Politics of Guinea takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Guinea is both head of state and head of government of Guinea. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly.

The Guinean Armed Forces are the armed forces of Guinea. They are responsible for the territorial security of Guinea's border and the defence of the country against external attack and aggression.

Conakry is the capital and largest city of Guinea. A port city, it serves as the economic, financial and cultural centre of Guinea. Its population as of the 2014 Guinea census was 1,660,973.
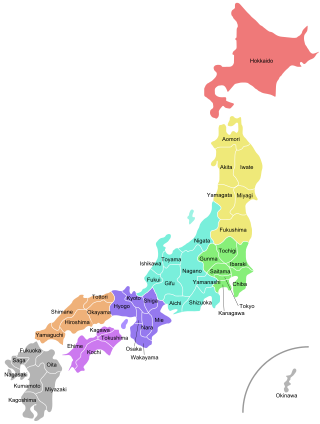
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one regional prefecture and one metropolis. In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.
ISO 3166-2:GN is the entry for Guinea in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.
Guinea-Bissau is divided into 8 regions and 1 autonomous sector. The regions are subdivided into a total of 37 sectors ; which are further subdivided into smaller groups called sections ; which are further subdivided into populated places. Here are the following listed below:

The bureaucratic administration of Japan is divided into three basic levels: national, prefectural, and municipal. They are defined by the Local Autonomy Law of 1947.

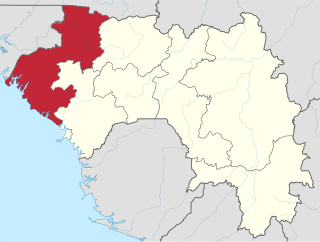
Faranah Region is located in east-central Guinea. It is bordered by the countries of Sierra Leone and Mali and the Guinean regions of Kankan, Mamou, Nzérékoré, and Labé.

Guinea is divided into 8 administrative regions. 7 regions other than Conakry Region are further subdivided into 33 prefectures.
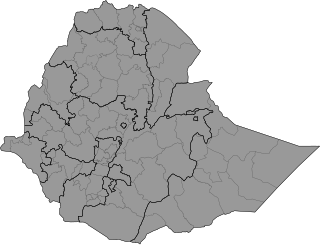
Ethiopia is administratively divided into four levels: regions, zones, woredas (districts) and kebele (wards). The country comprises 11 regions and two city administrations under these regions, plenty of zones, woredas and neighbourhood administration: kebeles. In addition to the nine federal states within the country, there are two federal-level city administrations in Addis Ababa and Dire Dava.

The constitution divides Cameroon into 10 semi-autonomous regions, each under the administration of an elected Regional Council. A presidential decree of 12 November 2008 officially instigated the change from provinces to regions. Each region is headed by a presidentially appointed governor. These leaders are charged with implementing the will of the president, reporting on the general mood and conditions of the regions, administering the civil service, keeping the peace, and overseeing the heads of the smaller administrative units. Governors have broad powers: they may order propaganda in their area and call in the army, gendarmes, and police. All local government officials are employees of the central government's Ministry of Territorial Administration, from which local governments also get most of their budgets.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Guinea:
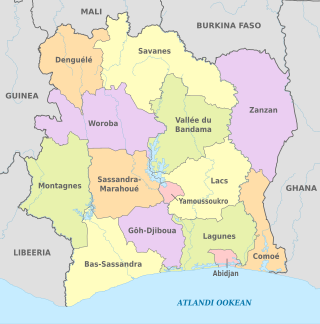
Ivory Coast is a relatively decentralised state. The country divided into 14 districts, of which two are cities organised as autonomous districts. The other 12 districts are subdivided into 31 second-level regions. The autonomous districts and the regions are divided into 111 third-level departments. The departments are divided into 510 fourth-level sub-prefectures. Sub-prefectures contain villages and, in some instances, several villages are combined into fifth-level communes. There are 197 communes.

Guinea is divided into four natural regions with distinct human, geographic, and climatic characteristics: