
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period. GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation rates of the countries; therefore using a basis of GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) is arguably more useful when comparing living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market.

International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services.

Fair trade is an arrangement designed to help producers in developing countries achieve sustainable and equitable trade relationships. Members of the fair trade movement add the payment of higher prices to exporters, as well as improved social and environmental standards. The movement focuses in particular on commodities, or products which are typically exported from developing countries to developed countries, but also used in domestic markets most notably handicrafts, coffee, cocoa, wine, sugar, fruit, flowers and gold. The movement seeks to promote greater equity in international trading partnerships through dialogue, transparency, and respect. It promotes sustainable development by offering better trading conditions to, and securing the rights of, marginalized producers and workers in developing countries. Fair trade is grounded in three core beliefs; first, producers have the power to express unity with consumers. Secondly, the world trade practices that currently exist promote the unequal distribution of wealth between nations. Lastly, buying products from producers in developing countries at a fair price is a more efficient way of promoting sustainable development than traditional charity and aid.
A variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region, including gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national income (NNI), and adjusted national income. All are specially concerned with counting the total amount of goods and services produced within the economy and by various sectors. The boundary is usually defined by geography or citizenship, and it is also defined as the total income of the nation and also restrict the goods and services that are counted. For instance, some measures count only goods & services that are exchanged for money, excluding bartered goods, while other measures may attempt to include bartered goods by imputing monetary values to them.

Inventory or stock is the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale.
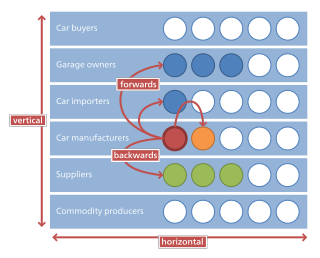
In microeconomics and management, vertical integration is an arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is owned by that company. Usually each member of the supply chain produces a different product or (market-specific) service, and the products combine to satisfy a common need. It is contrasted with horizontal integration, wherein a company produces several items that are related to one another. Vertical integration has also described management styles that bring large portions of the supply chain not only under a common ownership but also into one corporation.
Economies of scope are "efficiencies formed by variety, not volume". In economics, "economies" is synonymous with cost savings and "scope" is synonymous with broadening production/services through diversified products. For example, a gas station that sells gasoline can sell soda, milk, baked goods, etc. through their customer service representatives and thus gasoline companies achieve economies of scope.

A grocery store, grocer or grocery shop (U.K.), is a store primarily engaged in retailing a general range of food products, which may be fresh or packaged. In everyday U.S. usage, however, "grocery store" is a synonym for supermarket, and is not used to refer to other types of stores that sell groceries. In the U.K., shops that sell food are distinguished as grocers or grocery shops, though in everyday use, people usually use either the term "supermarket" or, for a smaller type of store that sells groceries, a "corner shop" or "convenience shop".
Dumping, in economics, is a kind of injuring pricing, especially in the context of international trade. It occurs when manufacturers export a product to another country at a price below the normal price with an injuring effect. The objective of dumping is to increase market share in a foreign market by driving out competition and thereby create a monopoly situation where the exporter will be able to unilaterally dictate price and quality of the product.

An export in international trade is a good or service produced in one country that is sold into another country. The seller of such goods and services is an exporter; the foreign buyer is an importer.

A farmers' market is a physical retail marketplace intended to sell foods directly by farmers to consumers. Farmers' markets may be indoors or outdoors and typically consist of booths, tables or stands where farmers sell their homegrown produce, live animals and plants, and sometimes prepared foods and beverages. Farmers' markets exist in many countries worldwide and reflect the local culture and economy. The size of the market may be just a few stalls or it may be as large as several city blocks. Due to their nature, they tend to be less rigidly regulated than retail produce shops.
Product stewardship is an approach to managing the environmental impacts of different products and materials and at different stages in their production, use and disposal. It acknowledges that those involved in producing, selling, using and disposing of products have a shared responsibility to ensure that those products or materials are managed in a way that reduces their impact, throughout their lifecycle, on the environment and on human health and safety. This approach focusses on the product itself, and everyone involved in the lifespan of the product is called upon to take up responsibility to reduce its environmental, health, and safety impacts.
New trade theory (NTT) is a collection of economic models in international trade which focuses on the role of increasing returns to scale and network effects, which were developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s.
Remanufacturing is "the rebuilding of a product to specifications of the original manufactured product using a combination of reused, repaired and new parts". It requires the repair or replacement of worn out or obsolete components and modules. Parts subject to degradation affecting the performance or the expected life of the whole are replaced. Remanufacturing is a form of a product recovery process that differs from other recovery processes in its completeness: a remanufactured machine should match the same customer expectation as new machines.

A business can use a variety of pricing strategies when selling a product or service. The price can be set to maximize profitability for each unit sold or from the market overall. It can be used to defend an existing market from new entrants, to increase market share within a market or to enter a new market.

Coffee is a popular beverage and an important commodity. Tens of millions of small producers in developing countries make their living growing coffee. Over 2.25 billion cups of coffee are consumed in the world every day. Over 90 percent of coffee production takes place in developing countries - mostly South America, while consumption happens mainly in the industrialized economies. There are 25 million small producers who rely on coffee for a living worldwide. In Brazil, where almost a third of the world's coffee is produced, over five million people are employed in the cultivation and harvesting of over three billion coffee plants; it is a more labour-intensive culture than alternative cultures of the same regions, such as sugar cane or cattle, as its cultivation is not automated, requiring frequent human attention.
A marketing channel is the people, organizations, and activities necessary to transfer the ownership of goods from the point of production to the point of consumption. It is the way products get to the end-user, the consumer; and is also known as a distribution channel. A marketing channel is a useful tool for management, and is crucial to creating an effective and well-planned marketing strategy.

Laiki agora, also common in the plural Laikes agores, are farmers' markets that operate all over Greece, selling foodstuffs and gardening or household equipment, as well as children toys and various "do it yourself" tools.
Supply-chain sustainability is a business issue affecting an organization’s supply chain or logistics network in terms of environmental, risk, and waste costs. There is a growing need for integrating environmentally sound choices into supply-chain management. Sustainability in the supply chain is increasingly seen among high-level executives as essential to deliver profitability and has replaced monetary cost, value, and speed as the dominant topic of discussion among purchasing and supply professionals. A sustainable supply chain seizes value creation opportunities and offers significant competitive advantages for early adopters and process innovators.
Sustainability standards and certifications are voluntary, usually third party-assessed, norms and standards relating to environmental such as IFGICT Standard, social, ethical and food safety issues, adopted by companies to demonstrate the performance of their organizations or products in specific areas. There are over 400 such standards across the world. The trend started in the late 1980s and 90s with the introduction of Ecolabels and standards for Organic food and other products. Most standards refer to the triple bottom line of environmental quality, social equity, and economic prosperity. A standard is normally developed by a broad range of stakeholders and experts in a particular sector and includes a set of practices or criteria for how a crop should be sustainably grown or a resource should be ethically harvested. This might cover, for instance, responsible fishing practices that don't endanger marine biodiversity, or respect for human rights and the payment of fair wages on a coffee or tea plantation. Normally sustainability standards are accompanied by a verification process - often referred to as "certification" - to evaluate that an enterprise complies with a standard, as well as a traceability process for certified products to be sold along the supply chain, often resulting in a consumer-facing label. Certification programmes also focus on capacity building and working with partners and other organisations to support smallholders or disadvantaged producers to make the social and environmental improvements needed to meet the standard.









