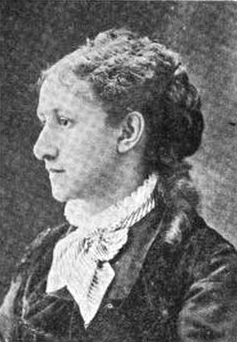Sidney Lewis Gulick was an educator, author, and missionary who spent much of his life working to promote greater understanding and friendship between Japanese and American cultures.

John Thomas Gulick was an American missionary and naturalist from Hawaii. He was one of the pioneers of modern evolutionary thinking based on his studies of Hawaiian snails of the genus Achatinella. He was among the first to describe the formation of species through geographic separation of breeding populations. He developed early ideas on the founder effect and what is now known as the Baldwin effect. He coined the term "divergent evolution".

Luther Halsey Gulick Jr. (1865–1918) was an American physical education instructor, international basketball official, and founder with his wife of the Camp Fire Girls, an international youth organization now known as Camp Fire.

Luther Halsey Gulick (1892–1993) was an American political scientist, Eaton Professor of Municipal Science and Administration at Columbia University, and Director of its Institute of Public Administration, known as an expert on public administration.

Dwight Baldwin was an American Christian missionary and medical doctor on Maui, one of the Hawaiian Islands, during the Kingdom of Hawaii. He was patriarch of a family that founded some of the largest businesses in the islands.

The 7th Operations Group is the operational flying component of the United States Air Force 7th Bomb Wing, stationed at Dyess Air Force Base, Texas. The 7th Operations Group currently flies the B-1 Lancer.

William DeWitt Alexander was an educator, author and linguist in the Kingdom of Hawaii and Republic of Hawaii. He then constructed maps for the Territory of Hawaii.

Peter Johnson Gulick was a missionary to the Kingdom of Hawaii and Japan. His descendants carried on the tradition of missionary work, and included several scientists.

Luther Halsey Gulick Sr. was a missionary to the Hawaiian Kingdom, and several other places. Although educated in medicine, in later life he became a newspaper editor while several of his children became active in public health.

Charles Thomas Gulick was a Kingdom of Hawaiʻi politician and one of the few members of the various missionary families of the time to side with the monarchy in the 1893 overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi.

Abner Wilcox was a missionary teacher from New England to the Kingdom of Hawaii.
Gulick is a surname, originally of Dutch origin, as 'van Gulick'. Notable people with the surname include:

Alice Gordon Gulick was an American missionary teacher in Spain.

Ursula Sophia Newell Emerson was an American missionary in the Hawaiian Islands who co-founded the Waialua Protestant Church, later renamed the Liliʻuokalani Protestant Church, with her husband John Smith Emerson.
Takie Okumura(奥村 多喜衛) was a Christian minister from Japan. He was the founder of the Makiki Christian Church in Honolulu, Hawaii, the "Okumura Boys and Girls Home", and some of Hawaii's first Japanese language schools.
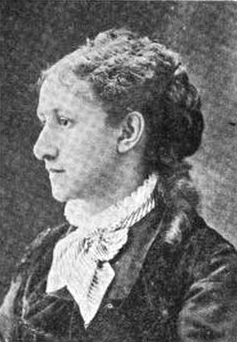
Alice Elmira Walbridge Gulick, was an American teacher, hospital matron, and Christian missionary affiliated with the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions (ABCFM).

Carrie Farnsworth Fowle, born Caroline Palmer Farnsworth, was an American missionary, born in Turkey.

Fanny Gulick was a 19th-century American Presbyterian missionary to the Hawaiian Kingdom and to Japan. Fanny and her husband, Rev. Peter Johnson Gulick had eight children, seven of whom also became missionaries. She was the first to instruct the island women in plaiting the straw-like covering of the sugarcane blossom into materials for hats and bonnets — an industry that soon became an important one.