Related Research Articles
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to agriculture:

Manihot esculenta, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca, is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil and parts of the Andes. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated as an annual crop in tropical and subtropical regions for its edible starchy root tuber, a major source of carbohydrates. Cassava is predominantly consumed in boiled form, but substantial quantities are used to extract cassava starch, called tapioca, which is used for food, animal feed, and industrial purposes. The Brazilian farinha, and the related garri of West Africa, is an edible coarse flour obtained by grating cassava roots, pressing moisture off the obtained grated pulp, and finally drying it.

Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming, conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of agricultural land area. It is characterized by a low fallow ratio, higher use of inputs such as capital and labour, and higher crop yields per unit land area.

Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starting with the Neolithic Revolution when animals were first domesticated, from around 13,000 BC onwards, predating farming of the first crops. By the time of early civilisations such as ancient Egypt, cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs were being raised on farms.

In agriculture, rotational grazing, as opposed to continuous grazing, describes many systems of pasturing, whereby livestock are moved to portions of the pasture, called paddocks, while the other portions rest. Each paddock must provide all the needs of the livestock, such as food, water and sometimes shade and shelter. The approach often produces lower outputs than more intensive animal farming operations, but requires lower inputs, and therefore sometimes produces higher net farm income per animal.

A legume is a plant in the family Fabaceae, or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock forage and silage, and as soil-enhancing green manure. Well-known legumes include beans, soybeans, chickpeas, peanuts, lentils, lupins, grass peas, mesquite, carob, tamarind, alfalfa, and clover. Legumes produce a botanically unique type of fruit – a simple dry fruit that develops from a simple carpel and usually dehisces on two sides.

The cowpea is an annual herbaceous legume from the genus Vigna. Its tolerance for sandy soil and low rainfall have made it an important crop in the semiarid regions across Africa and Asia. It requires very few inputs, as the plant's root nodules are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen, making it a valuable crop for resource-poor farmers and well-suited to intercropping with other crops. The whole plant is used as forage for animals, with its use as cattle feed likely responsible for its name.

Vigna subterranea is a member of the family Fabaceae. Its name is derived from the Bambara tribe. The plant originated in West Africa. As a food and source of income, the Bambara groundnut is considered to be the third most important leguminous crop in those African countries where it is grown, after peanut and cowpea. The crop is mainly cultivated, sold and processed by women, and is, thus, particularly valuable for female subsistence farmers.

Fodder, also called provender, is any agricultural foodstuff used specifically to feed domesticated livestock, such as cattle, rabbits, sheep, horses, chickens and pigs. "Fodder" refers particularly to food given to the animals, rather than that which they forage for themselves. Fodder includes hay, straw, silage, compressed and pelleted feeds, oils and mixed rations, and sprouted grains and legumes. Most animal feed is from plants, but some manufacturers add ingredients to processed feeds that are of animal origin.

Pastoral farming is aimed at producing livestock, rather than growing crops. Examples include dairy farming, raising beef cattle, and raising sheep for wool. In contrast, arable farming concentrates on crops rather than livestock. Finally, mixed farming incorporates livestock and crops on a single farm. Some mixed farmers grow crops purely as fodder for their livestock; some crop farmers grow fodder and sell it. In some cases pastoral farmers are known as graziers, and in some cases pastoralists. Pastoral farming is a non-nomadic form of pastoralism in which the livestock farmer has some form of ownership of the land used, giving the farmer more economic incentive to improve the land. Unlike other pastoral systems, pastoral farmers are sedentary and do not change locations in search of fresh resources. Rather, pastoral farmers adjust their pastures to fit the needs of their animals. Improvements include drainage, stock tanks, irrigation and sowing clover.
High-quality feed block or HQFB, is a solid block consisting of molasses, non-protein nitrogen (NPN), rumen by-pass protein, minerals and lipids. It is provided to livestock ruminants in a manner similar to a salt lick.

Animal feed is food given to domestic animals, especially livestock, in the course of animal husbandry. There are two basic types: fodder and forage. Used alone, the word feed more often refers to fodder. Animal feed is an important input to animal agriculture, and is frequently the main cost of the raising or keeping of animals. Farms typically try to reduce cost for this food, by growing their own, grazing animals, or supplementing expensive feeds with substitutes, such as food waste like spent grain from beer brewing.

