
The Royal African Company (RAC) was an English trading company established in 1660 by the House of Stuart and City of London merchants to trade along the West African coast. It was overseen by the Duke of York, the brother of Charles II of England; the RAC was founded after Charles II ascended to the English throne in the 1660 Stuart Restoration, and he granted it a monopoly on all English trade with Africa. While the company's original purpose was to trade for gold in the Gambia River, as Prince Rupert of the Rhine had identified gold deposits in the region during the Interregnum, the RAC quickly began trading in slaves, which became its largest commodity.

Elmina Castle was erected by the Portuguese in 1482 as Castelo de São Jorge da Mina, also known as Castelo da Mina or simply Mina, in present-day Elmina, Ghana, formerly the Gold Coast. It was the first trading post built on the Gulf of Guinea, and the oldest European building in existence south of the Sahara.

Cape Coast Castle is one of about forty "slave castles", or large commercial forts, built on the Gold Coast of West Africa by European traders. It was originally a Portuguese "feitoria" or trading post, established in 1555, which they named Cabo Corso.

Swedish overseas colonies consisted of the overseas colonies controlled by Sweden. Sweden possessed overseas colonies from 1638 to 1663, in 1733 and from 1784 to 1878. Sweden possessed five colonies, four of which were short lived. The colonies spanned three continents: Africa, Asia and North America.

The Dutch Gold Coast or Dutch Guinea, officially Dutch possessions on the Coast of Guinea was a portion of contemporary Ghana that was gradually colonized by the Dutch, beginning in 1612. The Dutch began trading in the area around 1598, joining the Portuguese which had a trading post there since the late 1400s. Eventually, the Dutch Gold Coast became the most important Dutch colony in West Africa after Fort Elmina was captured from the Portuguese in 1637, but fell into disarray after the abolition of the slave trade in the early 19th century. On 6 April 1872, the Dutch Gold Coast was, in accordance with the Anglo-Dutch Treaties of 1870–71, ceded to the United Kingdom.

The Brandenburger Gold Coast, later Prussian Gold Coast, was a part of the Gold Coast. The Brandenburg colony existed from 1682 to 1701, after which it became a Prussian colony from 1701 to 1721. In 1721 King Frederick William I of Prussia sold it for 7,200 ducats and 12 slaves to the Dutch West India Company.

The Swedish Gold Coast was a colony of the Swedish Africa Company founded in 1650 by Hendrik Carloff on the Gulf of Guinea in present-day Ghana in Africa. Under foreign occupation for much of its existence, it disappeared for good in April 1663 when it became part of the Dutch Gold Coast.

The Portuguese Gold Coast was a Portuguese colony on the West African Gold Coast along the Gulf of Guinea. Established in 1482, the colony was officially incorporated into Dutch territory in 1642. From their seat of power at the fortress of São Jorge da Mina, the Portuguese commanded a vast internal slave trade, creating a slave network that would expand after the end of Portuguese colonialism in the region. The primary export of the colony was gold, which was obtained through barter with the local population. Portuguese presence along the Gold Coast increased seamanship and trade in the Gulf, introduced American crops into the African agricultural landscape, and made Portuguese an enduring language of trade in the area.
In 1780, Great Britain declared war on the Dutch Republic, opening the Fourth Anglo-Dutch War. As part of its offensive strategy, the British organized an expedition against Dutch colonial outposts on the Gold Coast of Africa. Captain Thomas Shirley led the expedition, commanding HMS Leander and several transports carrying two small regiments of independently raised troops under the command of Captain Kenneth Mackenzie of the 78th Foot.

Fort Nassau, near Moree, Ghana, was the first fort that the Dutch established on what would become the Dutch Gold Coast. Because of its importance during the early European colonial period in West Africa and its testimony to the African gold trade and the Atlantic slave trade, the fort was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage list in 1979.

