
Guinea is a country on the coast of West Africa and is bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.

Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is a country in West Africa, on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. Senegal is bordered by Mauritania to the north, Mali to the east, Guinea to the southeast and Guinea-Bissau to the southwest. Senegal nearly surrounds The Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal's southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country. Senegal also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde. Senegal's economic and political capital is Dakar.

Senegal is a coastal West African nation located 14 degrees north of the equator and 14 degrees west of the Prime Meridian. The country's total area is 196,190 km2 of which 192,000 km2 is land and 4,190 km2 is water.

Senegal's first President, Léopold Senghor, advocated close relations with France and negotiation and compromise as the best means of resolving international differences after Senegal's independence from its status as a French colony. To a large extent, the two succeeding presidents, Abdou Diouf and Abdoulaye Wade, have carried on Senghor's policies and philosophies. Senegal has long supported functional integration among French-speaking West African states through the West African Economic and Monetary Union.

The Gambia, officially the Republic of The Gambia, and sometimes shortened to just Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland Africa and is surrounded by Senegal, except for its western coast on the Atlantic Ocean. The Gambia is situated on both sides of the lower reaches of the Gambia River, the nation's namesake, which flows through the centre of The Gambia and empties into the Atlantic Ocean, and elucidates the long shape of the country. It has an area of 11,300 square kilometres (4,400 sq mi) with a population of 1,857,181 as of the April 2013 census. Banjul is the Gambian capital and the country's largest metropolitan area, while the largest cities are Serekunda and Brikama.

Casamance is the area of Senegal south of the Gambia, including the Casamance River. It consists of the Lower Casamance and the Upper Casamance. The largest city of Casamance is Ziguinchor.
The Senegambia is, in the narrow sense, a historical name for a geographical region in West Africa, which lies between the Senegal River in the north and the Gambia River in the south. However, there are also text sources which state that Senegambia is understood in a broader sense and equated with the term the Western region. This refers to the coastal areas between Senegal and Sierra Leone, where the inland border in the east was not further defined.

The Gambia River is a major river in West Africa, running 1,120 kilometres (700 mi) from the Fouta Djallon plateau in north Guinea westward through Senegal and The Gambia to the Atlantic Ocean at the city of Banjul. It is navigable for about half that length.

The Casamance conflict is an ongoing low-level conflict that has been waged between the Government of Senegal and the Movement of Democratic Forces of Casamance (MFDC) since 1982. On May 1, 2014, the leader of the MFDC sued for peace and declared a unilateral ceasefire.

The Niokolo-Koba National Park is a World Heritage Site and natural protected area in south eastern Senegal near the Guinea border. It is served by Niokolo-Koba Airport, an unpaved airstrip.

Agriculture is one of the dominant parts of Senegal's economy, even though Senegal lies within the drought-prone Sahel region. As only about 5% of the land is irrigated, Senegal continues to rely on rain-fed agriculture. Agriculture occupies about 75% of the workforce. Despite a relatively wide variety of agricultural production, the majority of farmers produce for subsistence needs. Millet, rice, corn, and sorghum are the primary food crops grown in Senegal. Production is subject to drought and threats of pests such as locusts, birds, fruit flies, and white flies. Moreover, the effects of climate change in Senegal are expected to severely harm the agricultural economy due to extreme weather such as drought, as well as increased temperatures.

The wildlife of Senegal consists of the flora and fauna of this nation in West Africa. Senegal has a long Atlantic coastline and a range of habitat types, with a corresponding diversity of plants and animals. Senegal has 188 species of mammals and 674 species of bird.

Tourism in Senegal is a vital part of the West African nation's economy.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Senegal:
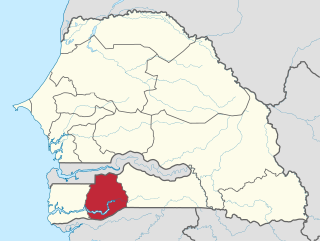
Sédhiou Region is a region of Senegal located in the southwest of the country in the natural region called Casamance.

The Guinean mangroves are a coastal ecoregion of mangrove swamps in rivers and estuaries near the ocean of West Africa from Senegal to Sierra Leone.

Ziguinchor is the capital of the Ziguinchor Region, and the chief town of the Casamance area of Senegal, lying at the mouth of the Casamance River. It has a population of over 230,000. It is the seventh largest city of Senegal, but largely separated from the north of the country by The Gambia.

The Senegambia bridge, also known as the Trans-Gambia Bridge, is a bridge in The Gambia that carries the Trans-Gambia Highway connecting northern and southern Gambia. It also provides access to the isolated Casamance province from the rest of Senegal. A bridge had been proposed for this location in 1956 but political considerations delayed construction which finally began in 2015. Construction was funded largely by a loan of US$ 65 million from the African Development Bank, with remaining funding coming from the Gambian government. Construction works were carried out by a joint venture of Spanish company Isolux Corsán and the Senegalese Arezki Group.

















