Medicare is the publicly funded universal health care insurance scheme in Australia, along with the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) operated by the nation's social security department, Services Australia. Medicare is the principal way Australian citizens and permanent residents access most health care services in Australia. The scheme either partially or fully covers the cost of most primary health care services in the public and private health care system. All Australian citizens and permanent residents have access to fully-covered health care in public hospitals, funded by Medicare, as well as state and federal contributions. International visitors from 11 countries have subsidised access to medically necessary treatment under reciprocal agreements.
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment, unemployment compensation, or simply unemployment, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a compulsory governmental insurance system, not taxes on individual citizens. Depending on the jurisdiction and the status of the person, those sums may be small, covering only basic needs, or may compensate the lost time proportionally to the previous earned salary.
The New Deal was a workfare programme introduced in the United Kingdom by the first New Labour government in 1998, initially funded by a one-off £5 billion windfall tax on privatised utility companies. The stated purpose was to reduce unemployment by providing training, subsidised employment and voluntary work to the unemployed. Spending on the New Deal was £1.3 billion in 2001.
Jobseeker's Allowance (JSA) is an unemployment benefit paid by the Government of the United Kingdom to people who are unemployed and actively seeking work. It is part of the social security benefits system and is intended to cover living expenses while the claimant is out of work.
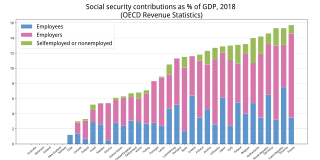
Social insurance is a form of social welfare that provides insurance against economic risks. The insurance may be provided publicly or through the subsidizing of private insurance. In contrast to other forms of social assistance, individuals' claims are partly dependent on their contributions, which can be considered insurance premiums to create a common fund out of which the individuals are then paid benefits in the future.
Benefit fraud is a form of welfare fraud as found within the system of government benefits paid to individuals by the welfare state in the United Kingdom.
Trade Adjustment Assistance (TAA) is a federal program of the United States government to act as a way to reduce the damaging impact of imports felt by certain sectors of the U.S. economy. The current structure features four components of Trade Adjustment Assistance: for workers, firms, farmers, and communities. Each cabinet-level department was tasked with a different sector of the overall Trade Adjustment Assistance program. The program for workers is the largest, and is administered by the U.S. Department of Labor. The program for farmers is administered by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, and the firms and communities programs are administered by the U.S. Department of Commerce.
Work for the Dole is an Australian Government program that is a form of workfare, or work-based welfare. It was first permanently enacted in 1998, having been trialled in 1997. It is one means by which job seekers can satisfy the "mutual obligation requirements" to receive the Newstart Allowance, now replaced by the JobSeeker Payment. Other "mutual obligation" measures can include: accredited study, part-time work, Australian Army Reserves, and volunteer work.
Active labour market policies (ALMPs) are government programmes that intervene in the labour market to help the unemployed find work, but also for the underemployed and employees looking for better jobs. In contrast, passive labour market policies involve expenditures on unemployment benefits and early retirement. Historically, labour market policies have developed in response to both market failures and socially/politically unacceptable outcomes within the labor market. Labour market issues include, for instance, the imbalance between labour supply and demand, inadequate income support, shortages of skilled workers, or discrimination against disadvantaged workers.
Social security, in Australia, refers to a system of social welfare payments provided by Australian Government to eligible Australian citizens, permanent residents, and limited international visitors. These payments are almost always administered by Centrelink, a program of Services Australia. In Australia, most payments are means tested.
Unemployment benefits in Sweden are payments made by the state or other authorized bodies to unemployed people. They can be divided into a voluntary scheme with income-related compensation up to a certain level, or a comprehensive scheme that provides a lower level of basic support.
Severn Tidal Power Feasibility Study is the name of a UK Government feasibility study into a tidal power project looking at the possibility of using the huge tidal range in the Severn Estuary and Bristol Channel to generate electricity.

A4e was a for-profit, welfare-to-work company based in the United Kingdom. The company began in Sheffield in 1991 with the objective to provide redundant steelworkers with the training required to obtain new jobs.

Youth unemployment in the United Kingdom is the level of unemployment among young people, typically defined as those aged 18–25. A related concept is graduate unemployment which is the level of unemployment among university graduates. Statistics for June 2010 show that there are 926,000 young people under the age of 25 who are unemployed which equates to an unemployment rate of 19.6% among young people. This is the highest youth unemployment rate in 17 years. In November 2011 youth unemployment hit 1.02 million, but had fallen to 767,000 by August 2014. The high levels of youth unemployment in the United Kingdom have led some politicians and media commentators to talk of a "lost generation".

The National Citizen Service (NCS) is a voluntary personal and social development program for 16–17 year olds in England funded largely by money from the UK Government. It was founded in 2009 and formally announced in 2010 by Prime Minister David Cameron as part of the Conservative–Liberal Democrat coalition government's Big Society initiative, and it was launched in England in 2011. After the 2015 general election, the programme was continued under the Conservative government. In October 2016 Cameron, who had resigned as Prime Minister, became chairman of the NCS Trust's patrons' board. The scheme was made permanent through the National Citizen Service Act 2017.With cross-party support, NCS became a Royal Charter Body in 2018.

The United Kingdom national debt is the total quantity of money borrowed by the Government of the United Kingdom at any time through the issue of securities by the British Treasury and other government agencies.

Workfare in the United Kingdom is a system of welfare regulations put into effect by UK governments at various times. Individuals subject to workfare must undertake work in return for their welfare benefit payments or risk losing them. Workfare policies are politically controversial. Supporters claim that such policies help people move off welfare and into employment whereas critics argue that they are analogous to slavery or indentured servitude and counterproductive in decreasing unemployment.
The Work Programme (WP) was a UK government welfare-to-work programme introduced in Great Britain in June 2011. It was the flagship welfare-to-work scheme of the 2010–2015 UK coalition government. Under the Work Programme the task of getting the long-term unemployed into work was outsourced to a range of public sector, private sector and third sector organisations. The scheme replaced a range of schemes which existed under previous New Labour governments including Employment Zones, New Deal, Flexible New Deal and the now abolished Future Jobs Fund scheme which aimed to tackle youth unemployment. Despite being the flagship welfare-to-work scheme of the Conservative-led coalition government, and then the incumbent Conservative government from May 2015, the DWP announced, in November 2015, that it was replacing the Work Programme and Work Choice with a new Work and Health Programme for the longer-term unemployed and those with health conditions. The DWP also announced that it would not be renewing Mandatory Work Activity and Help to Work which included Community Work Placements.

The Welfare Reform Act 2012 is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom which makes changes to the rules concerning a number of benefits offered within the British social security system. It was enacted by the Parliament of the United Kingdom on 8 March 2012.
The Troubled Families programme is a UK Government scheme under the Department for Communities and Local Government with the stated aim of helping troubled families turn their lives around.






