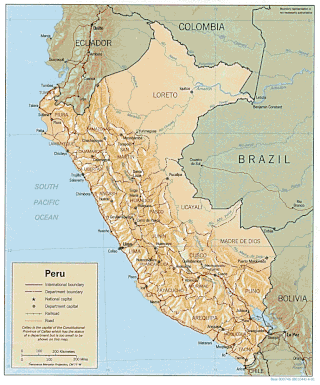
Peru is a country on the central western coast of South America facing the Pacific Ocean. It lies wholly in the Southern Hemisphere, its northernmost extreme reaching to 1.8 minutes of latitude or about 3.3 kilometres (2.1 mi) south of the equator. Peru shares land borders with Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Bolivia, and Chile, with its longest land border shared with Brazil.
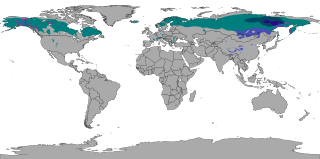
The subarctic climate is a continental climate with long, cold winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50°N to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Like other Class D climates, they are rare in the Southern Hemisphere, only found at some isolated highland elevations. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification Dfc, Dwc, Dsc, Dfd, Dwd and Dsd.

Somalia is a country located in the Horn of Africa which officially consists of the intra-46th meridian east territory, the seven federal member states, namely Galmudug, Hirshabelle, Jubaland, South West, Puntland, and the municipality of Benadir. It is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Somali Sea and Guardafui Channel to the east, and Kenya to the southwest. With a land area of 637,657 square kilometers, Somalia's terrain consists mainly of plateaus, plains and highlands. Its coastline is more than 3,333 kilometers in length, the longest of mainland Africa. It has been described as being roughly shaped "like a tilted number seven".

The United Kingdom straddles the higher mid-latitudes between 49° and 61°N on the western seaboard of Europe. Since the UK is always in or close to the path of the polar front jet stream, frequent changes in pressure and unsettled weather are typical. Many types of weather can be experienced in a single day.

The Sonoran Desert is a hot desert in North America and ecoregion that covers the northwestern Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur, as well as part of the southwestern United States. It is the hottest desert in both Mexico and the United States. It has an area of 260,000 square kilometers (100,000 sq mi).

Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64 °F) or higher in the coolest month, featuring hot temperatures and high humidity all year-round. Annual precipitation is often abundant in tropical climates, and shows a seasonal rhythm but may have seasonal dryness to varying degrees. There are normally only two seasons in tropical climates, a wet (rainy/monsoon) season and a dry season. The annual temperature range in tropical climates is normally very small. Sunlight is intense in these climates.

Choma is a town that serves as the capital of the Southern Province of Zambia. It is also the capital of Choma District, one of the 15 administrative districts in the province.
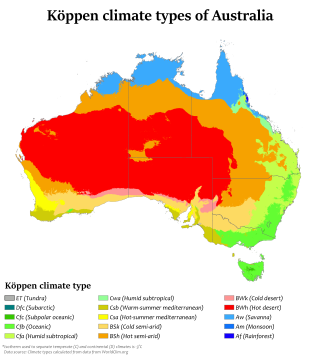
Australia's climate is governed mostly by its size and by the hot, sinking air of the subtropical high pressure belt. This moves north-west and north-east with the seasons. The climate is variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons, thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Australia has a wide variety of climates due to its large geographical size. The largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid. Only the south-east and south-west corners have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate, varying between grasslands and desert. Australia holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, and the highest sunshine duration.

