Flavokavains (also called flavokawains) are a class of chalconoids found in the kava plant. Currently identified types include flavokavain A, flavokavain B, and flavokavain C. [1]
Flavokavains (also called flavokawains) are a class of chalconoids found in the kava plant. Currently identified types include flavokavain A, flavokavain B, and flavokavain C. [1]

Kava or kava kava is a crop of the Pacific Islands. The name kava is from Tongan and Marquesan, meaning 'bitter'; other names for kava include ʻawa (Hawaiʻi), ʻava (Samoa), yaqona (Fiji), sakau (Pohnpei), seka (Kosrae), and malok or malogu. Kava is consumed for its sedating effects throughout the Pacific Ocean cultures of Polynesia, including Hawaii, Vanuatu, Melanesia, and some parts of Micronesia such as Palau. To a lesser extent, it is consumed in nations where it is exported as an herbal medicine.

Kavalactones are a class of lactone compounds found in the kava shrub. Kavalactones are under research for potential to have various psychotropic effects, including anxiolytic and sedative/hypnotic activities.

Hepatotoxicity implies chemical-driven liver damage. Drug-induced liver injury is a cause of acute and chronic liver disease caused specifically by medications.
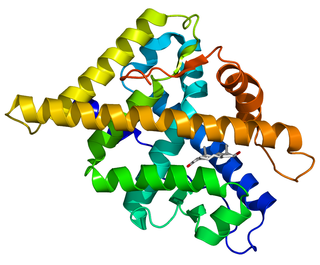
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.

Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2, also known as CD340, proto-oncogene Neu, Erbb2 (rodent), or ERBB2 (human), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ERBB2 gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene isolated from avian genome. It is also frequently called HER2 or HER2/neu.

Seliciclib is an experimental drug candidate in the family of pharmacological cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors that preferentially inhibit multiple enzyme targets including CDK2, CDK7 and CDK9, which alter the growth phase or state within the cell cycle of treated cells. Seliciclib is being developed by Cyclacel.This is a phase II, dose ranging, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Adecatumumab (MT201) is a recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody which is used to target tumor cells. It binds to the epithelial cell adhesion molecule, with the intent to trigger antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. It was developed by Micromet Inc, which was acquired by Amgen.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, also known as cell division protein kinase 2, or Cdk2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of Ser/Thr protein kinases. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28, and S. pombe cdc2, also known as Cdk1 in humans. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinase complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase of the cell cycle, where cells make proteins necessary for mitosis and replicate their DNA. This protein associates with and is regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin E or A. Cyclin E binds G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase while binding with Cyclin A is required to progress through the S phase. Its activity is also regulated by phosphorylation. Multiple alternatively spliced variants and multiple transcription initiation sites of this gene have been reported. The role of this protein in G1-S transition has been recently questioned as cells lacking Cdk2 are reported to have no problem during this transition.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 also known as cell division protein kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK4 gene. CDK4 is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family.
CD16, also known as FcγRIII, is a cluster of differentiation molecule found on the surface of natural killer cells, neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages. CD16 has been identified as Fc receptors FcγRIIIa (CD16a) and FcγRIIIb (CD16b), which participate in signal transduction. The most well-researched membrane receptor implicated in triggering lysis by NK cells, CD16 is a molecule of the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) involved in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). It can be used to isolate populations of specific immune cells through fluorescent-activated cell sorting (FACS) or magnetic-activated cell sorting, using antibodies directed towards CD16.

DNA-dependent protein kinase, catalytic subunit, also known as DNA-PKcs, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene designated as PRKDC or XRCC7. DNA-PKcs belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family. The DNA-Pkcs protein is a serine/threonine protein kinase comprising a single polypeptide chain of 4,128 amino acids.

Desmethoxyyangonin or 5,6-dehydrokavain is one of the six major kavalactones found in the Piper methysticum (kava) plant.

Kavain is the main kavalactone found mostly in the roots of the kava plant.
Fijian cuisine has traditionally been very healthy. Fijians prefer a more tuber and coconut based diet. High caloric foods are good for hard-working villagers who need extra calories while working on their farms but this causes a range of chronic illness such as obesity. Fiji is a multicultural country and is home to people of various races. In most Fijians' homes, food of other cultures is prepared on a regular basis such as Indian curries and Chinese dishes. Fiji is also famous for its seafood.
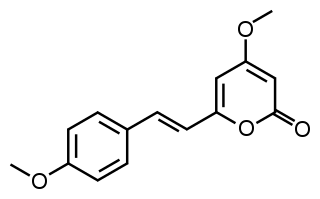
Yangonin is one of the six major kavalactones found in the kava plant. It has been shown to possess binding affinity for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 (Ki = 0.72 μM), and selectivity vs. the CB₂ receptor (K(i)>10 μM) where it behaves as an agonist. The CB₁ receptor affinity of yangonin suggests that the endocannabinoid system might contribute to the complex human psychopharmacology of the traditional kava drink and the anxiolytic preparations obtained from the kava plant.

Flavokavain A is a flavokavain found in the kava plant. It induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cells via a Bax protein-dependent and mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway.
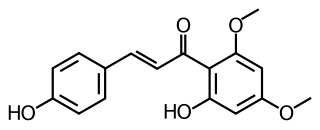
Flavokavain C is a flavokavain found in the kava plant.
The molecular formula C17H16O4 (exact mass : 284.104859, molar mass : 284.31 g/mol) may refer to :
The molecular formula C18H18O5 (molar mass: 314.33 g/mol, exact mass: 314.115424 u) may refer to:
Breast enlargement supplements are frequently portrayed as being a natural means to increase breast size, and with the suggestion that they are free from risk. The popularity of breast enlargement supplements stems from their heavy promotion toward women. Though there has been historical folklore about using herbs for breast enlargement, there is no scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of any breast enlargement supplement. At times, testimonials by companies have been faked. In the United States, both the Federal Trade Commission and the Food and Drug Administration have taken action against the manufacturers of these products for fraudulent practices. The Mayo Clinic advises that there may be serious drug interactions with their use.
| This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |