
Midway Atoll is a 2.4-square-mile (6.2 km2) atoll in the North Pacific Ocean at 28°12′N 177°21′W. Midway is roughly equidistant between North America and Asia. Midway Atoll is an unorganized, unincorporated territory of the United States. Midway continues to be the only island in the Hawaiian archipelago that is not part of the state of Hawaii. Unlike the other Hawaiian islands, Midway observes Samoa Time, which is one hour behind the time in the state of Hawaii. For statistical purposes, Midway is grouped as one of the United States Minor Outlying Islands. The Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge, encompassing 590,991.50 acres (239,165.77 ha) of land and water in the surrounding area, is administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS). The refuge and most of its surrounding area are part of the larger Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument.

An atoll, sometimes called a coral atoll, is a ring-shaped coral reef including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. The coral of the atoll often sits atop the rim of an extinct seamount or volcano which has eroded or subsided partially beneath the water. The lagoon forms over the volcanic crater or caldera while the higher rim remains above water or at shallow depths that permit the coral to grow and form the reefs. For the atoll to persist, continued erosion or subsidence must be at a rate slow enough to permit reef growth upward and outward to replace the lost height.

Bikini Atoll is an atoll in the Marshall Islands that was the site of 23 nuclear tests during the 1940s and 1950s. The atoll consists of 23 islands totalling 3.4 square miles (8.8 km2) surrounding a 229.4-square-mile (594.1 km2) central lagoon. It is at the northern end of the Ralik Chain, approximately 87 kilometres (54 mi) northwest of Ailinginae Atoll and 850 kilometres (530 mi) northwest of Majuro. Within Bikini Atoll, Bikini, Eneu, Namu and Enidrik islands comprise just over 70% of the land area. Bikini and Eneu are the only islands of the atoll that hosted a permanent population. Bikini Island is the northeastern most and largest islet. The atoll was also known as Eschscholtz Atoll, after German naturalist Johann Friedrich von Eschscholtz, until 1946, after the Marshall Islands were captured by the U.S. during World War II.

The Chagos Archipelago or Chagos Islands are a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 individual tropical islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos-Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean.

Rongelap Atoll RONG-gə-lap is a coral atoll of 61 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is 8 square miles (21 km2). It encloses a lagoon with an area of 1,000 square miles (2,600 km2). It is historically notable for its close proximity to US hydrogen bomb tests in 1954, and was particularly devastated by fallout from the Castle Bravo test. The population was evacuated from Rongelap following the test due to high radiation levels, however according to the most recent census in 2011 it has begun to recover with about eighty people living on the atoll.

Kili Island or Kili Atoll is a small, 81 hectares island located in the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. It is the temporary home of 548 inhabitants who are descended from islanders who originally lived on Bikini Atoll. They were relocated when they agreed to let the U.S. government temporarily use their home for nuclear testing in 1945. Kili Island became their home after two prior relocations failed. The island does not have a natural lagoon and cannot produce enough food to enable the islanders to be self-sufficient. It is part of the legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. The island is approximately 48 kilometers (30 mi) southwest of Jaluit. It is one of the smallest islands in the Marshall Islands.
Bigej or Begej Island is part of Kwajalein Atoll in the Ralik Chain in the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI), 2,100 nautical miles (3900 km) southwest of Honolulu, Hawaii.
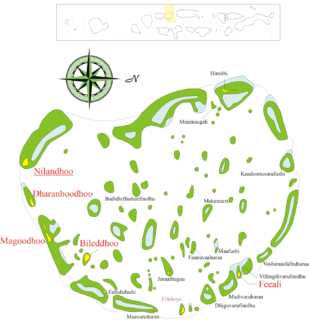
Faafu Atoll is an administrative division of the Maldives.
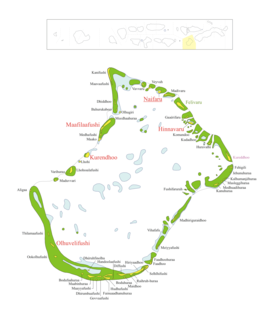
Lhaviyani Atoll is an administrative division of the Maldives. Its abbreviation is Lh.

Thinadhoo is the capital of Gaafu Dhaalu Atoll and the proposed capital for the Upper South Province of the Maldives. It has its own dialect of Dhivehi which is considerably different from northern and mid-Maldivian speech.
Maafilaafushi is one of the inhabited islands of Lhaviyani Atoll in the Maldives.
Maakandoodhoo is one of the uninhabited islands of the Shaviyani Atoll administrative division and geographically part of the Miladhummadulhu Atoll in the Maldives.

Milandhoo is an island in the Shaviyani Atoll administrative division of the Maldives and geographically part of the Miladhummadulhu group in Thiladhunmati Atoll.

The Carteret Islands are Papua New Guinea islands located 86 km (53 mi) north-east of Bougainville in the South Pacific. The atoll has a scattering of low-lying islands called Han, Jangain, Yesila, Yolasa and Piul, in a horseshoe shape stretching 30 km (19 mi) in north-south direction, with a total land area of 0.6 square kilometres (0.2 sq mi) and a maximum elevation of 1.5 metres above sea level.
The flag of Bikini Atoll, a member of the Marshall Islands, closely resembles the flag of the United States and was adopted in 1987. The flag is symbolic of the islanders' belief that a great debt is still owed by the United States to the people of Bikini because in 1954 the United States government detonated the Castle Bravo hydrogen bomb on the island, poisoning islanders and others with nuclear fallout.

Takuu, formerly known as Tauu and also known as Takuu Mortlock or Marqueen Islands, is a small, isolated atoll off the east coast of Bougainville in Papua New Guinea.
Taroa is an island in the east of Maloelap Atoll in the Marshall Islands. During World War II, it was the site of a major Japanese airfield. The airfield was destroyed towards the end of World War II, and wreckage and remnants of the base can still be seen around the island.

Faadhippolhu Atoll is an administrative division of the Maldives. It corresponds to the natural atoll of the same name.
Dhuvaafaru is an inhabited island of Maldives located in the eastern edge of Raa Atoll. Resettlement of the island started on 14 December 2008 to inhabit the displaced residents of Kandholhudhoo who were the victims of the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami.

The nuclear testing at Bikini Atoll program was a series of 23 nuclear devices detonated by the United States between 1946 and 1958 at seven test sites on the reef itself, on the sea, in the air and underwater. The test weapons produced a combined fission yield of 42.2 Mt of explosive power.














