
Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd. (KHI) is a Japanese public multinational corporation manufacturer of motorcycles, engines, heavy equipment, aerospace and defense equipment, rolling stock and ships, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It is also active in the production of industrial robots, gas turbines, pumps, boilers and other industrial products. The company is named after its founder, Shōzō Kawasaki. KHI is known as one of the three major heavy industrial manufacturers of Japan, alongside Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and IHI. Prior to the Second World War, KHI was part of the Kobe Kawasaki zaibatsu, which included Kawasaki Steel and Kawasaki Kisen. After the conflict, KHI became part of the DKB Group (keiretsu).

Leonardo S.p.A., formerly Leonardo-Finmeccanica and originally Finmeccanica, is an Italian multinational company specialising in aerospace, defence and security. Headquartered in Rome, Italy, the company has 180 sites worldwide. It is the 12th largest defence contractor in the world based on 2020 revenues. The company is partially owned by the Italian government, which holds 30.2% of the company's shares and is its largest shareholder.

IHI Corporation, formerly known as Ishikawajima-Harima Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. is a Japanese engineering corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan that produces and offers ships, space launch vehicles, aircraft engines, marine diesel engines, gas turbines, gas engines, railway systems, turbochargers for automobiles, plant engineering, industrial machinery, power station boilers and other facilities, suspension bridges and other structures.

The Ganz Machinery Works Holding is a Hungarian holding company. Its products are related to rail transport, power generation, and water supply, among other industries.

VM Motori S.p.A. is an Italian diesel engine manufacturing company which is wholly owned by Stellantis. VM headquarters and main production facilities are located in Cento, in Emilia-Romagna, Italy.

Ruston & Hornsby was an industrial equipment manufacturer in Lincoln, England founded in 1918. The company is best known as a manufacturer of narrow and standard gauge diesel locomotives and also of steam shovels. Other products included cars, steam locomotives and a range of internal combustion engines, and later gas turbines. It is now a subsidiary of Siemens.

John Brown and Company of Clydebank was a Scottish marine engineering and shipbuilding firm. It built many notable and world-famous ships including RMS Lusitania, RMS Aquitania, HMS Hood, HMS Repulse, RMS Queen Mary, RMS Queen Elizabeth and Queen Elizabeth 2.

Ettore Maserati was an Italian automotive engineer, one of five brothers who founded the Maserati firm in Bologna 1914. He was born in Voghera.

Ansaldo Energia S.p.A. is an Italian power engineering company based in Genoa, Italy. The original parent company, Gio. Ansaldo & C., was founded in 1853, and merged with Finmeccanica in 1993.
Franco Tosi was an Italian engineer, known for his contributions to steam engine technology.

Ansaldo was one of Italy's oldest and most important engineering companies, existing for 140 years from 1853 to 1993.
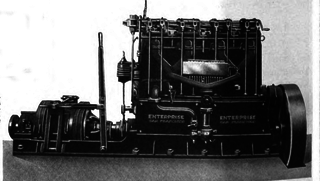
The Enterprise Foundry Company was incorporated in 1908. On 28 November 1940 the company name was changed to Enterprise Engine & Foundry Company to reflect the changed nature of the business. The original foundry was established in 1886.
The Yugoslav destroyer Split was a large destroyer designed for the Royal Yugoslav Navy in the late 1930s. Construction began in 1939, but she was captured incomplete by the Italians during the invasion of Yugoslavia in April 1941. They continued to build the ship, barring a brief hiatus, but she was not completed before she was scuttled after the Italian surrender in September 1943. The Germans occupied Split and refloated the destroyer later that year, but made no efforts to continue work. The ship was scuttled again before the city was taken over by the Yugoslav Partisans in late 1944. Split was refloated once more, but the new Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was able to do little with her before the Tito–Stalin Split in 1948 halted most work. Aid and equipment from the United States and the United Kingdom finally allowed her to be completed 20 years after construction began. She was commissioned in July 1958 and served as the navy's flagship for most of her career. Split became a training ship in the late 1970s after a boiler explosion. She was decommissioned in 1980, and scrapped six years later.

Agios Dimitrios Power Station is a power plant located near Agios Dimitrios, Kozani, Greece, situated between the towns of Kozani and Ellispontos village. In terms of its location in relation to a metropolis, the plant lies 140 kilometres (87 mi) west of Thessaloniki, a major city in northern Greece.
Hitachi Rail STS SpA or Hitachi Rail STS is an italian transportation company owned by Hitachi with a global presence in the field of railway signalling and integrated transport systems for passenger traffic and freight operations. Hitachi Rail STS plans, designs, manufactures, installs and commissions signaling systems, components and technologies for the management and control of newly built or upgraded railways, transit and freight lines worldwide.
Tranquillo Zerbi (1891-1939) was a leading Italian automotive engineer.

The thermal power station Regina Margherita was a large power station for the production of electricity, preserved at the Museo nazionale della scienza e della tecnologia Leonardo da Vinci in Milan, Italy. The station opened in 1895 and was originally installed in the Egidio e Pio Gavazzi silk factory in Desio (Milan), where it operated until 1954. It supplied electricity for lighting and for the operation of 1,800 looms, generating alternating electric current at a voltage of 200 V.

















