Four ships of the French Navy have borne the name Belle Poule.

Belle Poule was a French frigate of the Dédaigneuse class, which Léon-Michel Guignace built. She is most famous for her duel with the British frigate HMS Arethusa on 17 June 1778, which began the French involvement in the American War of Independence.
HMS Berwick was a 74-gun Elizabeth-class third rate of the Royal Navy, launched at Portsmouth Dockyard on 18 April 1775, to a design by Sir Thomas Slade. She fought the French at the Battle of Ushant (1778) and the Dutch at the Battle of Dogger Bank (1781). The French captured her in the Action of 8 March 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars and she served with them with some success then and at the start of the Napoleonic Wars until the British recaptured her at the Battle of Trafalgar. Berwick sank shortly thereafter in a storm.

The Musée national de la Marine is a maritime museum located in the Palais de Chaillot, Trocadéro, in the 16th arrondissement of Paris. It has annexes at Brest, Port-Louis, Rochefort, Toulon and Saint-Tropez. The permanent collection originates in a collection that dates back to Louis XV of France.

The Bretagne was a fast 130-gun three-decker of the French Navy, designed by engineer Jules Marielle. Built as a new capital ship meant to improve upon the very successful Océan class while avoiding the weaknesses found on Valmy, she retained most of the Océan design but ended up incorporating the philosophy of "fast ship of the line" pioneered by Napoléon, with a rounded stern and a two-cylinder, 8-boiler steam engine allowing her a speed of 13.5 knots. The propeller could be retracted to streamline the hull when sailing under sail only.

Count Honoré Joseph Antoine Ganteaume was a French Navy officer and Vice-admiral.

Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez was a French sailor, Navy officer, and admiral of the First French Empire.

HMS Belle Poule was a Royal Navy fifth rate frigate, formerly Belle Poule, a Virginie-class frigate of the French Navy, which was built by the Crucy family's shipyard at Basse-Indre to a design by Jacques-Noël Sané. She was launched on 17 April 1802, and saw active service in the East, but in 1806 a British squadron under Sir John Borlase Warren captured her off La Palma in the Canary Islands. The Admiralty commissioned her into the Royal Navy as HMS Belle Poule. She was sold in 1816.

Pierre-François-Henri-Étienne Bouvet de Maisonneuve was a French Navy officer and privateer.

Jean-Jacques Rousseau was a Téméraire class 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy, active during the French Directory, French Consulate and First French Empire. Renamed Marengo in 1802, she took part in Linois' operations in the Indian Ocean before her capture by the Royal Navy.

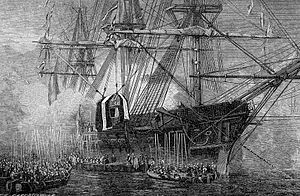
The retour des cendres was the return of the mortal remains of Napoleon I of France from the island of St Helena to France and their burial in the Hôtel des Invalides in Paris in 1840, on the initiative of Adolphe Thiers and King Louis-Philippe.

The Atlantic campaign of 1806 was one of the most important and complex naval campaigns of the post-Trafalgar Napoleonic Wars. Seeking to take advantage of the withdrawal of British forces from the Atlantic in the aftermath of the Battle of Trafalgar, Emperor Napoleon ordered two battle squadrons to sea from the fleet stationed at Brest, during December 1805. Escaping deep into the Atlantic, these squadrons succeeded in disrupting British convoys, evading pursuit by British battle squadrons and reinforcing the French garrison at Santo Domingo. The period of French success was brief: on 6 February 1806 one of the squadrons, under Vice-Admiral Corentin Urbain Leissègues, was intercepted by a British squadron at the Battle of San Domingo and destroyed, losing all five of its ships of the line.

Linois's expedition to the Indian Ocean was a commerce raiding operation launched by the French Navy during the Napoleonic Wars. Contre-Admiral Charles-Alexandre Durand Linois was ordered to the Indian Ocean in his flagship Marengo in March 1803 accompanied by a squadron of three frigates, shortly before the end of the Peace of Amiens. When war between Britain and France broke out in September 1803, Marengo was at Pondicherry with the frigates, but escaped a British squadron sent to intercept it and reached Isle de France. The large distances between naval bases in the Indian Ocean and the limited resources available to the British commanders in the region made it difficult to concentrate sufficient forces to combat a squadron of this size, and Linois was subsequently able to sustain his campaign for three years. From Isle de France, Linois and his frigates began a series of attacks on British commerce across the Eastern Indian Ocean, specifically targeting the large convoys of East Indiamen that were vital to the maintenance of trade within the British Empire and to the British economy. Although he had a number of successes against individual merchant ships and the small British trading post of Bencoolen, the first military test of Linois squadron came at the Battle of Pulo Aura on 15 February 1804. Linois attacked the undefended British China Fleet, consisting of 16 valuable East Indiamen and 14 other vessels, but failed to press his military superiority and withdrew without capturing a single ship.

The Action of 13 March 1806 was a naval engagement of the Napoleonic Wars, fought when a British and a French squadron met unexpectedly in the mid-Atlantic. Neither force was aware of the presence of the other prior to the encounter and were participating in separate campaigns. The British squadron consisted of seven ships of the line accompanied by associated frigates, led by Rear-Admiral Sir John Borlase Warren, were tasked with hunting down and destroying the French squadron of Contre-Admiral Jean-Baptiste Willaumez, which had departed Brest for raiding operations in the South Atlantic in December 1805, at the start of the Atlantic campaign of 1806. The French force consisted of one ship of the line and one frigate, all that remained of Contre-Admiral Charles-Alexandre Durand Linois' squadron that had sailed for the Indian Ocean in March 1803 during the Peace of Amiens. Linois raided British shipping lanes and harbours across the region, achieving limited success against undefended merchant ships but repeatedly withdrawing in the face of determined opposition, most notably at the Battle of Pulo Aura in February 1804. With his stores almost exhausted and the French ports east of the Cape of Good Hope that could have offered him replenishment eliminated, Linois decided to return to France in January 1806, and by March was inadvertently sailing across the cruising ground of Warren's squadron.

The Atalante was a 40-gun Virginie class frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1802.

François-Ferdinand-Philippe-Louis-Marie d'Orléans, prince de Joinville was the third son of Louis Philippe, Duke of Orléans, afterwards king of the French and his wife Marie Amalie of Bourbon-Sicilies. He was an admiral of the French Navy, and a talented artist.

Sphinx was a paddle steamer, initially rateed as a corvette, of the French Navy, and lead ship of her class. She was the first operational French naval steamer. She took part in the Invasion of Algiers in 1830, pioneering the role of steamers in navies of the mid-19th century, and later took part in the transfer of the Luxor Obelisk from Egypt to Paris.

The Action of 17 June 1778 also known as the Fight of Belle Poule and Arethusa was a minor naval action that took place off the coast of France between British and French frigates. The action was widely celebrated by both France and Great Britain and was the first between the two naval forces during the American Revolutionary War before a formal declaration of war was even announced.

The Normandie built in 1835, was a French paddle steamer working in conjunction with her sister ship the Seine (1836) on the lower reaches of the Seine. The route she serviced was between Le Havre and Rouen via Honfleur with secondary stops along the way. She gained fame by being a participant in the retour des cendres of Napoleon to France.