
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent, for 320 years (1206–1526). Following the invasion of South Asia by the Ghurid dynasty, five dynasties ruled over the Delhi Sultanate sequentially: the Mamluk dynasty (1206–1290), the Khalji dynasty (1290–1320), the Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1414), the Sayyid dynasty (1414–1451), and the Lodi dynasty (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh as well as some parts of southern Nepal.

The Second Battle of Panipat was fought on 5 November 1556, between Akbar and the king of Delhi, Hemu. Hemu had conquered Delhi and Agra a few weeks earlier by defeating Mughal forces under Tardi Beg Khan in the battle of Delhi and crowned himself Raja Vikramaditya at Purana Quila in Delhi.

Sultan Firuz Shah Tughlaq was a Muslim ruler from the Tughlaq dynasty, who reigned over the Sultanate of Delhi from 1351 to 1388. He succeeded his cousin Muhammad bin Tughlaq following the latter's death at Thatta in Sindh, where Muhammad bin Tughlaq had gone in pursuit of Taghi the rebellious Muslim governor of Gujarat. For the first time in the history of the Sultanate, a situation was confronted wherein nobody was ready to accept the reins of power. With much difficulty, the camp followers convinced Firoz to accept the responsibility. In fact, Khwaja Jahan, the Wazir of Muhammad bin Tughlaq had placed a small boy on the throne claiming him to be the son of Muhammad bin Tughlaq, who meekly surrendered afterwards. Due to widespread unrest, his realm was much smaller than Muhammad's. Tughlaq was forced by rebellions to concede virtual independence to Bengal and other provinces. He established Sharia across his realm.
Mahendra Sūri is the 14th century Jain astronomer who wrote the Yantraraja, the first Indian treatise on the astrolabe. He was trained by Madana Sūri, and was teacher to Malayendu Sūri. Jainism had a strong influence on mathematics particularly in the last couple of centuries BC. By the time of Mahendra Suri, however, Jainism had lost support as a national religion and was much less vigorous.
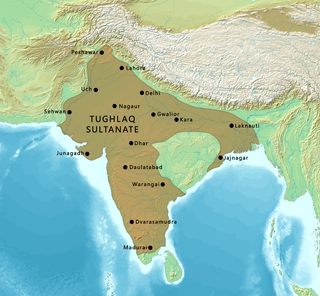
The Tughlaq dynasty was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq. The dynasty ended in 1413.
The Arghun dynasty ruled over the area adjoining Southern Afghanistan and then the Sindh Sultanate from the late 15th century to the early 16th century. Arghun rule can be divided into two branches: the Arghun branch of Dhu'l-Nun Beg Arghun that ruled until 1554, and the Tarkhan branch of Muhammad Isa Tarkhan that ruled until 1593.

Islam Shah Suri, born Jalal Khan, also known as Salim Shah Suri, was the second ruler of the Suri dynasty which ruled parts of India in the mid-16th century. He was the second son of Sher Shah Suri.

Muhammad Adil Shah was the fourth ruler of the Suri dynasty, a late medieval Afghan dynasty in the northern Indian subcontinent.

Adil Shah Suri was the seventh and final ruler of the Sur Empire. He was the brother in law of Sikandar Shah Suri, who ruled over a region east of Delhi after Sikandar Shah Suri was defeated by Humayun in 1555. He and Sikandar Shah Suri were contenders for the Delhi throne against the Mughal emperor Akbar.
Firuz-Shah Zarrin-Kolah was a Kurdish dignitary, and the seventh in the ancestral line of Shaykh Safi Ardabili, the eponym of the Safavid dynasty of Iran.

Ahmed Shah Al Wali Bahamani was the ruler of the Bahmani Sultanate from 1 October 1422 to 17 April 1436, and was a great patron of arts and culture. He brought Persian artisans from Iran, including the metal-worker Abdulla-bin-Kaiser, who was the master of Bidriware, the inlaying of zinc alloy with silver and gold.

Muhammad Khan Sur, also known by his regnal title Shamsuddin Muhammad Shah Ghazi, was the Sultan of Bengal from 1553 to 1555. He was initially appointed as a governor of Bengal by Emperor Islam Shah Suri of the Sur Empire in 1545, but after his death, he declared independence and re-established the Bengal Sultanate. He conquered Arakan of Burma, and ordered of striking silver 'tanka' coins for Bengal.
Feroz or variants such as Firuz, Firuze, Peroz or Piruz may refer to:

Taj ud-Din Firoz Shah, also known as Firoz Shah Bahmani, was the ruler of the Bahmani Sultanate from 16 November 1397 to 22 September 1422. Firuz Shah is considered an important ruler of the Bahamani Sultanate. He expanded his kingdom and even succeeded in conquering the Raichur Doab from Vijaynagara kingdoms.

The siege of Bijapur began in March 1685 and ended in September 1686 with a Mughal victory. The siege began when Aurangzeb dispatched his son, Muhammad Azam Shah, with a force of nearly 50,000 men to capture Bijapur Fort and defeat Sikandar Adil Shah, the then ruler of Bijapur, who refused to be a vassal of the Mughal Empire. The siege of Bijapur was among the longest military engagements of the Mughals, lasting more than 15 months until Aurangzeb personally arrived to organize a victory.
Events from the year 1554 in India.

ʿAlā ad-Dīn Fīrūz Shāh was the son and successor of Sultan Nasiruddin Nasrat Shah of Bengal. He served as a governor of Chittagong during his father's reign, and was a patron of Bengali literature. Firuz Shah ascended the throne in 1533, though it was not unanimously recognised by all the nobles of Bengal. The conflict with the Ahom kingdom continued during his reign and the Bengali army led by Turbak Khan had reached as far as Kaliabor. Within three months as Sultan, Firuz Shah was assassinated by his uncle, who succeeded him as Sultan Ghiyasuddin Mahmud Shah.
Gujarat, a region in western India, fell under the Delhi Sultanate following repeated expeditions under Alauddin Khalji around the end of the 13th century. He ended the rule of Vaghela dynasty under Karna II and established Muslim rule in Gujarat. Soon the Tughluq dynasty came to power in Delhi whose emperor carried out expeditions to quell rebellion in Gujarat and established their firm control over the region by the end of the century. Following Timur's invasion of Delhi, the Delhi Sultanate weakened considerably so that the last Tughluq governor Zafar Khan declared himself independent in 1407 and formally established the Gujarat Sultanate.

Yantrarāja is the Sanskrit name for the ancient astronomical instrument called astrolabe. It is also the title of a Sanskrit treatise on the construction and working of the astrolabe composed by a Jain astronomer Mahendra Sūri in around 1370 CE.











