
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophytasensu stricto. Bryophyta may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically 0.2–10 cm (0.1–3.9 in) tall, though some species are much larger. Dawsonia, the tallest moss in the world, can grow to 50 cm (20 in) in height. There are approximately 12,000 species.

Bryophytes are a group of land plants (embryophytes), sometimes treated as a taxonomic division, that contains three groups of non-vascular land plants: the liverworts, hornworts, and mosses. In the strict sense, the division Bryophyta consists of the mosses only. Bryophytes are characteristically limited in size and prefer moist habitats although some species can survive in drier environments. The bryophytes consist of about 20,000 plant species. Bryophytes produce enclosed reproductive structures, but they do not produce flowers or seeds. They reproduce sexually by spores and asexually by fragmentation or the production of gemmae.

The Marchantiophyta are a division of non-vascular land plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of genetic information. The division name was derived from the genus name Marchantia, named by French botanist Jean Marchant after his father.

Hornworts are a group of non-vascular Embryophytes constituting the division Anthocerotophyta. The common name refers to the elongated horn-like structure, which is the sporophyte. As in mosses and liverworts, hornworts have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of genetic information; the flattened, green plant body of a hornwort is the gametophyte stage of the plant.

Fissidens adianthoides, the maidenhair pocketmoss, is a North American moss in the family Fissidentaceae. It was first described by Johann Hedwig in 1801. The Nitinaht First Nations of Vancouver Island have used maidenhair moss to bandage wounds. It was named by the Anglo-Saxons based on its resemblance to pubic hair.

Takakia is a genus of two species of mosses known from western North America and central and eastern Asia. The genus is placed as a separate family, order and class among the mosses. It has had a history of uncertain placement, but the discovery of sporophytes clearly of the moss-type firmly supports placement with the mosses.
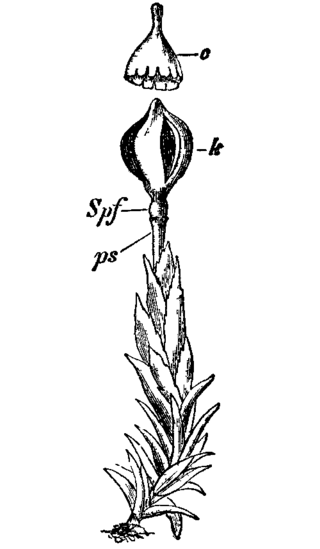
Andreaeaceae is a family of mosses which includes two genera, Andreaea, containing about 100 species, and the genus Acroschisma. The Andreaeaceae prefer rocky habitats ranging from tropical to arctic climates, on which they form tufted colonies, typically with reddish to blackish shoots. The capsules lack the peristome mechanism and dehisce longitudinally to release the spores, resulting in a paper-lantern appearance.

The Bryopsida constitute the largest class of mosses, containing 95% of all moss species. It consists of approximately 11,500 species, common throughout the whole world.

Buxbaumia is a genus of twelve species of moss (Bryophyta). It was first named in 1742 by Albrecht von Haller and later brought into modern botanical nomenclature in 1801 by Johann Hedwig to commemorate Johann Christian Buxbaum, a German physician and botanist who discovered the moss in 1712 at the mouth of the Volga River. The moss is microscopic for most of its existence, and plants are noticeable only after they begin to produce their reproductive structures. The asymmetrical spore capsule has a distinctive shape and structure, some features of which appear to be transitional from those in primitive mosses to most modern mosses.

Polytrichaceae is a common family of mosses. Members of this family tend to be larger than other mosses, with the larger species occurring in particularly moist habitats. The leaves have specialized sheaths at the base and a midrib that bears photosynthetic lamellae on the upper surface. These mosses are capable of sustaining high rates of photosynthesis in the presence of ample light and moisture. Unlike all other mosses, the hydroid-based vascular system of these mosses is continuous from stem to leaf and can extract water from the soil through transpiration. Species in this group are dioicous, though some are monoicous. In most species, the sporophytes are relatively large, the setae are rigid, and the calyptrae are hairy. Most species have nematodontous peristomes with 32–64 teeth in their sporangium; some early-diverging genera instead have a stopper mechanism, which consists of the apical section of the columella, that seals the mouth of the capsule shut prior to dehiscence.

Takakia ceratophylla is one of the two species of toothless mosses in the genus Takakia, under the Takakiaceae family. This species was first described by William Mitten in 1861. Takakia ceratophylla is vulnerable and threatened by habitat loss due to human activities.

Tetraphidaceae is a family of mosses. It includes only the two genera Tetraphis and Tetrodontium, each with two species. The defining feature of the family is the 4-toothed peristome.

Bryales is an order of mosses.

The Funariaceae are a family of mosses in the order Funariales. About 303 species are included in the family, with 200 species in Funaria and another 80 classified in Physcomitrium.

Encalyptales is an order of mosses in subclass Funariidae. It contains a single family.

Hypnales is the botanical name of an order of Bryophyta or leafy mosses. This group is sometimes called feather mosses, referring to their freely branched stems. The order includes more than 40 families and more than 4,000 species, making them the largest order of mosses.

Splachnaceae is a family of mosses, containing around 70 species in 6 genera. Around half of those species are entomophilous, using insects to disperse their spores, a characteristic found in no other seedless land plants.

Pogonatum urnigerum is a species of moss in the family Polytrichaceae, commonly called urn haircap. The name comes from "urna" meaning "urn" and "gerere" meaning "to bear" which is believed to be a reference made towards the plant's wide-mouthed capsule. It can be found on gravelly banks or similar habitats and can be identified by the blue tinge to the overall green colour. The stem of this moss is wine red and it has rhizoids that keep the moss anchored to substrates. It is an acrocarpous moss that grows vertically with an archegonium borne at the top of each fertilized female gametophyte shoot which develops an erect sporophyte.

Polytrichastrum formosum, commonly known as the bank haircap moss, is a species of moss belonging to the family Polytrichaceae.

Wijkia extenuata, commonly known as spear moss or spiky wiki, is a species of moss from the family Pylaisiadelphaceae. It can be divided into two varieties Wijkia extenuata var. caudata and Wijkia extenuata var. extenuata. It is commonly found throughout the tropical, subtropical, and temperate forests of eastern Australasia and New Zealand.



























