Related Research Articles
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, and a debugger. Some IDEs, such as IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse and Lazarus contain the necessary compiler, interpreter or both; others, such as SharpDevelop and NetBeans, do not.

An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. In 2009, it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems.

Pure Data (Pd) is a visual programming language developed by Miller Puckette in the 1990s for creating interactive computer music and multimedia works. While Puckette is the main author of the program, Pd is an open-source project with a large developer base working on new extensions. It is released under BSD-3-Clause. It runs on Linux, MacOS, iOS, Android and Windows. Ports exist for FreeBSD and IRIX.

In computing, a visual programming language, also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create programs by manipulating program elements graphically rather than by specifying them textually. A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms.

Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench (LabVIEW) is a graphical system design and developmentplatform produced and distributed by National Instruments, based on a programming environment that uses a visual programming language. It is widely used for data acquisition, instrument control, and industrial automation. It provides tools for designing and deploying complex test and measurement systems.

Fast Light Toolkit (FLTK) is a cross-platform widget library for graphical user interfaces (GUIs), developed by Bill Spitzak and others. Made to accommodate 3D graphics programming, it has an interface to OpenGL, but it is also suitable for general GUI programming.
BrickOS is an open-source operating system created by Markus Noga as firmware to operate as an alternative software environment for the Lego Mindstorms Robotic Invention System. BrickOS is the first open-source software made for Lego Mindstorms robots. It allows development using the C, C++, and Java programming languages. Programs are cross compiled using the g++ and Jack compilers, with the toolchain targeting the Hitachi H8 architecture used in Mindstorms devices.

The NASA Advanced Supercomputing (NAS) Division is located at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field in the heart of Silicon Valley in Mountain View, California. It has been the major supercomputing and modeling and simulation resource for NASA missions in aerodynamics, space exploration, studies in weather patterns and ocean currents, and space shuttle and aircraft design and development for almost forty years.
Robot software is the set of coded commands or instructions that tell a mechanical device and electronic system, known together as a robot, what tasks to perform. Robot software is used to perform autonomous tasks. Many software systems and frameworks have been proposed to make programming robots easier.

Qfix robot kits are an education tool for teaching robotics. They are used in schools, high schools and mechatronics training in companies. The robot kits are also used by hobby robot builders. The qfix kits are often found in the RoboCup Junior competition where soccer robots are built of the kit's components.

Microsoft Robotics Developer Studio is a discontinued Windows-based environment for robot control and simulation that was aimed at academic, hobbyist, and commercial developers and handled a wide variety of robot hardware. It requires a Microsoft Windows 7 operating system or later.
Specialized wind energy software applications aid in the development and operation of wind farms.
KNIME, the Konstanz Information Miner, is a free and open-source data analytics, reporting and integration platform. KNIME integrates various components for machine learning and data mining through its modular data pipelining "Building Blocks of Analytics" concept. A graphical user interface and use of JDBC allows assembly of nodes blending different data sources, including preprocessing, for modeling, data analysis and visualization without, or with minimal, programming.
CH is a proprietary cross-platform C and C++ interpreter and scripting language environment. It was designed by Harry Cheng as a scripting language for beginners to learn mathematics, computing, numerical analysis, and programming in C/C++. Ch is now developed and marketed by SoftIntegration, Inc.. Free versions include the student edition, and the non-commercial Professional Edition for Raspberry Pi.
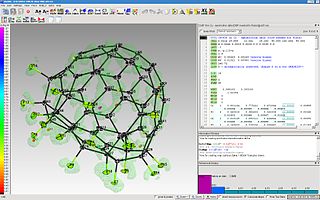
The program ShelXle is a graphical user interface for the structure refinement program SHELXL. ShelXle combines an editor with syntax highlighting for the SHELXL-associated .ins (input) and .res (output) files with an interactive graphical display for visualization of a three-dimensional structure including the electron density (Fo) and difference density (Fo-Fc) maps.

SPEDAS is an open-source data analysis tool intended for space physics users. It was developed using Interactive Data Language (IDL). Since its creation, the tool has also been ported to Python in the form of a program referred to as pySPEDAS.

PWCT is a free open source visual programming language for software development. The project was founded in December 2005 as a free open-source project that supports designing applications through visual programming then generating the source code. The software supports code generation in many textual programming languages.
References
- ↑ M. Rumpf, M. Wierse, Time-dependent flow. In Visualization Methods in High Performance Computing and Flow Simulation (1996)
- ↑ Introduction to GRAPE