The environmental impacts of animal agriculture vary because of the wide variety of agricultural practices employed around the world. Despite this, all agricultural practices have been found to have a variety of effects on the environment to some extent. Animal agriculture, in particular meat production, can cause pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, biodiversity loss, disease, and significant consumption of land, food, and water. Meat is obtained through a variety of methods, including organic farming, free-range farming, intensive livestock production, and subsistence agriculture. The livestock sector also includes wool, egg and dairy production, the livestock used for tillage, and fish farming.

In 2020, approximately 80% of Chad's labor force was employed in the agricultural sector. This sector of the economy accounts for 52.3% of the GDP, as of 2017. With the exception of cotton production, some small-scale sugar cane production, and a portion of the peanut crop, Chad's agriculture consists of subsistence food production.
Crop diversity or crop biodiversity is the variety and variability of crops, plants used in agriculture, including their genetic and phenotypic characteristics. It is a subset of and a specific element of agricultural biodiversity. Over the past 50 years, there has been a major decline in two components of crop diversity; genetic diversity within each crop and the number of species commonly grown.

Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals who are raised for consumption, and sometimes used to refer solely to farmed ruminants, such as cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs. Horses are considered livestock in the United States. The USDA classifies pork, veal, beef, and lamb (mutton) as livestock, and all livestock as red meat. Poultry and fish are not included in the category. The latter is likely due to the fact that fish products are not governed by the USDA, but by the FDA.

Agriculture in Liberia is a major sector of the country's economy worth 38.8% of GDP, employing more than 70% of the population and providing a valuable export for one of the world's least developed countries. Liberia has a climate favourable to farming, vast forests, and an abundance of water, yet low yields mean that over half of foodstuffs are imported, with net agricultural trade at -$73.12 million in 2010. This was dismissed as a "misconception" by Liberia's Minister of Agriculture.

A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for an individual or a population group, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and generally forming a significant proportion of the intake of other nutrients as well. For humans, a staple food of a specific society may be eaten as often as every day or every meal, and most people live on a diet based on just a small variety of food staples. Specific staples vary from place to place, but typically are inexpensive or readily available foods that supply one or more of the macronutrients and micronutrients needed for survival and health: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, and vitamins. Typical examples include grains, seeds, nuts and root vegetables. Among them, cereals, legumes and tubers account for about 90% of the world's food calories intake.

Feed manufacturing refers to the process of producing animal feed from raw agricultural products. Fodder produced by manufacturing is formulated to meet specific animal nutrition requirements for different species of animals at different life stages. According to the American Feed Industry Association (AFIA), there are four basic steps:
- Receive raw ingredients: Feed mills receive raw ingredients from suppliers. Upon arrival, the ingredients are weighed, tested and analyzed for various nutrients and to ensure their quality and safety.
- Create a formula: Nutritionists work side by side with scientists to formulate nutritionally sound and balanced diets for livestock, poultry, aquaculture and pets. This is a complex process, as every species has different nutritional requirements.
- Mix ingredients: Once the formula is determined, the mill mixes the ingredients to create a finished product.
- Package and label: Manufacturers determine the best way to ship the product. If it is prepared for retail, it will be "bagged and tagged," or placed into a bag with a label that includes the product's purpose, ingredients and instructions. If the product is prepared for commercial use, it will be shipped in bulk.
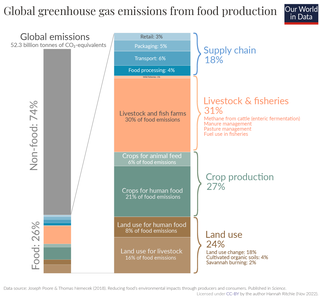
Agriculture contributes towards climate change through greenhouse gas emissions and by the conversion of non-agricultural land such as forests into agricultural land. The agriculture, forestry and land use sector contribute between 13% and 21% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Emissions of nitrous oxide, methane make up over half of total greenhouse gas emission from agriculture. Animal husbandry is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions.
References
- ↑ Wanapat, Metha; Kang, Sungchhang; Phesatcha, Kampanat (November 2013). "Enhancing Buffalo Production Efficiency through Rumen Manipulation and Nutrition". Buffalo Bulletin. 32 (1): 264. Retrieved 1 July 2022.