctic Ocean (Thesis). OCLC 858552741.
- ↑ McLaughlin, Fiona Ann (2000). The Canada basin, 1989-1995: upstream events and far-field effects of the Barents Sea branch (Thesis). Ottawa: National Library of Canada = Bibliothèque nationale du Canada. OCLC 47947449.
- ↑ Margaret Munro (19 November 2009). "Climate change causing 'corrosive' water to affect Arctic marine life: study". Canwest. Archived from the original on 2009-11-25.
- ↑ Grebmeier, J. M.; James E. Overland; Sue E. Moore; Ed V. Farley; Eddy C. Carmack; Lee W. Cooper; Karen E. Frey; John H. Helle; Fiona A. McLaughlin; S. Lyn McNutt (10 March 2006). "A Major Ecosystem Shift in the Northern Bering Sea". Science. 311 (5766): 1461–1464. Bibcode:2006Sci...311.1461G. doi:10.1126/science.1121365. PMID 16527980. S2CID 23505224.