Related Research Articles

A dental dam or rubber dam is a thin, 6-inch (150 mm) square sheet, usually latex or nitrile, used in dentistry to isolate the operative site from the rest of the mouth. Sometimes termed "Kofferdam", it was designed in the United States in 1864 by Sanford Christie Barnum. It is used mainly in endodontic, fixed prosthodontic and general restorative treatments. Its purpose is both to prevent saliva interfering with the dental work, and to prevent instruments and materials from being inhaled, swallowed or damaging the mouth. In dentistry, use of a rubber dam is sometimes referred to as isolation or moisture control.
Dental products are specially fabricated materials, designed for use in dentistry. There are many different types of dental products, and their characteristics vary according to their intended purpose.

Endodontics is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.

A bridge is a fixed dental restoration used to replace one or more missing teeth by joining an artificial tooth definitively to adjacent teeth or dental implants.
Dental restoration, dental fillings, or simply fillings are treatments used to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as to the replacement of such structure supported by dental implants. They are of two broad types—direct and indirect—and are further classified by location and size. A root canal filling, for example, is a restorative technique used to fill the space where the dental pulp normally resides.

In dentistry, a crown most commonly refers to a dental cap, a type of dental restoration that completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. A crown may be needed when a large dental cavity threatens the health of a tooth. A crown is typically bonded to the tooth by dental cement. They can be made from various materials, which are usually fabricated using indirect methods. Crowns are used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth and to halt deterioration. While beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be costly.

Dental composite resins are dental cements made of synthetic resins. Synthetic resins evolved as restorative materials since they were insoluble, of good tooth-like appearance, insensitive to dehydration, easy to manipulate and inexpensive. Composite resins are most commonly composed of Bis-GMA and other dimethacrylate monomers, a filler material such as silica and in most applications, a photoinitiator. Dimethylglyoxime is also commonly added to achieve certain physical properties such as flow-ability. Further tailoring of physical properties is achieved by formulating unique concentrations of each constituent.

A glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder and polyacrylic acid, an ionomer. Occasionally water is used instead of an acid, altering the properties of the material and its uses. This reaction produces a powdered cement of glass particles surrounded by matrix of fluoride elements and is known chemically as glass polyalkenoate. There are other forms of similar reactions which can take place, for example, when using an aqueous solution of acrylic/itaconic copolymer with tartaric acid, this results in a glass-ionomer in liquid form. An aqueous solution of maleic acid polymer or maleic/acrylic copolymer with tartaric acid can also be used to form a glass-ionomer in liquid form. Tartaric acid plays a significant part in controlling the setting characteristics of the material. Glass-ionomer based hybrids incorporate another dental material, for example resin-modified glass ionomer cements (RMGIC) and compomers.
A luting agent is an application of a dental cement connecting the underlying tooth structure to a fixed prosthesis. To lute means to glue two different structures together. There are two major purposes of luting agents in dentistry – to secure a cast restoration in fixed prosthodontics, and to keep orthodontic bands and appliances in situ.

A dental abscess is a localized collection of pus associated with a tooth. The most common type of dental abscess is a periapical abscess, and the second most common is a periodontal abscess. In a periapical abscess, usually the origin is a bacterial infection that has accumulated in the soft, often dead, pulp of the tooth. This can be caused by tooth decay, broken teeth or extensive periodontal disease. A failed root canal treatment may also create a similar abscess.
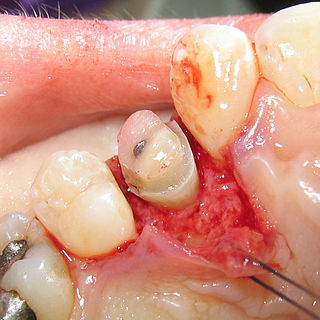
Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure performed by a dentist, or more frequently a specialist periodontist. There are a number of reasons for considering crown lengthening in a treatment plan. Commonly, the procedure is used to expose a greater amount of tooth structure for the purpose of subsequently restoring the tooth prosthetically. However, other indications include accessing subgingival caries, accessing perforations and to treat aesthetic disproportions such as a gummy smile. There are a number of procedures used to achieve an increase in crown length.
A post and core crown is a type of dental restoration required where there is an inadequate amount of sound tooth tissue remaining to retain a conventional crown. A post is cemented into a prepared root canal, which retains a core restoration, which retains the final crown.