Fort Saint Anthony was a fort built by the Portuguese in 1515 near the town of Axim, in what is now Ghana. In 1642, the Dutch captured the fort and subsequently made it part of the Dutch Gold Coast. The Dutch expanded the fort considerably before they turned it over, with the rest of their colony, to the British in 1872. The fort is now the property of the Ghanaian state and is open to the public.
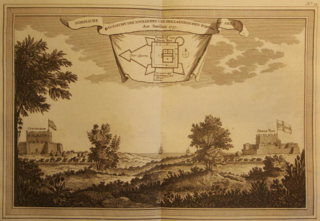
Ussher Fort is a fort in Accra, Ghana. It was built by the Dutch in 1649 as Fort Crèvecœur, and is two days' march from Elmina and to the east of Accra on a rocky point between two lagoons. It was one of three forts that Europeans built in the region during the middle of the 17th century. Fort Crèvecœur was part of the Dutch Gold Coast. The Anglo-Dutch Gold Coast Treaty (1867), which defined areas of influence on the Gold Coast, transferred it to the British in 1868. Because of its significance in the history of European colonial trade and exploitation in Africa, the fort was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979.

Fort Amsterdam is a former slave fort in Abandze, Central region, Ghana. It was built by the English between 1638 and 1645 as Fort Cormantin or Fort Courmantyne, and was captured by admiral Michiel de Ruyter of the Dutch West India Company in 1665, in retaliation for the capture of several Dutch forts by the English Admiral Holmes in 1664. It was subsequently made part of the Dutch Gold Coast, and remained part of it until the fort was traded with the British in 1868. The Fort is located at Abandze, on the north-east of Cape Coast in the Mfantseman District of the Central Region of Ghana. Because of its testimony to European economic and colonial influence in West Africa and its historical importance in the Atlantic slave trade, the fort was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979 along with other forts and castles in Ghana.

Fort Batenstein was a fort and trading post established by the Dutch on the Gold Coast in 1656. It was situated near Butre. The fort was ceded with the entire Dutch Gold Coast to Britain in 1872.

Fort de Goede Hoop or Fort Good Hope was a fort on the Dutch Gold Coast, established in 1667 near Senya Beraku.

The Dutch Gold Coast expedition of 1869–1870 followed the resistance to Dutch rule of the local Fante people surrounding the forts assigned to the Netherlands in the 1868 forts trade along the Gold Coast with Britain. Although the Dutch managed to eventually control the situation, the events marked the end of Dutch involvement in the Gold Coast. Without a profit for almost a century, the escalation finally made the political balance shift in favour of the liberal faction, which wanted to sell the colony to Britain, and away from the nationalist faction, which wanted to retain the colony for reasons of national prestige.

Fort Metal Cross, originally Fort Dixcove, is a military structure located on a promontory at the fishing community of Infuma in Dixcove, in the Western Region of Ghana. Because of its history in the Atlantic slave trade and its testimony to European-African trade, the Fort was included as one of the Forts and Castles of Volta, Greater Accra, Central and Western Regions that became a World Heritage Site in 1979.

Fort Komenda was a British fort on the Gold Coast, currently preserved as a ruin. Because of its testimony to the Atlantic slave trade and European economic and colonial influence in West Africa, the fort was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979, along with several other castles and forts in Ghana.
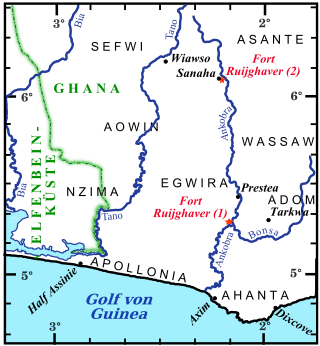
Fort Ruychaver, also Fort Ruijghaver, was a Dutch trading post in the hinterland of the Gold Coast, in contemporary Ghana. It existed between 1654 and 1660 on the banks of River Ankobra. The name of the post goes back to Jacob Ruijghaver, the director of the Dutch West India Company's possessions on the Gold Coast, who ordered its establishment.
The Dutch–Ahanta War was a conflict between the Netherlands and the Ahanta between 1837 and 1839. Beginning with a mere economic dispute between the Ahanta and the Dutch, who were based at the Dutch Gold Coast, the conflict ended with the hanging of Ahanta king Badu Bonsu II and the reorganization of the Ahanta state, establishing a Dutch protectorate over the Ahanta.



















