
The economy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo has declined drastically around the 1980s, despite being home to vast potential in natural resources and mineral wealth; their gross domestic product is $69.474 billion as of 2023.

Ground transport in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has always been difficult. The terrain and climate of the Congo Basin present serious barriers to road and rail construction, and the distances are enormous across this vast country. Furthermore, chronic economic mismanagement and internal conflict has led to serious under-investment over many years.

Kinshasa is the capital and largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Once a site of fishing and trading villages along the Congo River, Kinshasa is now one of the world's fastest-growing megacities. With an estimated population of 16 million residents, it's the most densely populated city in the DRC and the most populous city in Africa. It is Africa's third-largest metropolitan area and the leading economic, political, and cultural center of the DRC. It houses several industries, including low-tech manufacturing, such as such as plastic and foamwares, toilet paper, and bottled water, banking, and entertainment. The city also hosts some of DRC's significant institutional buildings, such as the Palais du Peuple, Palais de la Nation, Court of Cassation, Constitutional Court, Cité de l'Union Africaine, Palais de Marbre, Stade des Martyrs, Immeuble du Gouvernement, and multiple federal departments and agencies.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as Congo-Kinshasa, is a country in Central Africa. By land area, the DRC is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 112 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous officially Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Angola, the Cabinda exclave of Angola and the South Atlantic Ocean.

Coltan is a dull black metallic ore from which the elements niobium and tantalum are extracted. The niobium-dominant mineral in coltan is columbite, and the tantalum-dominant mineral is tantalite.

Mbuji-Mayi or Mbujimayi is a city and the capital of Kasai-Oriental Province in the south-central Democratic Republic of Congo. It is the second largest city in the country, following the capital Kinshasa but ahead of Lubumbashi, Kisangani and Kananga, though the exact population is not known. Estimates ranged from a 2010 CIA World Factbook estimated population of 1,480,000 to as many as 3,500,000 estimated by the United Nations in 2008.

Air Zaïre was the national airline of Zaire. Its head office was located on the grounds of N'djili Airport in Kinshasa.

The mining industry of the Democratic Republic of the Congo produces copper, diamonds, tantalum, tin, gold, and more than 63% of global cobalt production. Minerals and petroleum are central to the DRC's economy, making up more than 95% of the value of its exports.
Societé minière de Bakwanga is a diamond mining company based in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Historically, the company was the largest diamond producer in the world by volume. However, following decades of decline, the company currently produces only a small minority of the DRC's diamonds.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Democratic Republic of the Congo:

On 15 April 2008, Hewa Bora Airways Flight 122, a McDonnell Douglas DC-9-51 plane crashed into a residential and market area of Goma of the Democratic Republic of the Congo immediately south of Goma International Airport.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo was a net energy exporter in 2008. Most energy was consumed domestically in 2008. According to the IEA statistics the energy export was in 2008 small and less than from the Republic of Congo. 2010 population figures were 3.8 million for the RC compared to CDR 67.8 Million.

Its location in the center of Africa has made the Democratic Republic of the Congo a key player in the region since independence. Because of its size, mineral wealth, and strategic location, Zaire was able to capitalize on Cold War tensions to garner support from the West. In the early 1990s, however, with the end of the Cold War and in the face of growing evidence of human rights abuses, Western support waned as pressure for internal reform increased.

Congo Express was a regional airline created through a joint venture with South African Airlines and BizAfrika Congo, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The airline's long-term strategy is to transform air transport in the region, stimulate markets and economic growth in mining and other growth sectors, develop hubs, and provide important links between lucrative destinations.

Canada–Democratic Republic of the Congo relations are the bilateral relations between Canada and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Canada has an embassy in Kinshasa and D.R. Congo has an embassy in Ottawa.
In the Democratic Republic of the Congo there is a significant community of Chinese migrants located in the capital of Kinshasa and the mineral rich southern Haut-Katanga Province. According to official figures from the Chinese embassy, there are 5,000 Chinese living in the DR Congo, though the actual number is believed to be far higher. More recent estimates vary from 5,000 to 50,000. The Mining industry of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a main reason for Chinese people moving to the DRC.
Congo Airways S.A. is the state-owned flag carrier airline of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). With a paid-up capital of US$90 million, it started operations on 20 October 2015.
Noël Kabamba Tshiani Muadiamvita is a Congolese economist and politician. He was a presidential candidate in the 2018 Congolese general election. In 2021 and 2023, Tshiani proposed a law to restrict various government positions to only individuals who were born to Congolese parents.

Democratic Republic of the Congo–India relations are the international relations that exist between the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and India.
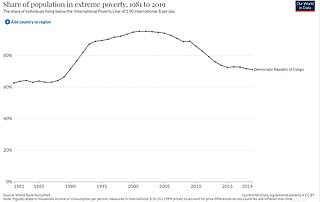
Poverty is widespread and unchecked across the 26 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Despite being the second-largest country in Africa, with an approximate area of 2.3 million square kilometres (890,000 sq mi), and being endowed with rich natural resources, the DRC is the second-poorest country in the world after Haiti. The average annual income is only $449 US dollars. In 2019, the United Nations (UN) Human Development Index (HDI) ranked the DRC as the 175th least-developed country out of 189 countries with an HDI of 0.480. More than 80% of Congolese people live on less than $1.25 a day, defined as the threshold for extreme poverty.




