Root canal treatment is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of the decontaminated tooth from future microbial invasion. Root canals, and their associated pulp chamber, are the physical hollows within a tooth that are naturally inhabited by nerve tissue, blood vessels and other cellular entities. Together, these items constitute the dental pulp.
Pulp necrosis is a clinical diagnostic category indicating the death of the pulp and nerves of the pulp chamber and root canal of a tooth which may be due to bacterial sequelae, trauma and chemical or mechanical irritation. It is often the end result of many cases of dental trauma, caries and irreversible pulpitis.
Dental pulpal testing is a clinical and diagnostic aid used in dentistry to help establish the health of the dental pulp within the pulp chamber and root canals of a tooth. Such investigations are important in aiding dentists in devising a treatment plan for the tooth being tested.

Dental trauma refers to trauma (injury) to the teeth and/or periodontium, and nearby soft tissues such as the lips, tongue, etc. The study of dental trauma is called dental traumatology.
In dentistry, the smear layer is a layer found on root canal walls after root canal instrumentation. It consists of microcrystalline and organic particle debris. It was first described in 1975 and research has been performed since then to evaluate its importance in bacteria penetration into the dentinal tubules and its effects on endodontic treatment. More broadly, it is the organic layer found over all hard tooth surfaces.
Materials that are used for biomedical or clinical applications are known as biomaterials. The following article deals with fifth generation biomaterials that are used for bone structure replacement. For any material to be classified for biomedical applications, three requirements must be met. The first requirement is that the material must be biocompatible; it means that the organism should not treat it as a foreign object. Secondly, the material should be biodegradable ; the material should harmlessly degrade or dissolve in the body of the organism to allow it to resume natural functioning. Thirdly, the material should be mechanically sound; for the replacement of load-bearing structures, the material should possess equivalent or greater mechanical stability to ensure high reliability of the graft.

Regenerative endodontic procedures is defined as biologically based procedures designed to replace damaged structures such as dentin, root structures, and cells of the pulp-dentin complex. This new treatment modality aims to promote normal function of the pulp. It has become an alternative to heal apical periodontitis. Regenerative endodontics is the extension of root canal therapy. Conventional root canal therapy cleans and fills the pulp chamber with biologically inert material after destruction of the pulp due to dental caries, congenital deformity or trauma. Regenerative endodontics instead seeks to replace live tissue in the pulp chamber. The ultimate goal of regenerative endodontic procedures is to regenerate the tissues and the normal function of the dentin-pulp complex.
An Endodontic crown or endocrown is a single prostheses fabricated from reinforced ceramics, indicated for endodontically treated molar teeth that have significant loss of coronal structure. Endocrowns are formed from a monoblock containing the coronal portion invaded in the apical projection that fills the pulp chamber space, and possibly the root canal entrances; they have the advantage of removing lower amounts of sound tissue compared to other techniques, and with much lower chair time needed. They are luted to the tooth structure by an adhesive material. The ceramic can be milled using computer-aided techniques or molded under pressure. Endocrowns can be an alternative to conventional crown restorations.
References
- ↑ The fracture resistance of dental materials, National Library of Medicine, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.1995.tb00236.x.
- ↑ Endodontic instrument fracture British Dental Journal volume 214, pages341–348 (2013)
- ↑ Fracture resistance and flexural strength of endodontically treated teeth Gamal, W., Abdou, A. & Salem, G.A. Fracture resistance and flexural strength of endodontically treated teeth restored by different short fiber resin composites: a preclinical study. Bull Natl Res Cent 46, 276 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-022-00964-0
- ↑ What Does Fracture Resistance Mean? Trenchlesspedia dictionary
- ↑ Formation Pore Pressure and Fracture Resistance Ch.6 in "Applied Drilling Engineering" (1986) 978-1-61399-919-6
- ↑ International Conference on Hydrogen Safety slide7, Compatibility and Suitability of Existing Steel Pipelines. September 13, 2017, Hamburg, Germany