Overview
The 25 provinces of DR Congo are divided into 145 territories (fr. territoires, sing. territoire) and 33 cities (fr. villes, sing. ville). [1] Each provincial division is also a constituency of the National Assembly as well as of the Provincial Assembly of its province.
Each territory is led by a territory administrator (fr. administrateur de territoire) assisted by two assistant territory administrators (fr. administrateurs de territoire assistants). They are appointed by the central government and put under the direction of the provincial governor. [3]
The divisions of a territory are: sectors (fr. secteurs, sing. secteur), chiefdoms (fr. chefferies, sing. chefferie) and communes. [1] A territory has at least one commune that is the administrative center and also one or more collectivities (a sector or chiefdom).
Unlike its counterpart, the city, or its divisions, the territory is not a juridical person. However, the actions of its authorities are under administrative control and subject to judicial appeal. [4]
In 2018 73% of the electorate were in territories. [5]

The Third Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a unitary state with a five-level hierarchy of types of administrative division. There are nine different types of country subdivision in a new hierarchy with no new types but with two from the previous one abolished.

In French Polynesia, there are two levels of administrative divisions: five administrative subdivisions and 48 communes. Many of the communes are further subdivided into communes associées. The breakdown into administrative subdivisions was as a result of the law #71-1028, dated December 24, 1971. The compositions of the administrative subdivisions and the communes were defined in the decrees #72-408 and #72-407 of May 17, 1972, respectively. These subdivisions were confirmed in the decree #2005-1611 of December 20, 2005. Below are several lists of the divisions, according to different sorting schemes.

The communes of the Democratic Republic of the Congo are administrative divisions of both cities and territories. They are led by government appointed burgomasters and are further divided into quarters and embedded groupings.

Lemba is one of the 24 communes that are the administrative divisions of Kinshasa, the capital city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Limete is one of the 24 communes that are the administrative divisions of Kinshasa, the capital city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Matete is one of the 24 communes that are the administrative divisions of Kinshasa, the capital city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Kanyabayonga is a town straddling the Lubero and Rutshuru territories of North Kivu province in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Administratively, the part which is in Lubero is the commune of Kanyabayonga and, the part in Rutshuru belongs to the Kanyabayonga groupement (grouping) which extends well south of the town and is within the Bwito chiefdom. The region as a whole has seen much armed conflict since 1993.

In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, chiefdoms and sectors are rural administrative divisions of territories. They are further subdivided into groupings which themselves are divided into villages. Chiefdoms and groupings are led by traditional leaders officially recognized by the government, whereas sector chiefs are appointed directly by the government.
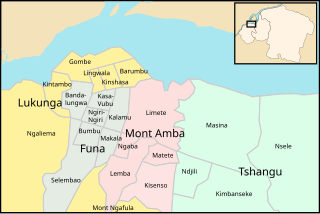
Mont Amba is an area of the capital city of Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo, comprising five of the city-province's twenty-four administrative divisions—the communes of Kisenso, Lemba, Limete, Matete and Ngaba. It is one of the four so-called districts of Kinshasa. These were the administrative divisions of Kinshasa during much of the Mobutu years (1965-1997) and around which a number of government systems and services are still organized. For instance, Mont Amba makes up an eleven-member National Assembly constituency designated as Kinshasa III. However, these districts are not part of Congo's territorial organization.

Tshangu is an area of the capital city of Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo, comprising five of the city-province's twenty-four administrative divisions—the communes of Kimbanseke, Maluku, Masina, Ndjili and Nsele. It is one of the four so-called districts of Kinshasa. These were the administrative divisions of Kinshasa during much of the Mobutu years (1965-1997) and around which a number of government systems and services are still organized. For instance, Tshangu makes up an eighteen-member National Assembly constituency designated as Kinshasa IV. However, these districts are not part of Congo's territorial organization.

Lukunga is an area of the capital city of Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo, comprising seven of the city-province's twenty-four administrative divisions—the communes of Barumbu, Gombe, Kinshasa, Kintambo, Lingwala, Mont Ngafula and Ngaliema. It is one of the four so-called districts of Kinshasa. These were the administrative divisions of Kinshasa during much of the Mobutu years (1965-1997) and around which a number of government systems and services are still organized. For instance, Lukunga makes up a fourteen-member National Assembly constituency designated as Kinshasa I. However, these districts are not part of Congo's territorial organization.

Funa is an area of the capital city of Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo, comprising seven of the city-province's twenty-four administrative divisions—the communes of Bandalungwa, Bumbu, Kalamu, Kasa-Vubu, Makala, Ngiri-Ngiri and Selembao. It is one of the four so-called districts of Kinshasa. These were the administrative divisions of Kinshasa during much of the Mobutu years (1965-1997) and around which a number of government systems and services are still organized. For instance, Funa makes up a twelve-member National Assembly constituency designated as Kinshasa II. However, these districts are not part of Congo's territorial organization.
Luiza is a territory of Kasai-Central province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It covers an area of 14,702 square kilometers. As of March 2021, its inhabitants numbered 1,515,339. It is represented in the National Assembly by four elected deputies.
Gbadolite is a commune of the city of Gbadolite, the capital of Nord-Ubangi province, Democratic Republic of Congo. It is located in the rainforest, about a dozen kilometers south of the banks of the Ubangi River. Gbado, as it is sometimes called, covers 11.2 km 2. This is one of three communes of the city of Gbadolite.
Nzinda or Nzida is a commune and a town in the city of Kikwit in the Democratic Republic of Congo.

General elections were held in the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 20 December 2023. Combined elections were held for the President, 484 of the 500 members of the National Assembly, 700 of the 716 elected members of the 26 provincial assemblies, and for the first time under the new constitution, 951 members of a scaled down number of commune (municipal) councils. On election day, the Congolese government extended voting to 21 December for polling stations that had not opened on 20 December. Agence France-Presse reported that some polling stations would open as late as 24 December.
The cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo are administrative divisions of provinces with the exception of Kinshasa which itself has the status of a province. Cities are further divided into communes. They are led by mayors except for Kinshasa which is led by a governor.
The Luindi Chiefdom, also known as the Lwindi Chiefdom, is a chiefdom located in the Mwenga Territory, within the South Kivu Province in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It is situated in the mountainous area of the Itombwe Massif.
The Basile Chiefdom is a chiefdom located in the Mwenga Territory of South Kivu Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It shares borders with the Luindi Chiefdom to the east, the Wamuzimu Chiefdom to the west, and is bounded by the Shabunda Territory and Walungu Territory to the north, as well as the Itombwe Sector to the south.

The Ngweshe Chiefdom is a chiefdom located in Walungu Territory, within the South Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It shares borders with Kabare Territory to the north, Rwanda and Burundi to the northeast, Mwenga Territory and Shabunda Territory to the south, and Kaziba Chiefdom to the east. According to the territory's 2018 annual report, the chiefdom has an estimated population of 672,436.










