
The Faranah Region is located in east-central Guinea. It is bordered by the countries of Sierra Leone and Mali and the Guinean regions of Kankan, Mamou, Nzérékoré, and Labé.

Tougué is a prefecture located in the Labé Region of Guinea. The capital is Tougué. The prefecture covers an area of 6,400 km². and has an estimated population of 132,000.

Lélouma is a prefecture located in the Labé Region of Guinea. The capital is Lélouma. The prefecture covers an area of 2,140 km.² In census of 2014, it had population of 163,000.
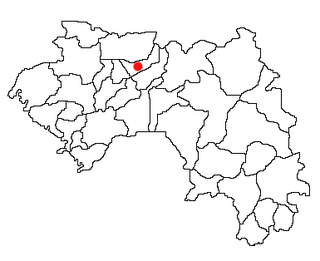
Koubia is a prefecture located in the Labé Region of Guinea in the Fouta Djallon mountains. Fulas are the majority ethnic group in the region with Fula (Pular) as the primary language. The capital is Koubia. The prefecture covers an area of 2,800 km.² and has an estimated population of 114,000.

Labé is a prefecture in the Labé Region of Guinea. The capital is Labé. The prefecture covers an area of 3,014 km.² and has an estimated population of 204,000.

The Kindia Region is located in western Guinea. It is bordered by the country of Sierra Leone and the Guinean regions of Conakry, Labé, Mamou, and Boké.

The Labé Region is located in north-central Guinea. It is bordered by the countries of Senegal and Mali and the Guinean regions of Faranah, Kindia, Mamou, and Boké.

Moussadou is a town and sub-prefecture in the Beyla Prefecture in the Nzérékoré Region of south-eastern Guinea.

Lisso is a town and sub-prefecture in the Boffa Prefecture in the Boké Region of western Guinea. As of 2014 it had a population of 11,861 people.

Marela is a town and sub-prefecture in the Faranah Prefecture in the Faranah Region of Guinea. As of 2014 it had a population of 32,638 people.

Passayah is a town and sub-prefecture in the Faranah Prefecture in the Faranah Region of Guinea. As of 2014 it had a population of 19,849 people.

Sandéniah is a town and sub-prefecture in the Faranah Prefecture in the Faranah Region of Guinea. As of 2014 it had a population of 17,454 people.

Koumbia is a town and sub-prefecture in the Gaoual Prefecture in the Boké Region of north-western Guinea. As of 2014 it had a population of 45,970 people.

Donghol-Sigon is a town and sub-prefecture in the Mali Prefecture in the Labé Region of northern Guinea.

Yimbéring is a town and sub-prefecture in the Mali Prefecture in the Labé Region of northern Guinea.

Nyagara is a town and sub-prefecture in the Mamou Prefecture in the Mamou Region of Guinea.

Bourouwal-Tappé is a town and sub-prefecture in the Pita Prefecture in the Mamou Region of northern-central Guinea.

Franwalia is a town and sub-prefecture in the Siguiri Prefecture in the Kankan Region of northern Guinea.

Maléa is a town and sub-prefecture in the Siguiri Prefecture in the Kankan Region of northern Guinea.

Sarékaly is a town and sub-prefecture in the Télimélé Prefecture in the Kindia Region of western-central Guinea.














