
The economy of Burkina Faso is based primarily on subsistence farming and livestock raising. Burkina Faso has an average income purchasing-power-parity per capita of $1,900 and nominal per capita of $790 in 2014. More than 80% of the population relies on subsistence agriculture, with only a small fraction directly involved in industry and services. Highly variable rainfall, poor soils, lack of adequate communications and other infrastructure, a low literacy rate, and a stagnant economy are all longstanding problems of this landlocked country. The export economy also remained subject to fluctuations in world prices.

The economy of Cameroon was one of the most prosperous in Africa for a quarter of a century after independence. The drop in commodity prices for its principal exports – petroleum, cocoa, coffee, and cotton – in the mid-1980s, combined with an overvalued currency and economic mismanagement, led to a decade-long recession. Real per capita GDP fell by more than 60% from 1986 to 1994. The current account and fiscal deficits widened, and foreign debt grew. Yet because of its oil reserves and favorable agricultural conditions, Cameroon still has one of the best-endowed primary commodity economies in sub-Saharan Africa.

The CFA franc is the name of two currencies, the West African CFA franc, used in eight West African countries, and the Central African CFA franc, used in six Central African countries. Although separate, the two CFA franc currencies have always been at parity and are effectively interchangeable. The ISO currency codes are XAF for the Central African CFA franc and XOF for the West African CFA franc. On 22 December 2019, it was announced that the West African currency would be replaced by an independent currency to be called Eco.

The economy of Equatorial Guinea has traditionally been dependent on commodities such as cocoa and coffee, but is now heavily dependent on petroleum due to the discovery and exploitation of significant oil reserves in the 1980s. In 2017, it graduated from "Least Developed Country" status, the only Sub-Saharan African nation that managed to do so besides Botswana.

Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers 36,125 square kilometres (13,948 sq mi) with an estimated population of 1,726,000. It borders Senegal to the north and Guinea to the south-east.

The economy of Guinea-Bissau comprises a mixture of state-owned and private companies. Guinea-Bissau is among the world's least developed nations and one of the 10 poorest countries in the world, and depends mainly on agriculture and fishing. Cashew crops have increased remarkably in recent years, and the country ranked ninth in cashew production for the year of 2019.

The economy of Niger is based largely on internal markets, subsistence agriculture, and the export of raw commodities: foodstuffs to neighbors and raw minerals to world markets. Niger, a landlocked West African nation that straddles the Sahel, has consistently been ranked on the bottom of the Human development index, with a relatively low GDP and per capita income, and ranks among the least developed and most heavily indebted countries in the world, despite having large raw commodities and a relatively stable government and society not currently affected by civil war or terrorism. Economic activity centers on subsistence agriculture, animal husbandry, re-export trade, and export of uranium.

The economy of Senegal is driven by mining, construction, tourism, fishing and agriculture, which are the main sources of employment in rural areas, despite abundant natural resources in iron, zircon, gas, gold, phosphates, and numerous oil discoveries recently. Camille Senegal's economy gains most of its foreign exchange from fish, phosphates, groundnuts, tourism, and services. As one of the dominant parts of the economy, the agricultural sector of Senegal is highly vulnerable to environmental conditions, such as variations in rainfall and climate change, and changes in world commodity prices.

The economy of Togo has struggled greatly. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) ranks it as the tenth poorest country in the world, with development undercut by political instability, lowered commodity prices, and external debts. While industry and services play a role, the economy is dependent on subsistence agriculture, with industrialization and regional banking suffering major setbacks.

The Economic Community of West African States is a regional political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa. Collectively, these countries comprise an area of 5,114,162 km2 (1,974,589 sq mi), and in 2015 had an estimated population of over 349 million.

The Republic of Guinea-Bissau follows a nonaligned foreign policy and seeks friendly and cooperative relations with a wide variety of states and organizations. France, Portugal, Angola, Brazil, Egypt, Nigeria, Libya, Cuba, the Palestine Liberation Organization,Ghana, and Russia have diplomatic offices in Bissau.
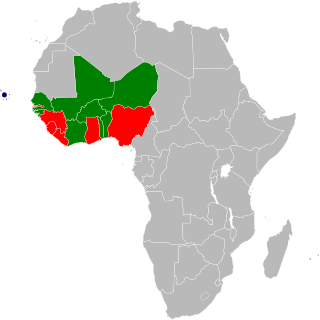
The eco is the name for the proposed common currency of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS). Plans originally called for the West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ) states to introduce the currency first, which would eventually be merged with the CFA franc which is used by the French-speaking west African region within the West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA). This will also enable the UEMOA states to gain complete fiscal and monetary independence from France. The UEMOA states have alternatively proposed to reform the CFA franc into the eco first, which could then be extended to all ECOWAS states.

Bolama is an administrative region in Guinea-Bissau, consisting primarily of the Bijagós Archipelago of the country's southern coast, together with a small coastal strip centred on the coastal town of São João. It has an area of 2,624 km2. Its capital is Bolama, on the island of the same name. It is a coastal region covered with Mangrove swamps, rain forest and tangled forest and receives an annual rainfall of more than 1,000 mm (39 in).

The Central African CFA franc is the currency of six independent states in Central Africa: Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea and Gabon. These six countries have a combined population of 55.2 million people, and a combined GDP of US$113.322 billion.

The West African CFA franc is the currency of eight independent states in West Africa: Benin, Burkina Faso, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Mali, Niger, Senegal and Togo. These eight countries had a combined population of 105.7 million people in 2014, and a combined GDP of US$128.6 billion.

In international relations, Françafrique is France's sphere of influence over former French and Belgian colonies in sub-Saharan Africa. The term was derived from the expression France-Afrique, which was used by the first president of Ivory Coast, Félix Houphouët-Boigny, in 1955 to describe his country's close ties with France. It was later renamed Françafrique by François-Xavier Verschave in 1998 to criticise the alleged corrupt and clandestine activities of various Franco-African political, economic and military networks.

The Central Bank of West African States is a central bank serving the eight west African countries which share the common West African CFA franc currency and comprise the West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA):

The African Monetary Union (AMU) is the proposed creation of an economic and monetary union for the countries of the African Union, administered by the African Central Bank. Such a union would call for the creation of a new unified currency, similar to the euro; the hypothetical currency is sometimes referred to as the afro or afriq.

The United Nations Integrated Peacebuilding Office in Guinea-Bissau (UNIOGBIS) is a United Nations peacebuilding mission in Guinea-Bissau.

With the world’s largest production of cacao and cashew nuts, Ivory Coast is one of the leading economic powers in West Africa. It joined the IMF in 1963. Since then, Ivory Coast participated in 14 arrangements and purchased more than 1016 millions in procurement and loans. It now possesses 650.4 million SDR of quotas.





















