USS Baltimore was a ship of the United States Navy.

The third USS Boston was a 32-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted frigate of the United States Navy. Boston was built by public subscription in Boston under the Act of 30 June 1798. Boston was active during the Quasi-War with France and the First Barbary War. On 12 October 1800, Bostonengaged and captured the French corvette Berceau. Boston was laid up in 1802, and considered not worth repairing at the outbreak of the War of 1812. She was burned at the Washington Naval Yard on 24 August 1814 to prevent her capture by British forces.

USS Adams was a 28-gun (rated) sailing frigate of the United States Navy. She was laid down in 1797 at New York City by John Jackson and William Sheffield and launched on 8 June 1799. Captain Richard Valentine Morris took command of the ship.

USS Constellation was a nominally rated 38-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted frigate of the United States Navy.

The first USS Essex of the United States Navy was a 36-gun or 32-gun sailing frigate that participated in the Quasi-War with France, the First Barbary War, and in the War of 1812. The British captured her in 1814 and she then served as HMS Essex until sold at public auction on 6 June 1837.
The first USS Norfolk was a brig in the United States Navy during the Quasi-War with France.
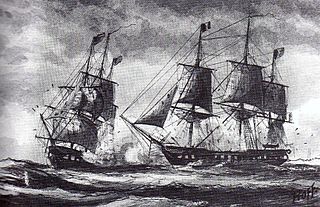
L'Insurgente was a 40-gun Sémillante-class frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1793. During the Quasi War with the United States, the United States Navy frigate USS Constellation, with Captain Thomas Truxtun in command, captured her off the island of Nevis. After her capture she served in the United States Navy as USS Insurgent, patrolling the waters in the West Indies. In September 1800 she was caught up in a severe storm and was presumed lost at sea.
The second USS Delaware was a ship which served in the United States Navy during Quasi-War with France.
USS Augusta was a brig purchased by the US Navy on 30 June 1799 at Norfolk, Virginia. She mistakenly went to Trenton, New Jersey arriving on 13 September, she was then ordered to Marcus Hook, Pennsylvania for inspection by naval constructor Joshua Humphreys to see if the transport would be suitable for use as a warship. Capt. Bird was replaced by Lieutenant Archibald McElroy on the 13th. Humphreys approved and fitting out began in September. She was placed in commission for service in the Quasi-War with France sometime late in 1799.
USS Richmond was a brig purchased for the US Navy in 1798 by the citizens of Richmond, Petersburg, Manchester and Norfolk, Virginia, while being built at Norfolk as Augusta for a Mr. Myers. Renamed Richmond, she was fitted out in the fall of that year and in December stood out from Hampton Roads for the Caribbean with Captain Samuel Barron in command for service in the Quasi-War with France.

HMS Vengeance was originally the 48-gun French Navy frigate Vengeance and lead ship of her class. She engaged USS Constellation during the Quasi-War, in an inconclusive engagement that left both ships heavily damaged. During the French Revolutionary Wars, HMS Seine hunted Vengeance down and captured her after a sharp action. She was recommissioned in the Royal Navy as the 38-gun fifth rate HMS Vengeance, but the British apparently never returned her to seagoing service. Accounts are divided as to her eventual fate. She may have been broken up in 1803 after grounding in 1801, or continued as a prison ship until 1814.

Berceau was a 22-gun corvette of the French Navy, built to a design by Jacques-Noël Sané, and launched in 1794. The Americans captured her in 1800 but restored her to France the next year. She then served in the Indian Ocean before returning to Spain, where she was broken up in 1804.
HMS Electra was a 16-gun brig-sloop. She was built by the Enterprise Ethéart, Saint-Malo, as the French Curieux-class brig Espiègle and launched in 1804. She was armed in 1807 at Saint Servan. The British frigate Sybille captured her on 16 August 1808. There was already an Espiegle in the Royal Navy so the Navy took the vessel they had just captured into service as HMS Electra, her predecessor Electra having been wrecked in March. Electra captured one American privateer before she was sold in 1816.

Gracieuse was a 32-gun Charmante-class frigate of the French Navy. Renamed to Unité in 1793, she took part in the French Revolutionary Wars. The Royal Navy captured her in 1796 off Île d'Yeu and brought her into British service as HMS Unite. She was sold in 1802

HMS Barbuda was commissioned into the Royal Navy in 1780 after having briefly served as an American privateer. Barbuda was one of the two sloops that captured Demerara and Essequibo in 1781, but the French Navy captured her there in 1782 and took her into service as Barboude. The French Navy sold her to private owners in 1786, and she served briefly as a privateer in early 1793 before the French Navy purchased her again and named her Légère. She served them until mid-1796 when the Royal Navy captured her and took her into service as HMS Legere. She was wrecked off the coast of Colombia, without loss of life, in February 1801.

The French corvette Naïade was launched at Brest in 1793 as a brig-corvette for the French Navy. The Royal Navy captured her in 1805 and took her into service as HMS Melville. She was sold for breaking up in 1808.

HMS Vesuve was the French brick-cannonièreVésuve, name vessel of her class of seven bricks-cannonière. She was launched at Saint-Malo in 1793. The British Royal Navy captured her in 1795 and took her into service as HMS Vesuve. The Navy sold her in 1802.

HMS Eclipse was a French Navy Vésuve-class brick-canonnier or chaloupe-canonnière, (gunbrig) launched at Saint-Malo in 1793 as Volage. She was renamed Venteux in 1795 (possibly also Vérité on 30 May 1795, although this might have been a second ship of the same name. The British Royal Navy captured her in 1803 and took her into service as HMS Eagle, but then renamed her HMS Eclipse in 1804. She had a completely unremarkable career before the Navy sold her in 1807.

HMS Albacore was launched in 1793 at Rotherhithe. She captured several privateers and a French Navy corvette before she was sold in 1802.

Experiment was a 50-gun ship of the line of the British Royal Navy. Captured by Sagittaire during the War of American Independence, she was recommissioned in the French Navy, where she served into the 1800s.













