Related Research Articles

Hans-Georg Gadamer was a German philosopher of the continental tradition, best known for his 1960 magnum opus on hermeneutics, Truth and Method.
Historicism is an approach to explaining the existence of phenomena, especially social and cultural practices, by studying the process or history by which they came about. The term is widely used in philosophy, anthropology, and sociology.

Jürgen Habermas is a German philosopher and social theorist in the tradition of critical theory and pragmatism. His work addresses communicative rationality and the public sphere.

Hermeneutics is the theory and methodology of interpretation, especially the interpretation of biblical texts, wisdom literature, and philosophical texts. As necessary, hermeneutics may include the art of understanding and communication.
Bohm Dialogue is a freely flowing group conversation in which participants attempt to reach a common understanding, experiencing everyone's point of view fully, equally and nonjudgmentally. This can lead to new and deeper understanding. The purpose is to solve the communication crises that face society, and indeed the whole of human nature and consciousness. It utilizes a theoretical understanding of the way thoughts relate to universal reality. It is named after physicist David Bohm who originally proposed this form of dialogue.

The Critique of Judgment, also translated as the Critique of the Power of Judgment, is a 1790 book by the German philosopher Immanuel Kant. Sometimes referred to as the "third critique", the Critique of Judgment follows the Critique of Pure Reason (1781) and the Critique of Practical Reason (1788).

Wilhelm Dilthey was a German historian, psychologist, sociologist, and hermeneutic philosopher, who held Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel's Chair in Philosophy at the University of Berlin. As a polymathic philosopher, working in a modern research university, Dilthey's research interests revolved around questions of scientific methodology, historical evidence and history's status as a science.
Intercultural communication is a discipline that studies communication across different cultures and social groups, or how culture affects communication. It describes the wide range of communication processes and problems that naturally appear within an organization or social context made up of individuals from different religious, social, ethnic, and educational backgrounds. In this sense, it seeks to understand how people from different countries and cultures act, communicate, and perceive the world around them. Intercultural communication focuses on the recognition and respect of those with cultural differences. The goal is mutual adaptation between two or more distinct cultures which leads to biculturalism/multiculturalism rather than complete assimilation. It promotes the development of cultural sensitivity and allows for empathic understanding across different cultures.
Biblical hermeneutics is the study of the principles of interpretation concerning the books of the Bible. It is part of the broader field of hermeneutics, which involves the study of principles of interpretation, both theory and methodology, for all forms of communication, nonverbal and verbal. While Jewish and Christian biblical hermeneutics have some overlap and dialogue, they have distinctly separate interpretative traditions.
Verstehen, in the context of German philosophy and social sciences in general, has been used since the late 19th century – in English as in German – with the particular sense of the "interpretive or participatory" examination of social phenomena. The term is closely associated with the work of the German sociologist Max Weber, whose antipositivism established an alternative to prior sociological positivism and economic determinism, rooted in the analysis of social action. In anthropology, Verstehen has come to mean a systematic interpretive process in which an outside observer of a culture attempts to relate to it and understand others.
Dalibor Vesely was a Czech-born architectural historian and theorist who was influential through his teaching and writing in promoting the role of hermeneutics and phenomenology as part of the discourse of architecture and of architectural design.
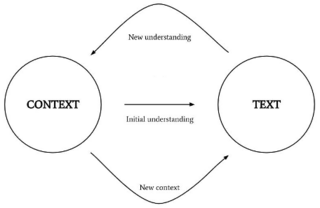
The hermeneutic circle describes the process of understanding a text hermeneutically. It refers to the idea that one's understanding of the text as a whole is established by reference to the individual parts and one's understanding of each individual part by reference to the whole. The circle is a metaphor for the procedure of transforming one's understanding of the part and the whole through iterative recontextualization.

Truth and Method is a 1960 book by the philosopher Hans-Georg Gadamer, in which the author deploys the concept of "philosophical hermeneutics" as it is worked out in Martin Heidegger's Being and Time (1927). The book is considered Gadamer's major work.

Jeff Malpas is an Australian philosopher and emeritus distinguished professor at the University of Tasmania in Hobart. Known internationally for his work across the analytic and continental traditions, Malpas is also at the forefront of contemporary philosophical research on the concept of "place", as first and most comprehensively presented in his Place and Experience: A Philosophical Topography—now in its second edition—and further developed in numerous subsequent works.
Common sense is "knowledge, judgement, and taste which is more or less universal and which is held more or less without reflection or argument". As such, it is often considered to represent the basic level of sound practical judgement or knowledge of basic facts that any adult human being ought to possess. It is "common" in the sense of being shared by nearly all people. The everyday understanding of common sense is ultimately derived from historical philosophical discussions. Relevant terms from other languages used in such discussions include Latin sensus communis, Ancient Greek κοινὴ αἴσθησις, and French bon sens. However, these are not straightforward translations in all contexts, and in English different shades of meaning have developed. In philosophical and scientific contexts, since the Age of Enlightenment the term "common sense" has been used for rhetorical effect both approvingly and disapprovingly. On the one hand it has been a standard for good taste, good sense, and source of scientific and logical axioms. On the other hand it has been equated to conventional wisdom, vulgar prejudice, and superstition.

Andrzej Wierciński is a hermeneutician, philosopher, and theologian. As the transdisciplinary thinker, he is Professor of Liberal Arts, Faculty of Artes Liberales at the University of Warsaw, President-Founder (2001) of the International Institute for Hermeneutics (IIH), and President of Agora Hermeneutica (IIH).
Jessica Frazier is Lecturer in Theology and Religion at Trinity College, Oxford, and a Fellow of the Oxford Centre for Hindu studies. Her work explores key philosophical themes across cultures, from Indian concepts of Being to 20th century phenomenology. She is particularly interested in questions about ontology, value, selfhood and human flourishing. Frazier is the founding editor of the Journal of Hindu Studies and a frequent contributor to BBC radio.

Cynthia R. Nielsen is an American philosopher and Professor of Philosophy at the University of Dallas. She is known for her expertise in the field of hermeneutics, the philosophy of music, aesthetics, ethics, and social philosophy. Since 2015 she has taught at the University of Dallas. Prior to her appointment at the University of Dallas, she taught at Villanova University as a Catherine of Sienna Fellow in the Ethics ProgramArchived 2018-12-19 at the Wayback Machine. Nielsen serves on the executive committee of the North American Society for Philosophical Hermeneutics.
Nicholas Davey is a British philosopher and professor of philosophy at the University of Dundee. He is known for his expertise in aesthetics, hermeneutics, and his work on Hans-Georg Gadamer. Davey has also played a leading role in founding several research groups and institutes at the University of Dundee, which include Theoros, Hermeneutica Scotia, and the university's Arts and Humanities Research Institute.

Hans-Herbert Kögler, is a German-American philosopher.
References
- Malpas, Jeff (2003). "Hans-Georg Gadamer". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy .