Anatomy is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology.

Māori, or te reo Māori, commonly shortened to te reo, is an Eastern Polynesian language and the language of the Māori people, the indigenous population of mainland New Zealand. A member of the Austronesian language family, it is related to Cook Islands Māori, Tuamotuan, and Tahitian. The Maori Language Act 1987 gave the language recognition as one of New Zealand's official languages. There are regional dialects. Prior to contact with Europeans, Māori lacked a written language or script. Written Māori now uses the Latin script, which was adopted and the spelling standardised by Northern Māori in collaboration with English Protestant clergy in the 19th century.

The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments: vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles.
Barnes & Barnes were an American musical duo, formed in Los Angeles in 1970. Most commonly associated with novelty music and comedy rock, their music also incorporated elements of new wave, synth-pop, and folk rock.
Tahitian is a Polynesian language, spoken mainly on the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It belongs to the Eastern Polynesian group.

Of Montreal is an American indie pop band from Athens, Georgia. It was founded by frontperson Kevin Barnes in 1996, named after a failed romance between Barnes and a woman "of Montreal". The band is identified as part of the Elephant 6 collective. Throughout its existence, of Montreal's musical style has evolved considerably and drawn inspiration from 1960s psychedelic pop acts.

Wellington Harbour, officially called Wellington Harbour / Port Nicholson, is a large natural harbour on the southern tip of New Zealand's North Island. The harbour entrance is from Cook Strait. Central Wellington is located on parts of the western and southern sides of the harbour, and the suburban area of Lower Hutt is to the north and east.
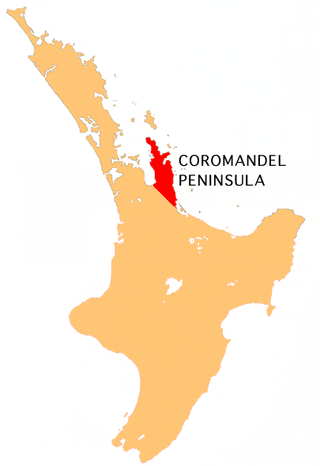
The Coromandel Peninsula on the North Island of New Zealand extends 85 kilometres (53 mi) north from the western end of the Bay of Plenty, forming a natural barrier protecting the Hauraki Gulf and the Firth of Thames in the west from the Pacific Ocean to the east. It is 40 kilometres (25 mi) wide at its broadest point. Almost its entire population lives on the narrow coastal strips fronting the Hauraki Gulf and the Bay of Plenty. In clear weather the peninsula is clearly visible from Auckland, the country's biggest city, which lies on the far shore of the Hauraki Gulf, 55 kilometres (34 mi) to the west. The peninsula is part of the Thames-Coromandel District and the Waikato Region.

Lake Karapiro is an artificial reservoir lake on the Waikato River at Karapiro, 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) south-east of Cambridge in New Zealand's North Island. The lake was formed in 1947 by the damming of the Waikato River to store water for the 96-megawatt Karapiro power station. The lake is also one of two premier rowing venues in New Zealand and is the base for the country's high-performance rowing programme.
Cook Islands Māori is an Eastern Polynesian language that is the official language of the Cook Islands. Cook Islands Māori is closely related to New Zealand Māori, but is a distinct language in its own right. Cook Islands Māori is simply called Māori when there is no need to disambiguate it from New Zealand Māori, but it is also known as Māori Kūki ʻĀirani or, controversially, Rarotongan. Many Cook Islanders also call it Te reo Ipukarea, literally "the language of the Ancestral Homeland".

Māori mythology and Māori traditions are two major categories into which the remote oral history of New Zealand's Māori may be divided. Māori myths concern tales of supernatural events relating to the origins of what was the observable world for the pre-European Māori, often involving gods and demigods. Māori tradition concerns more folkloric legends often involving historical or semi-historical forebears. Both categories merge in whakapapa to explain the overall origin of the Māori and their connections to the world which they lived in.
In Māori mythology, as in other Polynesian traditions, Māui is a culture hero and a trickster, famous for his exploits and cleverness. He possessed superhuman strength, and was capable of shapeshifting into animals such as birds and worms.
Tamambo, or Malo, is an Oceanic language spoken by 4,000 people on Malo and nearby islands in Vanuatu. It is one of the most conservative Southern Oceanic languages.
Staring at the Sun may refer to:

The mouth is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity, is also the first part of the alimentary canal, which leads to the pharynx and the gullet. In tetrapod vertebrates, the mouth is bounded on the outside by the lips and cheeks — thus the oral cavity is also known as the buccal cavity — and contains the tongue on the inside. Except for some groups like birds and lissamphibians, vertebrates usually have teeth in their mouths, although some fish species have pharyngeal teeth instead of oral teeth.
The following lists events that happened during 1885 in New Zealand.
"Fish Heads" is a novelty song by comedy rock duo Barnes & Barnes, released as a single in 1978 and later featured on their 1980 album Voobaha. It is the most requested song on the Dr. Demento radio show, and a music video for the song made in 1980 was in regular rotation on MTV. The song was featured on Barnes & Barnes' 1982 Fish Heads 12-inch on Rhino Records.

The skull roof or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes and all land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium.

A plate in animal anatomy may refer to several things:
Sutherland Sound Marine Reserve is a marine reserve covering an area of 449 hectares of Sutherland Sound / Sutherland Sound, in Fiordland on New Zealand's South Island. It was established in 2005 and is administered by the Department of Conservation.










