Related Research Articles

A fossil fuel is a carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material such as coal, oil, and natural gas, formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of prehistoric organisms, a process that occurs within geological formations. Reservoirs of such compound mixtures can be extracted and burned as a fuel for human consumption to provide heat for direct use, to power heat engines that can propel vehicles, or to generate electricity via steam turbine generators. Some fossil fuels are further refined into derivatives such as kerosene, gasoline and diesel.

Alternative fuels, also known as non-conventional and advanced fuels, are fuels derived from sources other than petroleum. Alternative fuels include gaseous fossil fuels like propane, natural gas, methane, and ammonia; biofuels like biodiesel, bioalcohol, and refuse-derived fuel; and other renewable fuels like hydrogen and electricity.

A zero-emission vehicle, or ZEV, is a vehicle that does not emit exhaust gas or other pollutants from the onboard source of power. The California definition also adds that this includes under any and all possible operational modes and conditions. This is because under cold-start conditions for example, internal combustion engines tend to produce the maximum amount of pollutants. In a number of countries and states, transport is cited as the main source of greenhouse gases (GHG) and other pollutants. The desire to reduce this is thus politically strong.

A green vehicle, clean vehicle, eco-friendly vehicle or environmentally friendly vehicle is a road motor vehicle that produces less harmful impacts to the environment than comparable conventional internal combustion engine vehicles running on gasoline or diesel, or one that uses certain alternative fuels. Presently, in some countries the term is used for any vehicle complying or surpassing the more stringent European emission standards, or California's zero-emissions vehicle standards, or the low-carbon fuel standards enacted in several countries.

A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel, such as coal, oil, or natural gas, to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small plants, a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from the expansion of a hot gas, either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist, all thermal power station conversion methods have their efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat.

The National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL) is a U.S. national laboratory under the Department of Energy Office of Fossil Energy. NETL focuses on applied research for the clean production and use of domestic energy resources. It performs research and development on the supply, efficiency, and environmental constraints of producing and using fossil energy resources while maintaining affordability.
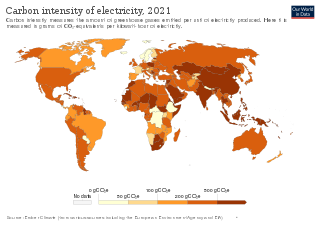
An emission intensity is the emission rate of a given pollutant relative to the intensity of a specific activity, or an industrial production process; for example grams of carbon dioxide released per megajoule of energy produced, or the ratio of greenhouse gas emissions produced to gross domestic product (GDP). Emission intensities are used to derive estimates of air pollutant or greenhouse gas emissions based on the amount of fuel combusted, the number of animals in animal husbandry, on industrial production levels, distances traveled or similar activity data. Emission intensities may also be used to compare the environmental impact of different fuels or activities. In some case the related terms emission factor and carbon intensity are used interchangeably. The jargon used can be different, for different fields/industrial sectors; normally the term "carbon" excludes other pollutants, such as particulate emissions. One commonly used figure is carbon intensity per kilowatt-hour (CIPK), which is used to compare emissions from different sources of electrical power.

Synthetic fuel or synfuel is a liquid fuel, or sometimes gaseous fuel, obtained from syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, in which the syngas was derived from gasification of solid feedstocks such as coal or biomass or by reforming of natural gas.
Renewable fuels are fuels produced from renewable resources. Examples include: biofuels, Hydrogen fuel, and fully synthetic fuel produced from ambient carbon dioxide and water. This is in contrast to non-renewable fuels such as natural gas, LPG (propane), petroleum and other fossil fuels and nuclear energy. Renewable fuels can include fuels that are synthesized from renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar. Renewable fuels have gained in popularity due to their sustainability, low contributions to the carbon cycle, and in some cases lower amounts of greenhouse gases. The geo-political ramifications of these fuels are also of interest, particularly to industrialized economies which desire independence from Middle Eastern oil.

Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide, from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is one of the most important factors in causing climate change. The largest emitters are China followed by the United States. The United States has higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 GtC, of which 484±20 GtC from fossil fuels and industry, and 219±60 GtC from land use change. Land-use change, such as deforestation, caused about 31% of cumulative emissions over 1870–2022, coal 32%, oil 24%, and gas 10%.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.

