Related Research Articles
In mathematics and physics, a scalar field is a function associating a single number to each point in a region of space – possibly physical space. The scalar may either be a pure mathematical number (dimensionless) or a scalar physical quantity.
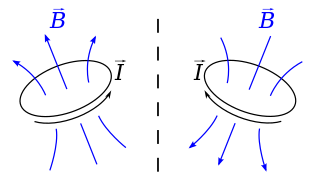
In physics and mathematics, a pseudovector is a quantity that behaves like a vector in many situations, but its direction does not conform when the object is rigidly transformed by rotation, translation, reflection, etc. This can also happen when the orientation of the space is changed. For example, the angular momentum is a pseudovector because it is often described as a vector, but by just changing the position of reference, angular momentum can reverse direction, which is not supposed to happen with true vectors.
Multilinear algebra is the study of functions with multiple vector-valued arguments, with the functions being linear maps with respect to each argument. It involves concepts such as matrices, tensors, multivectors, systems of linear equations, higher-dimensional spaces, determinants, inner and outer products, and dual spaces. It is a mathematical tool used in engineering, machine learning, physics, and mathematics.
A conformal field theory (CFT) is a quantum field theory that is invariant under conformal transformations. In two dimensions, there is an infinite-dimensional algebra of local conformal transformations, and conformal field theories can sometimes be exactly solved or classified.
The Chern–Simons theory is a 3-dimensional topological quantum field theory of Schwarz type developed by Edward Witten. It was discovered first by mathematical physicist Albert Schwarz. It is named after mathematicians Shiing-Shen Chern and James Harris Simons, who introduced the Chern–Simons 3-form. In the Chern–Simons theory, the action is proportional to the integral of the Chern–Simons 3-form.
In gauge theory and mathematical physics, a topological quantum field theory is a quantum field theory which computes topological invariants.

In physics, specifically relativistic quantum mechanics (RQM) and its applications to particle physics, relativistic wave equations predict the behavior of particles at high energies and velocities comparable to the speed of light. In the context of quantum field theory (QFT), the equations determine the dynamics of quantum fields. The solutions to the equations, universally denoted as ψ or Ψ, are referred to as "wave functions" in the context of RQM, and "fields" in the context of QFT. The equations themselves are called "wave equations" or "field equations", because they have the mathematical form of a wave equation or are generated from a Lagrangian density and the field-theoretic Euler–Lagrange equations.
In mathematics, monstrous moonshine, or moonshine theory, is the unexpected connection between the monster group M and modular functions, in particular the j function. The initial numerical observation was made by John McKay in 1978, and the phrase was coined by John Conway and Simon P. Norton in 1979.
In mathematics, a vertex operator algebra (VOA) is an algebraic structure that plays an important role in two-dimensional conformal field theory and string theory. In addition to physical applications, vertex operator algebras have proven useful in purely mathematical contexts such as monstrous moonshine and the geometric Langlands correspondence.
In theoretical physics and mathematics, a Wess–Zumino–Witten (WZW) model, also called a Wess–Zumino–Novikov–Witten model, is a type of two-dimensional conformal field theory named after Julius Wess, Bruno Zumino, Sergei Novikov and Edward Witten. A WZW model is associated to a Lie group, and its symmetry algebra is the affine Lie algebra built from the corresponding Lie algebra. By extension, the name WZW model is sometimes used for any conformal field theory whose symmetry algebra is an affine Lie algebra.
In mathematics, Tannaka–Krein duality theory concerns the interaction of a compact topological group and its category of linear representations. It is a natural extension of Pontryagin duality, between compact and discrete commutative topological groups, to groups that are compact but noncommutative. The theory is named after Tadao Tannaka and Mark Grigorievich Krein. In contrast to the case of commutative groups considered by Lev Pontryagin, the notion dual to a noncommutative compact group is not a group, but a category of representations Π(G) with some additional structure, formed by the finite-dimensional representations of G.
In theoretical physics, a primary field, also called a primary operator, or simply a primary, is a local operator in a conformal field theory which is annihilated by the part of the conformal algebra consisting of the lowering generators. From the representation theory point of view, a primary is the lowest dimension operator in a given representation of the conformal algebra. All other operators in a representation are called descendants; they can be obtained by acting on the primary with the raising generators.
Asım Orhan Barut was a Turkish-American theoretical physicist.
In conformal field theory and representation theory, a W-algebra is an associative algebra that generalizes the Virasoro algebra. W-algebras were introduced by Alexander Zamolodchikov, and the name "W-algebra" comes from the fact that Zamolodchikov used the letter W for one of the elements of one of his examples.
In physics, a charge is any of many different quantities, such as the electric charge in electromagnetism or the color charge in quantum chromodynamics. Charges correspond to the time-invariant generators of a symmetry group, and specifically, to the generators that commute with the Hamiltonian. Charges are often denoted by , and so the invariance of the charge corresponds to the vanishing commutator , where is the Hamiltonian. Thus, charges are associated with conserved quantum numbers; these are the eigenvalues of the generator . A "charge" can also refer to a point-shaped object with an electric charge and a position, such as in the method of image charges.
Sergio Ferrara is an Italian physicist working on theoretical physics of elementary particles and mathematical physics. He is renowned for the discovery of theories introducing supersymmetry as a symmetry of elementary particles and of supergravity, the first significant extension of Einstein's general relativity, based on the principle of "local supersymmetry". He is an emeritus staff member at CERN and a professor emeritus at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Representation theory is a branch of mathematics that studies abstract algebraic structures by representing their elements as linear transformations of vector spaces, and studies modules over these abstract algebraic structures. In essence, a representation makes an abstract algebraic object more concrete by describing its elements by matrices and their algebraic operations.
In mathematics, a Verlinde algebra is a finite-dimensional associative algebra introduced by Erik Verlinde, with a basis of elements φλ corresponding to primary fields of a rational two-dimensional conformal field theory, whose structure constants Nν
λμ describe fusion of primary fields.
The conformal bootstrap is a non-perturbative mathematical method to constrain and solve conformal field theories, i.e. models of particle physics or statistical physics that exhibit similar properties at different levels of resolution.
A two-dimensional conformal field theory is a quantum field theory on a Euclidean two-dimensional space, that is invariant under local conformal transformations.
References
- ↑ Fuchs, J (1994). "Fusion rules in conformal field theory". Fortschritte der Physik/Progress of Physics. 42 (1994): 1–48. arXiv: hep-th/9306162 . Bibcode:1994ForPh..42....1F. doi:10.1002/prop.2190420102. S2CID 14139601.