Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially originating from Algeria, but later expanding across modern-day Tunisia, Libya, and some parts of Morocco. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii in the east and the Masaesyli in the west. During the Second Punic War, Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into one kingdom. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state.

Hippo Regius is the ancient name of the modern city of Annaba, Algeria. It historically served as an important city for the Phoenicians, Berbers, Romans, and Vandals. Hippo was the capital city of the Vandal Kingdom from 435 to 439 AD until it was shifted to Carthage following the Vandal Capture of Carthage (439).

Parthenia was a Roman–Berber town in the former Roman province of Mauretania Sitifensis, the easternmost part of ancient Mauretania. It was located in what is now northern Algeria.

The līmes is a modern term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting system of Ancient Rome marking the borders of the Roman Empire, but it was not used by the Romans for that purpose. The term has been extended to refer to the frontier defences in other parts of the empire, such as in the east and in Africa.

Oea was an ancient city in present-day Tripoli, Libya. It was founded by the Phoenicians in the 7th century BC and later became a Roman–Berber colony. As part of the Roman Africa Nova province, Oea and surrounding Tripolitania were prosperous. It reached its height in the 2nd and 3rd centuries AD, when the city experienced a golden age under the Severan dynasty in nearby Leptis Magna. The city was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate with the spread of Islam in the 7th century and came to be known as Tripoli during the 9th century.

The History of North Africa during the period of Classical Antiquity can be divided roughly into the history of Egypt in the east, the history of Ancient Libya in the middle and the history of Numidia and Mauretania in the West. The Roman Republic established the province of Africa in 146 BCE after the defeat of Carthage. The Roman Empire eventually controlled the entire Mediterranean coast of Africa, adding Egypt in 30 BCE, Creta et Cyrenaica in 20 BCE, and Mauretania in CE 44.

Africa Proconsularis was a Roman province on the northern African coast that was established in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the coast of western Libya along the Gulf of Sirte. The territory was originally inhabited by Berber people, known in Latin as Mauri indigenous to all of North Africa west of Egypt; in the 9th century BC, Phoenicians built settlements along the Mediterranean Sea to facilitate shipping, of which Carthage rose to dominance in the 8th century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic.

Utica was an ancient Phoenician and Carthaginian city located near the outflow of the Medjerda River into the Mediterranean, between Carthage in the south and Hippo Diarrhytus in the north. It is traditionally considered to be the first colony to have been founded by the Phoenicians in North Africa. After Carthage's loss to Rome in the Punic Wars, Utica was an important Roman colony for seven centuries.

Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria. Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city was Russicada. Although Numidia was a key ally of the ancient Roman Republic during the Punic Wars, Cirta was subject to Roman invasions during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC. Eventually it fell under Roman dominion during the time of Julius Caesar. Cirta was then repopulated with Roman colonists by Caesar and Augustus and was surrounded by the autonomous territory of a "Confederation of four free Roman cities", ruled initially by Publius Sittius. The city was destroyed in the beginning of the 4th century and was rebuilt by the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, who gave his name to the newly constructed city, Constantine. The Vandals damaged Cirta, but emperor Justinian I reconquered and improved the Roman city. It declined in importance after the Muslim invasions, but a small community continued at the site for several centuries. Its ruins are now an archaeological site.
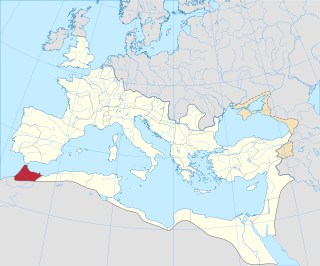
Mauretania Tingitana was a Roman province located in the Berber world, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The territory stretched from the northern peninsula opposite Gibraltar, to Sala Colonia and Volubilis to the south, and as far east as the Mulucha river. Its capital city was Tingis, which is the modern Tangier. Other major cities of the province were Iulia Valentia Banasa, Septem, Rusadir, Lixus and Tamuda.

Caesarea in Mauretania was a Roman colony in Roman-Berber North Africa. It was the capital of Mauretania Caesariensis and is now called Cherchell, in modern Algeria. In the present time is Caesarea used as a titular see for Catholic and Eastern Orthodox bishops.

The area of North Africa which has been known as Libya since 1911 was under Roman domination between 146 BC and 672 AD. The Latin name Libya at the time referred to the continent of Africa in general. What is now coastal Libya was known as Tripolitania and Pentapolis, divided between the Africa province in the west, and Creta et Cyrenaica in the east. In 296 AD, the Emperor Diocletian separated the administration of Crete from Cyrenaica and in the latter formed the new provinces of "Upper Libya" and "Lower Libya", using the term Libya as a political state for the first time in history.
For nearly 250 years, Berber kings of the 'House of Masinissa' ruled in Numidia, which included much of Tunisia, and later in adjacent regions, first as sovereigns allied with Rome and then eventually as Roman clients. This period commenced with the defeat of Carthage by the Roman Army, assisted by Berber cavalry led by Masinissa at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC, and it lasted until the year 40 AD, during the reign of the Roman Emperor Gaius, also known as Caligula.

Madauros was a Roman-Berber city and a former diocese of the Catholic Church in the old state of Numidia, in present-day Algeria.

Fossatum Africae is one or more linear defensive structures claimed to extend over 750 km (470 mi) or more in northern Africa constructed during the Roman Empire to defend and control the southern borders of the Empire in Africa. It is considered to be part of the greater frontier system in Roman Africa.
Solomon was an East Roman (Byzantine) general from northern Mesopotamia, who distinguished himself as a commander in the Vandalic War and the reconquest of North Africa in 533–534. He spent most of the next decade in Africa as its governor general, combining the military post of magister militum with the civil position of praetorian prefect. Solomon successfully confronted the large-scale rebellion of the native Berbers (Mauri), but was forced to flee following an army mutiny in spring of 536. His second tenure in Africa began in 539 and it was marked by victories over the Berbers, which led to the consolidation of the Byzantine position. A few years of prosperity followed, but were cut short by the rekindled Berber revolt and Solomon's defeat and death at the Battle of Cillium in 544.

Roman colonies in Berber Africa are the cities—populated by Roman citizens—created in Berber North Africa by the Roman Empire, mainly in the period between the reigns of Augustus and Trajan. These colonies were created in the area—now called Tamazgha by the Berbers—located between Morocco and Libyan Tripolitania.

Roman-Africans were the ancient Northwest African populations of Roman North Africa that had a Romanized culture and used to speak their own variety of Latin as a result. They existed mostly from the Roman conquest in the antiquity until their language gradually faded out after the Arab conquest of North Africa in the Early Middle Ages.

The Limes Mauretaniae was a portion of a 4,000-kilometre (2,500 mi) Roman fortified border (limes) in Africa approximately 100 kilometres (62 mi) south of the modern day Algiers.

The Mauro-Roman Kingdom was an independent Christian Berber kingdom centred in the capital city of Altava which controlled much of the ancient Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis. The kingdom was first formed in the fifth century as Roman control over the province weakened and Imperial resources had to be concentrated elsewhere, notably in defending the Italian Peninsula itself from invading Germanic tribes.