Fossil fuel phase-out is the gradual reduction of the use and production of fossil fuels to zero, to reduce deaths and illness from air pollution, limit climate change, and strengthen energy independence. It is part of the ongoing renewable energy transition, but is being hindered by fossil fuel subsidies.
This is a list of climate change topics.
The environmental impact of transport in Australia are considerable. Australia subsidizes fossil fuel energy, keeping prices artificially low and raising greenhouse gas emissions due to the increased use of fossil fuels as a result of the subsidies. The Australian Energy Regulator and state agencies such as the New South Wales' Independent Pricing and Regulatory Tribunal set and regulate electricity prices, thereby lowering production and consumer cost.

A low-carbon fuel standard (LCFS) is an emissions trading rule designed to reduce the average carbon intensity of transportation fuels in a given jurisdiction, as compared to conventional petroleum fuels, such as gasoline and diesel. The most common methods for reducing transportation carbon emissions are supplying electricity to electric vehicles, supplying hydrogen fuel to fuel cell vehicles and blending biofuels, such as ethanol, biodiesel, renewable diesel, and renewable natural gas into fossil fuels. The main purpose of a low-carbon fuel standard is to decrease carbon dioxide emissions associated with vehicles powered by various types of internal combustion engines while also considering the entire life cycle, in order to reduce the carbon footprint of transportation.
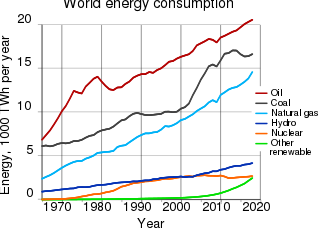
The environmental impact of the energy industry is significant, as energy and natural resource consumption are closely related. Producing, transporting, or consuming energy all have an environmental impact. Energy has been harnessed by human beings for millennia. Initially it was with the use of fire for light, heat, cooking and for safety, and its use can be traced back at least 1.9 million years. In recent years there has been a trend towards the increased commercialization of various renewable energy sources. Scientific consensus on some of the main human activities that contribute to global warming are considered to be increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases, causing a warming effect, global changes to land surface, such as deforestation, for a warming effect, increasing concentrations of aerosols, mainly for a cooling effect.

The environmental impact of the petroleum industry is extensive and expansive due to petroleum having many uses. Crude oil and natural gas are primary energy and raw material sources that enable numerous aspects of modern daily life and the world economy. Their supply has grown quickly over the last 150 years to meet the demands of the rapidly increasing human population, creativity, knowledge, and consumerism.
Carbon-neutral fuel is fuel which produces no net-greenhouse gas emissions or carbon footprint. In practice, this usually means fuels that are made using carbon dioxide (CO2) as a feedstock. Proposed carbon-neutral fuels can broadly be grouped into synthetic fuels, which are made by chemically hydrogenating carbon dioxide, and biofuels, which are produced using natural CO2-consuming processes like photosynthesis.

The long tailpipe is an argument stating that usage of electric vehicles does not always result in fewer emissions compared to those from non-electric vehicles. While the argument acknowledges that plug-in electric vehicles operating in all-electric mode have no greenhouse gas emissions from the onboard source of power, it claims that these emissions are shifted from the vehicle tailpipe to the location of the electrical generation plants. From the point of view of a well-to-wheel assessment, the extent of the actual carbon footprint depends on the fuel and technology used for electricity generation, as well as the impact of additional electricity demand on the phase-out of fossil fuel power plants.
Michael Wang is a distinguished fellow, a senior scientist, and director of the Systems Assessment Center of the Energy Systems Division at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory. He is also a faculty associate in the Energy Policy Institute at The University of Chicago; a senior fellow at the Northwestern-Argonne Institute of Science and Engineering at Northwestern University.
References
- ↑ "H.R.5376 — 117th Congress (2021-2022)". US: Congress. August 16, 2022. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- ↑ "R&D GREET Model Platforms". US: Argonne National Laboratory. Retrieved August 6, 2024.