Related Research Articles

The economy of Afghanistan is listed as the 124th largest in the world in terms of nominal gross domestic product (GDP), and 102nd largest in the world in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP). With a population of around 41 million people, Afghanistan's GDP (nominal) stands at $14.58 billion as of 2021, amounting to a GDP per capita of $363.7. Its annual exports exceed $2 billion, with agricultural, mineral and textile products accounting for 94% of total exports. The nation's total external debt is $1.4 billion as of 2022.

The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is an independent agency of the United States government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. With a budget of over $50 billion, USAID is one of the largest official aid agencies in the world and accounts for more than half of all U.S. foreign assistance—the highest in the world in absolute dollar terms.
Roots of Peace is a humanitarian organization dedicated to the removal of landmines and the subsequent replanting and rebuilding of war-torn regions. Founded in 1997 by Heidi Kuhn, the goal of Roots of Peace is to turn minefields into farmland and support victims of landmine accidents. The organization is funded by private and public funding, including the California Wine Industry, and is based in San Rafael, California.

A Provincial Reconstruction Team (PRT) was a unit introduced by the United States government, consisting of military officers, diplomats, and reconstruction subject matter experts, working to support reconstruction efforts in unstable states. PRTs were first established in Afghanistan in early 2002, and were used in Iraq as well. While the concepts are similar, PRTs in Afghanistan and Iraq had separate compositions and missions. Their common purpose, however, was to empower local governments to govern their constituents more effectively.

Andrew S. Natsios is an American public servant and Republican politician originally from Massachusetts, who served in a number of positions in the administrations of Governor Paul Cellucci and President George W. Bush.

CGIAR is a global partnership that unites international organizations engaged in research about food security. CGIAR research aims to reduce rural poverty, increase food security, improve human health and nutrition, and sustainable management of natural resources.
The Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS) is the foreign affairs agency with primary responsibility for the United States Department of Agriculture's (USDA) overseas programs – market development, international trade agreements and negotiations, and the collection of statistics and market information. It also administers the USDA's export credit guarantee and food aid programs and helps increase income and food availability in developing nations by mobilizing expertise for agriculturally led economic growth. The FAS mission statement reads, "Linking U.S. agriculture to the world to enhance export opportunities and global food security," and its motto is "Linking U.S. Agriculture to the World."

The Kajaki Dam is "an earth and rockfill embankment type dam" located on the Helmand River in the Kajaki District of Helmand Province in Afghanistan, about 161 km (100 mi) northwest of Kandahar. It has a hydroelectric power station, which is operated by the Helmand and Arghandab Valley Authority through the Ministry of Energy and Water.
The International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA), a member of CGIAR, supported by the CGIAR Fund, is a non-profit agricultural research institute that aims to improve the livelihoods of the resource-poor across the world's dry areas.
Pakistan receives foreign aid from several countries and international organizations.
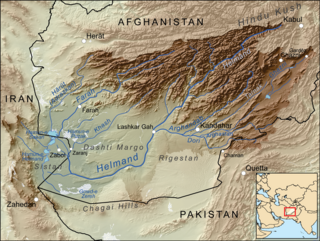
The Helmand and Arghandab Valley Authority (HAVA) based in Lashkar Gah, Afghanistan, originally named the Helmand Valley Authority (HVA) until its expansion in 1965, was established on December 4, 1952, as an agency of the Afghan Government. The agency was modeled on the Tennessee Valley Authority in the United States, with a remit covering lands in Farah Province, Ghazni Province, Helmand Province, Herat Province, and Kandahar Province.

Afghanistan-Norway relations are bilateral diplomatic relations between Afghanistan and Norway. Afghanistan has an embassy in Oslo. Norway has an embassy in Kabul, although has been closed since the August 2021 Taliban takeover of Kabul.

