This article is about the Transport in Zambia.

Lake Mweru is a freshwater lake on the longest arm of Africa's second-longest river, the Congo. Located on the border between Zambia and Democratic Republic of the Congo, it makes up 110 kilometres (68 mi) of the total length of the Congo, lying between its Luapula River (upstream) and Luvua River (downstream) segments.

Bangweulu — 'where the water sky meets the sky' — is one of the world's great wetland systems, comprising Lake Bangweulu, the Bangweulu Swamps and the Bangweulu Flats or floodplain. Situated in the upper Congo River basin in Zambia, the Bangweulu system covers an almost completely flat area roughly the size of Connecticut or East Anglia, at an elevation of 1,140 m straddling Zambia's Luapula Province and Northern Province. It is crucial to the economy and biodiversity of northern Zambia, and to the birdlife of a much larger region, and faces environmental stress and conservation issues.

The Luapula River is a north-flowing river of central Africa, within the Congo River watershed. It rises in the wetlands of Lake Bangweulu (Zambia), which are fed by the Chambeshi River. The Luapula flows west then north, marking the border between Zambia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo before emptying into Lake Mweru. The river gives its name to Zambia's Luapula Province.
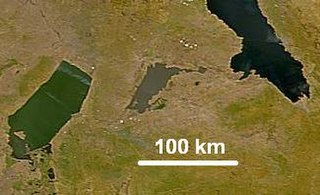
Lake Mweru Wantipa or Mweru-wa-Ntipa meaning "muddy lake" is a lake and swamp system in the Northern Province of Zambia. It has been regarded in the past as something of mystery, displaying fluctuations in water level and salinity which were not entirely explained by variation in rainfall levels; it has been known to dry out almost completely. This is compounded by its remoteness and it not receiving the same attention from geographers and geologists as its larger and more accessible neighbours, Lake Tanganyika, 25 km east, and Lake Mweru, 40 km west, with which its name is sometimes confused.

The 1,576 kilometres (979 mi) long Kafue River is the longest river lying wholly within Zambia. Its water is used for irrigation and for generating hydroelectric power. It is the largest tributary of the Zambezi, and of Zambia's principal rivers, it is the most central and the most urban. More than 50% of Zambia's population live in the Kafue River Basin and of these around 65% are urban.

Northern Province is one of Zambia's ten provinces. It covers approximately one-sixth of Zambia in land area. The provincial capital is Kasama. The province is made up of 12 districts, namely Kasama District, Chilubi District, Kaputa District, Luwingu District, Mbala District, Mporokoso District, Mpulungu District, Mungwi District, Nsama District, Lupososhi District, Lunte District and Senga Hill District. Currently, only Kasama and Mbala have attained municipal council status, while the rest are still district councils. It is widely considered to be the heartland of the Bemba, one of the largest tribes in Zambia.

Mansa is the capital of the Luapula Province of Zambia, and headquarters of Mansa District. It takes its name from the local Chief Mansa and the small Mansa River which flows west to the Luapula River. During British rule the city was named Fort Rosebery.
Samfya is a town located in the Zambian province of Luapula. It is the centre of Samfya District. The town is located on the south-western shore of Lake Bangweulu, on the longest stretch of well-defined shore of that lake. Samfya has a few guesthouses and a number of white sandy beaches which are used for recreation, although the lake does have crocodiles.
The Livingstone Memorial, built in 1899, marks the spot where missionary explorer David Livingstone died on 1 May 1873, in Chief Chitambo's village at Chipundu, near the edge of the Bangweulu Swamps in Zambia. His body was embalmed and his heart was buried there under a mpundu tree by his followers, now led by his loyal attendants Chuma and Susi, who then departed for the coast carrying his body. In their party was an Indian-educated African man named Jacob Wainwright who carved the inscription "LIVINGSTONE MAY 4 1873" and the names of the attendants on the tree.

The Congo Pedicle is the southeast salient of the Haut-Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, which divides neighbouring Zambia into two lobes. In area, the pedicle is similar in size to Wales or New Jersey. 'Pedicle' is used in the sense of 'a little foot'. 'Congo Pedicle' or 'the Pedicle' is also used to refer to the Congo Pedicle road, which crosses it.
Water transport and the many navigable inland waterways in Zambia have a long tradition of practical use except in parts of the south. Since draught animals such as oxen were not heavily used, water transport was usually the only alternative to going on foot until the 19th century. The history and current importance of Zambian waterways, as well as the types of indigenous boats used, provide information on this important aspect of Zambian economy.

Lukanga Swamp is a major wetland in the Central Province of Zambia, about 50 km west of Kabwe. Its permanently swampy area consists of a roughly circular area with a diameter of 40 to 50 km covering 1850 km2, plus roughly 250 km2 in the mouths of and along rivers discharging into it such as the Lukanga River from the north-east, plus another 500 km2 either side of the Kafue River to the west and north-west, making 2600 km2 in total. It contains many lagoons such as Lake Chiposhye and Lake Suye but few large channels, and its average depth is only 1.5 m.

Chilubi is a settlement on an island in Lake Bangweulu and its swamps, and is headquarters of Chilubi District in the Northern Province of Zambia.

The wildlife of Zambia refers to the natural flora and fauna of Zambia. This article provides an overview, and outline of the main wildlife areas or regions, and compact lists of animals focusing on prevalence and distribution in the country rather than on taxonomy. More specialized articles on particular groups are linked from here.

The Zambezian flooded grasslands is an ecoregion of southern and eastern Africa that is rich in wildlife.
The biomes and ecoregions in the ecology of Zambia are described, listed and mapped here, following the World Wildlife Fund's classification scheme for terrestrial ecoregions, and the WWF freshwater ecoregion classification for rivers, lakes and wetlands. Zambia is in the Zambezian region of the Afrotropical biogeographic realm. Three terrestrial biomes are well represented in the country . The distribution of the biomes and ecoregions is governed mainly by the physical environment, especially climate.

Samfya District is located in Luapula Province, Zambia. The headquarters is at Samfya.

Lunga District is one of the newly created districts in the Luapula Province of Zambia. It was declared a district in 2012 by Michael Sata. The district comprises archipelago of islands in the Bangweulu Wetlands in the South East of Lake Bangweulu.

Chilubi is a constituency of the National Assembly of Zambia. It covers a rural area (Chilubi) on the eastern shore of Lake Bangweulu in Chilubi District of Northern Province.
















