Related Research Articles

Yellowstone National Park is a national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowstone National Park Protection Act and signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant on March 1, 1872. Yellowstone was the first national park in the U.S. and is also widely held to be the first national park in the world. The park is known for its wildlife and its many geothermal features, especially the Old Faithful geyser, one of its most popular. While it represents many types of biomes, the subalpine forest is the most abundant. It is part of the South Central Rockies forests ecoregion.

The Old Faithful Inn is a hotel in the western United States with a view of the Old Faithful Geyser, located in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. The Inn has a multi-story log lobby, flanked by long frame wings containing guest rooms. In the western portion of the park, it sits at an approximate elevation of 7,350 feet (2,240 m) above sea level.

Old Faithful is a cone geyser in Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming, United States. It was named in 1870 during the Washburn–Langford–Doane Expedition and was the first geyser in the park to be named. It is a highly predictable geothermal feature and has erupted every 44 minutes to two hours since 2000. The geyser and the nearby Old Faithful Inn are part of the Old Faithful Historic District.

The geothermal areas of Yellowstone include several geyser basins in Yellowstone National Park as well as other geothermal features such as hot springs, mud pots, and fumaroles. The number of thermal features in Yellowstone is estimated at 10,000. A study that was completed in 2011 found that a total of 1,283 geysers have erupted in Yellowstone, 465 of which are active during an average year. These are distributed among nine geyser basins, with a few geysers found in smaller thermal areas throughout the Park. The number of geysers in each geyser basin are as follows: Upper Geyser Basin (410), Midway Geyser Basin (59), Lower Geyser Basin (283), Norris Geyser Basin (193), West Thumb Geyser Basin (84), Gibbon Geyser Basin (24), Lone Star Geyser Basin (21), Shoshone Geyser Basin (107), Heart Lake Geyser Basin (69), other areas (33). Although famous large geysers like Old Faithful are part of the total, most of Yellowstone's geysers are small, erupting to only a foot or two. The hydrothermal system that supplies the geysers with hot water sits within an ancient active caldera. Many of the thermal features in Yellowstone build up sinter, geyserite, or travertine deposits around and within them.

Riverside Geyser is a geyser in Yellowstone National Park in the U.S. state of Wyoming.

Fort Yellowstone was a U.S. Army fort, established in 1891 at Mammoth Hot Springs in Yellowstone National Park. Yellowstone was designated in 1872 but the Interior Department was unable to effectively manage the park. Administration was transferred to the War Department in August 1886 and General Philip Sheridan sent a company of cavalry to Mammoth Hot Springs to build a cavalry post. The army originally called the post Camp Sheridan in honor of General Sheridan but the name was changed to Fort Yellowstone in 1891 when construction of the permanent fort commenced. The army administered the park until 1918 when it was transferred to the newly created National Park Service. The facilities of Fort Yellowstone now comprise the Yellowstone National Park headquarters, the Horace Albright Visitor Center and staff accommodations.

The Firehole River is located in northwestern Wyoming, and is one of the two major tributaries of the Madison River. It flows north approximately 21 miles (34 km) from its source in Madison Lake on the Continental Divide to join the Gibbon River at Madison Junction in Yellowstone National Park. It is part of the Missouri River system.

National Park Service rustic – sometimes colloquially called Parkitecture – is a style of architecture that developed in the early and middle 20th century in the United States National Park Service (NPS) through its efforts to create buildings that harmonized with the natural environment. Since its founding in 1916, the NPS sought to design and build visitor facilities without visually interrupting the natural or historic surroundings. The early results were characterized by intensive use of hand labor and a rejection of the regularity and symmetry of the industrial world, reflecting connections with the Arts and Crafts movement and American Picturesque architecture.
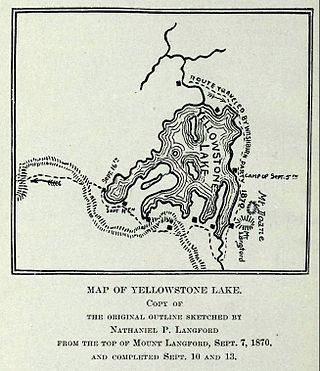
The Washburn Expedition of 1870 explored the region of northwestern Wyoming that two years later became Yellowstone National Park. Led by Henry D. Washburn and Nathaniel P. Langford, and with a U.S. Army escort headed by Lt. Gustavus C. Doane, the expedition followed the general course of the Cook–Folsom–Peterson Expedition made the previous year.

Isa Lake is located in Yellowstone National Park, in the U.S. state of Wyoming. The lake straddles the continental divide at Craig Pass. Indigenous peoples have lived in the Yellowstone region for at least 11,000 years. In the 1800s, at the time of the first European exploration of the area, the region was home to several Indigenous Nations including the Nimíipuu, Absaroke, and Shoshone Nations. Hiram M. Chittenden became the first known European to sight the lake in 1891, while searching for the best routes connecting Old Faithful and the West Thumb Geyser Basin. Chittenden named the lake after Miss Isabel Jelke, from Cincinnati, though it is not clear why.

