The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times, due to China's large population and geographical area. The constitution of China provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there are five levels of local government; the provincial, prefecture, county, township, and village.

A prefecture-level city or prefectural city is an administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC), ranking below a province and above a county in China's administrative structure.
A sub-provincial division in China is a prefecture-level city governed by a province promoted by half a level. Thus, it is half a level under the provincial level but half a level above the prefecture-level.
Subprefecture of Japan are a Japanese form of self-government which focuses on local issues below the prefectural level. It acts as part of the greater administration of the state and as part of a self-government system.
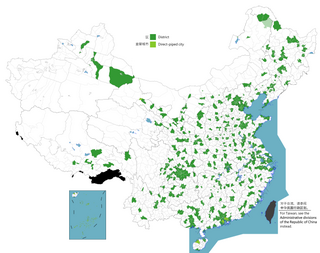
The term district, in the context of China, is used to refer to several unrelated political divisions in both ancient and modern China.

Guinea is divided into 8 regions among which the national capital Conakry ranks as a special zone. The other 7 regions are further subdivided into 33 prefectures and thence into sub-prefectures; which are later subdivided into local units and further subdivided into smaller units.
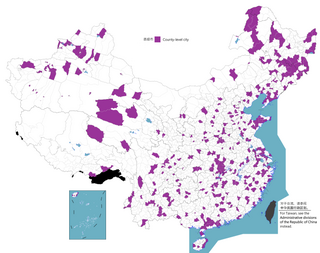
A county-level municipality, county-level city or county city, formerly known as prefecture-controlled city, is a county-level administrative division of the People's Republic of China. County-level cities have judicial but no legislative rights over their own local law and are usually governed by prefecture-level divisions, but a few are governed directly by province-level divisions.

The bureaucratic administration of Japan is divided into three basic levels: national, prefectural, and municipal. They are defined by the Local Autonomy Law of 1947.

An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.

Lélouma is a prefecture located in the Labé Region of Guinea. The capital is Lélouma. The prefecture covers an area of 2,140 km.² In census of 2014, it had population of 163,000.

Guinea is divided into 8 administrative regions. 7 regions other than Conakry Region are further subdivided into 33 prefectures.

In Morocco, the 75 second-level administrative subdivisions are 13 prefectures and 62 provinces. They are subdivisions of the 12 regions of Morocco. Each prefecture or province is subdivided into arrondissements, municipalities or urban municipalities in other urban areas, and districts in rural areas. The districts are subdivided into rural municipalities. One prefecture (Casablanca) is also subdivided into préfectures d'arrondissements, similar to districts (cercles) except they are grouping a few arrondissements instead of rural municipalities.
Bolodou is a town and sub-prefecture in the Guéckédou Prefecture in the Nzérékoré Region of south-western Guinea. The sub-prefecture had a population of 13,643 in 2014, up from 11,750 in 1996. The town itself has 94 houses with an unknown population. The Bolodou Sub-Prefecture is divided into seven quarters (districts), which are Beddou, Bolodou Centre, Faindou, Gbandou, Koleadou, Kongoma and Soumtou. Each of these towns can further be split into sectors, which are the smallest administrative divisions in Guinea.
Madina-Wora is a town and sub-prefecture in the Mali Prefecture in the Labé Region of northern Guinea. It is listed under Geocode 2608 and Has code GN.ML.MW. It is a third-order administrative division.

Guinea is divided into four natural regions with distinct human, geographic, and climatic characteristics:

A direct-administrated municipality, commonly known as municipality, is one of four types of province-level divisions of China. It is the highest level of classification for cities used by the People's Republic of China.
Districts, also known as rural districts or counties, are one of several types of second-tier administrative subdivisions of Vietnam, the other types being urban districts, provincial cities, municipal city, and district-level towns. The districts are subdivisions of the first-tier divisions, namely the provinces and municipalities. Districts are subdivided into third-tier units, namely townships and communes.
Fu is a traditional administrative division of Chinese origin used in the East Asian cultural sphere, translated variously as commandery, prefecture, urban prefecture, or city. They were first instituted as a regular form of administrative division of China's Tang Empire, but were later adopted in Vietnam, Japan and Korea. At present, only two fu still remain: the prefectures of Kyoto and Osaka in Japan.











