
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau.

Since 1848 the Swiss Confederation has been a federal republic of relatively autonomous cantons, some of which have a history of federation that goes back more than 700 years, putting them among the world's oldest surviving republics.
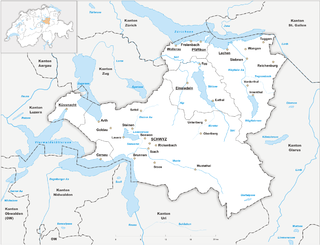
The canton of Schwyz is a canton in central Switzerland between the Alps in the south, Lake Lucerne to the west and Lake Zürich in the north, centred on and named after the town of Schwyz.

Appenzell Ausserrhoden, in English sometimes Appenzell Outer Rhodes, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of twenty municipalities. The seat of the government and parliament is Herisau, and the seat of judicial authorities are in Trogen. It is traditionally considered a "half-canton", the other half being Appenzell Innerrhoden.

Thurgau, anglicized as Thurgovia, and formally as the Canton of Thurgau, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts. Its capital is Frauenfeld.

Appenzell was a canton in the northeast of Switzerland, and entirely surrounded by the canton of St. Gallen, in existence from 1403 to 1597.

The Helvetic Republic was a sister republic of France that existed between 1798 and 1803, during the French Revolutionary Wars. It was created following the French invasion and the consequent dissolution of the Old Swiss Confederacy, marking the end of the ancien régime in Switzerland. Throughout its existence, the republic incorporated most of the territory of modern Switzerland, excluding the cantons of Geneva and Neuchâtel and the old Prince-Bishopric of Basel.

The Sonderbund War of November 1847 was a civil war in Switzerland, then still a relatively loose confederacy of cantons. It ensued after seven Catholic cantons formed the Sonderbund in 1845 to protect their interests against a centralization of power. The war concluded with the defeat of the Sonderbund. It resulted in the emergence of Switzerland as a federal state, concluding the period of political "restoration and regeneration" in Switzerland.

The Old Swiss Confederacy began as a late medieval alliance between the communities of the valleys in the Central Alps, at the time part of the Holy Roman Empire, to facilitate the management of common interests such as free trade and to ensure the peace along the important trade routes through the mountains. The Hohenstaufen emperors had granted these valleys reichsfrei status in the early 13th century. As reichsfrei regions, the cantons of Uri, Schwyz, and Unterwalden were under the direct authority of the emperor without any intermediate liege lords and thus were largely autonomous.

The Protestant Reformation in Switzerland was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrate, Mark Reust, and the population of Zürich in the 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matters in Zürich and spread to several other cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy. Seven cantons remained Catholic, however, which led to intercantonal wars known as the Wars of Kappel. After the victory of the Catholic cantons in 1531, they proceeded to institute Counter-Reformation policies in some regions. The schism and distrust between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons defined their interior politics and paralysed any common foreign policy until well into the 18th century.
The wars of Kappel (Kappelerkriege) is a collective term for two armed conflicts fought near Kappel am Albis between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy during the Reformation in Switzerland.

The Second War of Kappel was an armed conflict in 1531 between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy during the Reformation in Switzerland.

The Old Swiss Confederacy, also known as Switzerland or the Swiss Confederacy, was a loose confederation of independent small states, initially within the Holy Roman Empire. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerland.

The Freiamt or Freie Ämter is a region in Switzerland and is located in the southeast of Canton of Aargau. It comprises the area between the Lindenberg and Heitersberg and from the terminal moraine at Othmarsingen to Reuss river in Dietwil. Today the area of the Bremgarten and Muri Districts are called the Freiamt. Previously, the area around Affoltern District in the canton of Zurich was called the (Zurich) Freiamt.

The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic countries of Europe, or Christendom. Other motives during the wars involved revolt, territorial ambitions and great power conflicts. By the end of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), Catholic France had allied with the Protestant forces against the Catholic Habsburg monarchy. The wars were largely ended by the Peace of Westphalia (1648), which established a new political order that is now known as Westphalian sovereignty.

Kappel Abbey is a former Cistercian monks monastery located in Kappel am Albis in the Swiss canton of Zurich.

The First War of Villmergen was a Swiss religious war which lasted from 5 January until 7 March 1656, at the time of the Old Swiss Confederacy. On one side were the Protestant cantons of Zürich and Bern, on the other the Catholic cantons of Central Switzerland. The Protestants tried to break the political hegemony of the Catholics, that had been in existence ever since the Second Kappel Landfrieden of 1531. The casus belli was the expulsion and execution of Protestants from the Schwyz commune of Arth. The Zürcher unsuccessfully besieged the Central Swiss-allied city of Rapperswil and thereby drove their forces together. The Bernese were defeated and repelled in the First Battle of Villmergen. The Third Landfrieden ended the conflict and restored the pre-war balance of power.
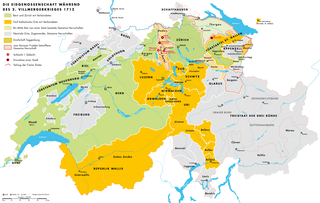
The Toggenburg War, also known as the Second War of Villmergen or the Swiss Civil War of 1712, was a Swiss civil war during the Old Swiss Confederacy from 12 April to 11 August 1712. The Catholic "inner cantons" and the Imperial Abbey of Saint Gall fought the Protestant cantons of Bern and Zürich as well as the abbatial subjects of Toggenburg. The conflict was a religious war, a war for hegemony in the Confederacy and an uprising of subjects. The war ended in a Protestant victory and upset the balance of political power within the Confederacy.

Uri is a Swiss Talschaft and canton in the upper Reuss valley.

The Thurgau was a pagus of the Duchy of Alamannia in the early medieval period. A County of Thurgau existed from the 13th century until 1798. Parts of Thurgau were acquired by the Old Swiss Confederacy during the early 15th century, and the entire county passed to the Confederacy as a condominium in 1460.

