Pomegranate production in Afghanistan is a significant contributor to the country's agricultural economy. It likely existed in the country since ancient time. Pomegranates are a major fruit crop in many provinces, particularly in Kandahar, Helmand, Wardak, Ghazni, Paktia, Farah, Kapisa and Balkh, and are the source of the livelihoods of thousands of people.
International Relief and Development, Inc. (IRD), renamed Blumont, is an organization that purports to provide relief, stabilization, and development programs worldwide. In 2015, IRD was the subject of a Washington Post investigation that highlighted the organization's performance and management of taxpayer money. Among other irregularities, the organization had charged the US Government $1.1 million for staff parties and retreats at exclusive resorts. In January 2016, IRD announced that it was changing its name to Blumont and relocating to Madison, Wisconsin.

The Sarda Dam is located near the town of Sardeh Band, in the eastern part of Andar District of Ghazni Province of Afghanistan. Part of its reservoir, which provides fresh water to much of southern Ghazni, is in neighboring Paktika Province. In recent years, the locals proposed to turn the area into a national park, similar to the Band-e Amir National Park in Bamyan Province.
Chemonics International, Inc. is a private international development firm based in Washington, D.C. It was established in 1975 by Thurston F. (Tony) Teele as a subsidiary of Erly Industries. The employee-owned company offers a variety of services globally and with more than $1.5 billion in USAID contracts in 2019 is the largest for-profit recipient of U.S. government foreign aid. As of 2019 the company has approximately 5,000 employees in 100 countries.

Jordan has been granted considerate amounts of international aid moneys toward environmental conservation. Foreign aid goes into mitigation projects in the areas of water scarcity, loss of arable land for agriculture, and renewable energy. Moreover, foreign aid goes toward the development of the eco-tourism sector. Jordan receives aid from different kinds of international agents. Principal institutions that donate money toward environmentalism in Jordan are the Global Environmental Facility (GEF), United States Agency for International Development (USAID), and World Bank. Recently, Jordan has had problems to control its budgetary deficit, which directly affects its ability to manage its environmental problems. That has made some point out that Jordan depends on International aid to control environmental-related issues. One of the examples of that is related to the construction of the East Ghor Canal.

The Board for International Food and Agricultural Development (BIFAD) advises the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) on issues concerning agriculture, higher education in developing countries, and food insecurity. BIFAD was established and recognized by Title XII of the Foreign Assistance Act, and both the BIFAD board and Title XII recognize the critical role of U.S. land-grant institutions in food and agricultural security, domestically and abroad. BIFAD consists of seven board members appointed by the White House, four of whom must have been part of the US Academic community. The board's mission is to draw on the expertise and scientific knowledge of those in higher education to advise the US international assistance on the effect of domestic efforts to end food insecurity.

Almond production in Afghanistan is a significant contributor to the nation's agricultural economy. In 2009, it was ranked ninth in the FAO list of almond-producing countries of the world, though its domestic production is limited to 2% of the world production. Afghanistan's almond production has shown a rising trend in the recent decades. Within the country, the southwestern and northern regions have the maximum area under cultivation with Kandahar and Samangan provinces, accounting for much of its production, followed by the provinces of Uruzgan, Kunduz, Balkh, Saripul and Daykundi. As of 2012, the cultivated area of almonds was 13,490 ha with a yield rate of 45,960 hectograms per ha, recording a total yield of 62,000 tonnes, with conducive climatic conditions for growing variety of almond landraces of hard shell and soft shell varieties. The preferred markets for the export of Afghan almonds are India and Pakistan, with the former preferred because of better profitability.

Geoffrey Hawtin OBE is an agricultural scientist and World Food Prize laureate who has served in public institutions working in agricultural biodiversity, plant genetic resources, crop breeding and research management. He was awarded an OBE by Queen Elizabeth II and has been recognized for his career "dedicated to using agriculture as a weapon in the war against poverty in developing countries." He played key roles in the creation of the Svalbard Global Seed Vault and the negotiation of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources. He has headed two CGIAR Research Centers and currently is on the Executive Board of the Crop Trust.
References
- ↑ "Afghanistan Minister of Agriculture Opens Steering Committee Meeting of Future Harvest Consortium". Reliefweb. 10 March 2005. Retrieved 2012-05-28.
- ↑ "Afghanistan & ICARDA". International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas. Archived from the original on 2012-03-16. Retrieved 2012-05-28.
- ↑ "Rebuilding Agriculture In Afghanistan" (PDF). Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock. May 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-10-01. Retrieved 2024-04-11.