Herbert Maier was an American architect and public administrator, most notable as an architect for his work at Yosemite, Grand Canyon and Yellowstone National Parks. Maier, as a consultant to the National Park Service, designed four trailside museums in Yellowstone, three of which survive as National Historic Landmarks. Maier played a significant role in the Park Service's use of the National Park Service Rustic style of architecture in western national parks.

Mission 66 was a United States National Park Service ten-year program that was intended to dramatically expand Park Service visitor services by 1966, in time for the 50th anniversary of the establishment of the Park Service.

Angling in Yellowstone National Park is a major reason many visitors come to the park each year and since it was created in 1872, the park has drawn anglers from around the world to fish its waters. In 2006, over 50,000 park fishing permits were issued to visitors. The park contains hundreds of miles of accessible, high-quality trout rivers containing wild trout populations—over 200 creeks, streams and rivers are fishable. There are 45 fishable lakes and several large lakes are easily accessible to visitors. Additionally, the park's remote sections provide anglers ample opportunity to visit rivers, streams, creeks and lakes that receive little angling pressure. With the exception of one specially designated drainage, all the park's waters are restricted to artificial lures and fly fishing. The Madison, Firehole and a section of the Gibbon rivers are restricted to fly fishing only.

The following articles relate to the history, geography, geology, flora, fauna, structures and recreation in Yellowstone National Park.

Firehole Falls is a waterfall on the Firehole River in southwestern Yellowstone National Park in the United States. The falls are located approximately 0.5 miles (0.80 km) upstream from the confluence of the Firehole and Gibbon Rivers at Madison Junction. Firehole Falls has a drop of approximately 40 feet (12 m). The falls are located within Firehole Canyon on Firehole Canyon Drive, a one-way road that parallels the main Madison Junction to Old Faithful road.

Marshall's Hotel, subsequently known as the Firehole Hotel was the first public accommodations built in the Firehole River geyser basins of Yellowstone National Park and among the earliest tourist hotels in Yellowstone. The first hotel was built in 1880 by George W. Marshall (1838-1917) and his partner John B. Goff and was located just west of confluence of the Firehole River and Nez Perce Creek. A second hotel, the Firehole Hotel, was built in 1884 in partnership with George Graham Henderson very near the present day Nez Perce Picnic area. The hotels operated for eleven years under various ownership ceasing operation in 1891. By 1895, all the structures except a few cabins associated with the two hotels had been razed.
The Old Faithful Museum of Thermal Activity was one of a series of four "trailside" museums built in Yellowstone National Park in 1929. Funded by a grant of $118,000 from Laura Spelman Rockefeller, the museums interpreted park features for visitors, and represented an early version of the visitor information center concept that became widespread throughout the National Park Service. The four museums were notable examples of the National Park Service Rustic style, and all were designed by Park Service architect Herbert Maier. The surviving Norris Museum, Fishing Bridge Museum and the Madison Museum are collectively listed as National Historic Landmarks.

Since before the creation of Yellowstone National Park in 1872, entrepreneurs have established hotels and permanent tourist camps to accommodate visitors to the park. Today, Xanterra Parks and Resorts operates hotel and camping concessions in the park on behalf of the National Park Service. This is a list of hotels and permanent tourist camps that have operated or continue to operate in the park.

The Canyon Hotel was built in Yellowstone National Park in 1910 by the Yellowstone Park Company to accommodate visitors to the area of the Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone and Yellowstone Falls. The hotel was built on a huge scale, with a perimeter measurement of one mile. Situated on a hill to the west of the falls, it dominated the landscape. It had an elegant resort-like air when first built. After World War II it was regarded by the National Park Service as outdated. Suffering from neglect, it was abandoned in the late 1950s and was in the process of demolition when it was destroyed by fire in 1960.

Grant Village is a developed area of Yellowstone National Park, offering lodging, camping and other visitor services. It is located on the southwest side of Yellowstone Lake, about 2 miles (3.2 km) south of West Thumb Geyser Basin. Grant Village was developed by the National Park Service and concessioners under the Mission 66 program, in an effort to relocate land-consuming visitor services and accommodations away from the park's major attractions and sensitive features. Grant Village was planned to allow the removal of development encroaching on the thermal basin at West Thumb. Originally named "Thumb Bay," the development was first proposed in 1955 by Park Service director Conrad L. Wirth to accommodate 2500 visitors with restaurants, gas stations, concessions and a marina.
References
- ↑ Carr, Ethan (2007). Mission 66: Modernism and the National Park Dilemma. University of Massachusetts Press. pp. 95–96. ISBN 978-1-55849-587-6.
- ↑ Haines, Aubrey L. (1996). The Yellowstone Story: A History of Our First National Park. University Press of Colorado. pp. 476, 478, 480. ISBN 0-87081-390-0.
- ↑ Barringer, Mark Daniel (2002). Selling Yellowstone: Capitalism and the Construction of Nature. University Press of Kansas. ISBN 0-7006-1167-3.