The climate of Zambia in Central and Southern Africa is definitely tropical modified by altitude (elevation). In the Köppen climate classification, most of the country is classified as humid subtropical or tropical wet and dry, with small patches of semi-arid steppe climate in the south-west.
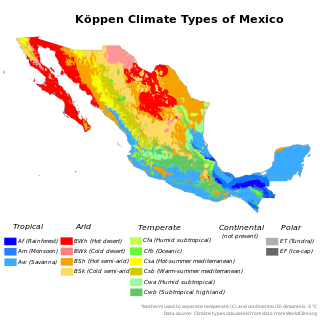
The climate of Mexico is very diverse. The Tropic of Cancer effectively divides the country into temperate and tropical zones. Land that is north of the twenty-fourth parallel experiences lower temperatures during the winter months. South of the twenty-fourth parallel, temperatures are fairly consistent all year round and vary solely as a function of elevation. The north of the country usually receives less precipitation than the south.
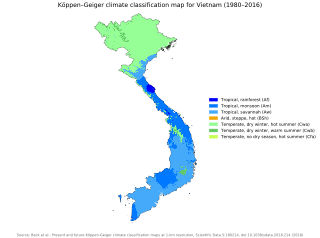
Vietnam has a monsoon-influenced climate typical of that of mainland Southeast Asia. The diverse topography, long latitude, and influences from the South China Sea lead to climatic conditions varying significantly between regions. The northern region experiences a monsoonal and temperate climate (Cfa) with four distinct seasons with winters typically dry and summers ranging from hot to mild. In southern and central areas, the climate is tropical monsoon (Aw) with only two seasons. In addition, a temperate climate exists in mountainous areas, which are found in Sa Pa and Da Lat, while a more continental climate exists in Lai Châu Province and Sơn La Province.
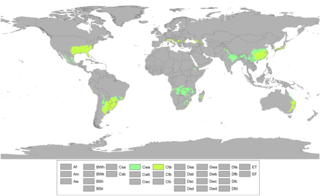
A humid subtropical climate is a temperate climate type characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents, generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates, and equatorward from either humid continental or oceanic climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications.

Mbala District is a district of Zambia, located in Northern Province. The capital lies at Mbala. As of the 2022 Zambian Census, the district had a population of 161,595 people.
Mpulungu District is a district of Zambia, located in Northern Province. The capital lies at Mpulungu. As of the 2022 Zambian Census, the district had a population of 153,564 people.

Mungwi District is a district of Zambia, located in Northern Province. The capital lies at Mungwi. As of the 2022 Zambian Census, the district had a population of 205,096 people.

Cyprus has a subtropical climate, Mediterranean and semi-arid type according to Köppen climate classification, with very mild winters on sea level and warm to hot summers. Snow is possible only in the Troodos mountains in the central part of the island. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry.
Nsama District is a district of Northern Province, Zambia. It was created in February 2012 by splitting Kaputa District. As of the 2022 Zambian Census, the district had a population of 77,651 people.

Senga District is a district of Northern Province, Zambia. It was separated from Mbala District in 2016. As of the 2022 Zambian Census, the district had a population of 126,308 people.
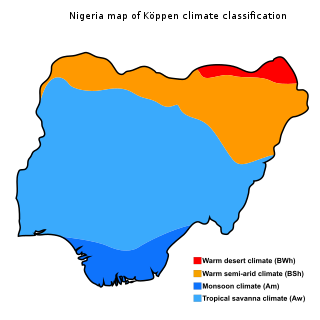
The climate of Nigeria is mostly tropical. Nigeria has three distinct climatic zones, two seasons, and an average temperature ranging between 21 °C and 35 °C. Two major elements determine the temperature in Nigeria: the altitude of the sun and the atmosphere's transparency. Its rainfall is mediated by three distinct conditions including convectional, frontal, and orographical determinants. Statistics from the World Bank Group showed Nigeria's annual temperature and rainfall variations, the nation's highest average annual mean temperature was 28.1 °C in 1938, while its wettest year was 1957 with an annual mean rainfall of 1,441.45mm.

The Climate of Ethiopia is highly diverse, ranging from equatorial rainforest with high rainfall and humidity in the south and southwest, to Afromontane regions on the summits of Semien and Bale Mountains to desert region in northeast, east and southeast Ethiopia. Ethiopia has three climatic zones, Alpine vegetated zones also known as Dega, the temperate zone, and the hot zone (Qola).




















