
The Throgs Neck Bridge is a suspension bridge in New York City, carrying six lanes of Interstate 295 (I-295) over the East River where it meets the Long Island Sound. The bridge connects the Throggs Neck section of the Bronx with the Bay Terrace section of Queens.

The Robert F. Kennedy Bridge is a complex of bridges and elevated expressway viaducts in New York City. The bridges link the boroughs of Manhattan, Queens, and the Bronx. The viaducts cross Randalls and Wards Islands, previously two islands and now joined by landfill.

The Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge is a suspension bridge connecting the boroughs of Staten Island and Brooklyn in New York City, United States. It spans the Narrows, a body of water linking the relatively enclosed New York Harbor with Lower New York Bay and the Atlantic Ocean. It is the only fixed crossing of the Narrows. The double-deck bridge carries 13 lanes of Interstate 278: seven on the upper level and six on the lower level. The span is named for Giovanni da Verrazzano, who in 1524 was the first European explorer to enter New York Harbor and the Hudson River.

The Great South Bay is a lagoon situated between Long Island and Fire Island, in the State of New York. It is about 45 miles (72 km) long and has an average depth of 4 feet 3 inches (1.3 m) and is 20 feet (6.1 m) at its deepest. It is protected from the Atlantic Ocean by Fire Island, a barrier island, as well as the eastern end of Jones Beach Island and Captree Island.

The Marine Parkway–Gil Hodges Memorial Bridge is a vertical-lift bridge in New York City, New York, that crosses Rockaway Inlet. The bridge, which opened on July 3, 1937, connects the Rockaway Peninsula in Queens, with Flatbush Avenue to Floyd Bennett Field, Belt Parkway, and the Marine Park neighborhood in Brooklyn. The bridge is designated as New York State Route 901B, an unsigned reference route.

Jones Beach State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of New York. It is located in southern Nassau County on Jones Beach Island, a barrier island linked to Long Island by the Meadowbrook State Parkway, Wantagh State Parkway, and Ocean Parkway. The park was created during Robert Moses' administration as President of the Long Island State Park Commission as part of the development of parkways on Long Island.
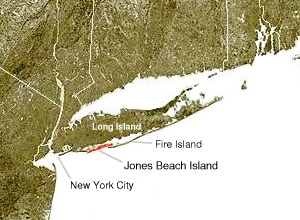
Jones Beach Island is one of the outer barrier islands off the southern coast of Long Island in the U.S. state of New York.

Fire Island is the large center island of the outer barrier islands parallel to the South Shore of Long Island in the U.S. state of New York.

The Bronx–Whitestone Bridge is a suspension bridge in New York City, carrying six lanes of Interstate 678 over the East River. The bridge connects Throggs Neck and Ferry Point Park in the Bronx, on the East River's northern shore, with the Whitestone neighborhood of Queens on the southern shore.

The Robert Moses Causeway is an 8.10-mile (13.04 km) state parkway in Suffolk County, New York on Long Island. It is named for the master builder and urban planner Robert Moses. The parkway, originally known as the Captree Causeway, connects West Islip on Long Island to the barrier beach islands, such as Captree Island, Jones Beach Island, and the western tip of Fire Island, to the south. It is designated New York State Route 908J (NY 908J), an unsigned reference route.

Fire Island National Seashore (FINS) is a United States National Seashore that protects a 26-mile (42 km) section of Fire Island, an approximately 30-mile (48 km) long and 0.5-mile (0.80 km) wide barrier island separated from Long Island by the Great South Bay. The island is part of New York State's Suffolk County and the Outer Barrier.

The Francis Scott Key Bridge, more commonly known as the Key Bridge, is a six-lane reinforced concrete arch bridge carrying U.S. Route 29 (US 29) across the Potomac River between the Rosslyn neighborhood of Arlington County, Virginia, and the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C. Completed in 1923, it is Washington's oldest surviving road bridge across the Potomac River.

The Outer Barrier, also known as the Long Island and New York City barrier islands, refers to the string of barrier islands that divide the lagoons south of Long Island, New York from the Atlantic Ocean. These islands include Long Beach Barrier Island, Barnum Island, Jones Beach Island, Fire Island and Westhampton Island. The outer barrier extends 75 miles (121 km) along the South Shore of Long Island, from the Rockaway Peninsula in New York City to the east end of Shinnecock Bay in Suffolk County.

The East Rockaway Inlet is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean which separates the Rockaway Peninsula from the barrier island which includes the Nassau County, New York communities of Atlantic Beach, Long Beach and Lido Beach. The inlet is on the south shore of Long Island. It provides for a channel 12 feet deep and 250 feet wide. A 3,000 foot jetty on the western side of the channel was authorized but never constructed, and was eventually deauthorized by Congress in 1977.

The Great South Bay Bridge is a twin-span bridge on the southwest side of Suffolk County, New York, on Long Island. It carries the Robert Moses Causeway over the Great South Bay, between Long Island's South Shore and Captree Island. It serves as access via the Robert Moses Causeway to both of the downstream crossings, the State Boat Channel Bridge and the Fire Island Inlet Bridge, also leading visitors and on-lookers to the Captree State Park, Fire Island Lighthouse, Jones Beach Island, or Robert Moses State Park.

The Smith Point Bridge is a steel bascule drawbridge in Shirley, New York that connects Long Island to Fire Island. Located on the south shore of central Suffolk County, the bridge carries William Floyd Parkway across The Narrows between Bellport Bay and Moriches Bay. It connects Long Island with Smith Point County Park and the Otis Pike Fire Island High Dune Wilderness, both are a part of the Fire Island National Seashore.

The State Boat Channel Bridge is a twin-span bascule bridge in Suffolk County, New York, United States. It carries the Robert Moses Causeway over the Long Island New York State Boat Channel between Captree Island and Jones Beach Island, in Oak Beach and Captree on the Babylon–Islip town border.
In 1938, after the destruction to Fire Island from the Long Island Express hurricane, Robert Moses and W. Earle Andrews, both part of the Long Island State Park Commission, proposed reconstruction of the island. This proposal included an extension of the Ocean Parkway out from its terminus at Captree State Park across Fire Island to Westhampton. This new parkway, which would boast 22 feet (6.7 m) wide roadways, would have connections back to the mainland at Smith Point County Park and Ponquogue with parkway spurs across Shinnecock Bay and the Great South Bay. The new spur at Ponquogue, deemed the Ponquogue Parkway, would have marked the eastern terminus of the new Ocean Parkway extension. The proposal lived until the cut-back to Smith Point County Park in 1962 for environmental issues with such a construction, ending any proposal for a parkway in the area of Hampton Bays.

The Mill Basin Bridge is a seven-lane, fixed girder bridge in Brooklyn. It is owned and maintained by the New York City Department of Transportation (NYCDOT) and spans Mill Basin inlet. Completed in February 2019, the span replaces a Bascule bridge originally constructed in 1940. The bridge carries passenger vehicles via the Belt Parkway and pedestrians and cyclists via the Jamaica Bay Greenway.

Captree is a census-designated place (CDP) in the towns of Islip and Babylon in Suffolk County, New York, United States. It occupies Captree Island in Great South Bay, as well as the east end of Jones Beach Island to the south, comprising Captree State Park. It was first listed as a CDP prior to the 2020 census. Prior to that it was part of the Oak Beach–Captree CDP.





















