|
|---|
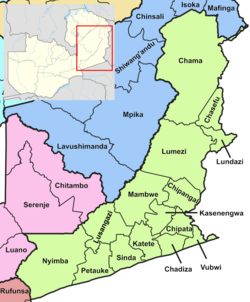
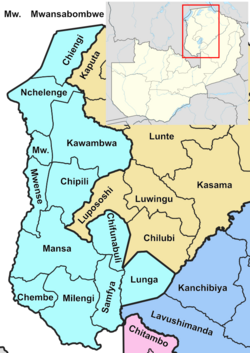
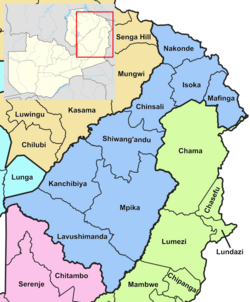
The ten provinces of Zambia are divided into a total of 116 districts as of 2018.
Contents
- Provincial districts in Zambia
- List of districts per province
- Central Province
- Copperbelt Province
- Eastern Province
- Luapula Province
- Lusaka Province
- Muchinga Province
- Northern Province
- North-Western Province
- Southern Province
- Western Province
- See also
- References
- External links
Article 109 in part VIII of the constitution of Zambia deals with local government. It states only that there should be some form of local government, and that this local government should be based on democratically elected councils on the basis of universal adult suffrage. [1]