Guinea is a country on the coast of West Africa and is bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.

Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, informally Salone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It has a tropical climate, with a diverse environment ranging from savanna to rainforests. The country has a total area of 71,740 km2 (27,699 sq mi) and a population of 7,075,641 as of the 2015 census. Sierra Leone is a constitutional republic with a directly elected president and a unicameral legislature. The country's capital and largest city is Freetown. Sierra Leone is made up of five administrative regions: the Northern Province, North West Province, Eastern Province, Southern Province and the Western Area. These regions are subdivided into sixteen districts.

A refugee camp is a temporary settlement built to receive refugees and people in refugee-like situations. Refugee camps usually accommodate displaced persons who have fled their home country, but there are also camps for internally displaced persons. Usually refugees seek asylum after they've escaped war in their home countries, but some camps also house environmental- and economic migrants. Camps with over a hundred thousand people are common, but as of 2012, the average-sized camp housed around 11,400. They are usually built and run by a government, the United Nations, international organizations, or NGOs. There are also unofficial refugee camps, like Idomeni in Greece or the Calais jungle in France, where refugees are largely left without support of governments or international organizations.

Koidu Town is the capital and largest city of the diamond-rich Kono District in the Eastern Province of Sierra Leone. The population of Koidu Town is 124,662 based on the 2015 Sierra Leone Census. Koidu Town is the fifth largest city in Sierra Leone by population, after Freetown, Kenema, Bo and Makeni. Koidu Town is a major urban, business, commercial and diamond trade center. Koidu Town lies approximately 270 miles east of Freetown, and about 54 miles north of Kenema.

Kissidougou (Kiss-eh-dow-goo) is a city in southern Guinea. It is the capital of in the Kissidougou Prefecture. Following intensified conflicts in Sierra Leone and Liberia during the fall and winter of 2000, many people from the city of Guéckédou fled to Kissidougou and stayed. As of 2014 it had a population of 102,675 people.

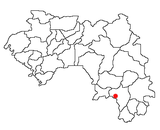
Nzérékoré, (en-zeer-eh-core) also spelled N'Zérékoré, is the second largest city in Guinea by population, after the capital Conakry and the largest city in the Guinée forestière region of south-eastern Guinea. The city is the capital of the Nzérékoré Prefecture. Nzérékoré is a commercial and economic center and lies approximately 354 miles/569 km southeast of Conakry.

Guinée forestière is a forested mountainous region in southeastern Guinea, extending into northeastern Sierra Leone. It is one of four natural regions into which Guinea is divided and covers 23% of the country. It includes all of the Nzérékoré administrative region.

The Nzérékoré Region is a region in the southern part of Guinea. Its capital and largest city is Nzérékoré. It is one of the eight regions of Guinea. It is bordered by the countries of Sierra Leone, Liberia, and Ivory Coast, and the Guinean regions of Kankan and Faranah.

The Sierra Leone Civil War (1991–2002) began on 23 March 1991 when the Revolutionary United Front (RUF), with support from the special forces of Charles Taylor’s National Patriotic Front of Liberia (NPFL), intervened in Sierra Leone in an attempt to overthrow the Joseph Momoh government. The resulting civil war lasted 11 years, enveloped the country, and left over 50,000 dead.

Buduburam is a refugee camp located 44 kilometers (27 mi) west of Accra, Ghana. Opened by the UNHCR in 1990, the camp is home to more than 12,000 refugees from Liberia who fled their country during the First Liberian Civil War (1989–1996) and the Second Liberian Civil War (1999–2003), in addition to refugees from Sierra Leone who also escaped from the ravages of their civil war (1991–2001). The camp is served by Liberian and international NGO groups and volunteer organizations. The Carolyn A. Miller Elementary School provides free education to nearly 500 children in the camp.
Jalozai is a village located in Nowshera District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Jalozai is famous for Afghan refugee camp which is located about 35 kilometres southeast of Peshawar, Pakistan.
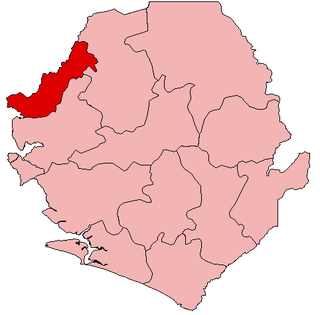
Kambia District is a district in the Northern Province of Sierra Leone. Its capital and largest city is the town of Kambia. As of the 2015 census, The District had a population of 343,686. Kambia District borders the Republic of Guinea to the north, Port Loko District to the south and Bombali District to the east. The district provides an important Trade route to or from the Sierra Leonean capital Freetown to the Guinean capital Conakry.

Sérédou is a town and sub-prefecture in the Macenta Prefecture in the Nzérékoré Region of south-eastern Guinea.

Liberia – Sierra Leone relations refers to the historical and current relationship between Liberia and Sierra Leone. The two countries signed a non-aggression pact in 2007 when Sierra Leonean President Ernest Bai Koroma took office. In January 2011, an African diplomat described relations as "cordial".
The Ghana Refugee Board was established under the Ghana Refugee Law 1992, and is charged with the management of activities relating to refugees in Ghana. It is under the control of the Ministry of the Interior.
In 1994, the Rwandan Genocide unfolded before the world's eyes and with it, several hundred thousand people were murdered in the heart of Africa. At this time, Dr. Dawit Zawde, a medical doctor in Ethiopia, noticed the lack of an African response and organized a medical team to respond out of Kigali. Formally launched in Addis Ababa, within months of its opening, Africa Humanitarian Action (AHA) sent two teams of young health and relief professionals during the Rwandan crisis. These professionals hailed from seven African countries—Benin, Cameroon, Ethiopia, Guinea, Malawi, Rwanda, and Senegal, becoming the first African-only NGO operating in Rwanda. The AHA teams targeted returnee populations and the internally displaced as they were deployed at two health centers, one in the northwest region at Tare in the Kigali Prefecture and a second at Kabarondo in Kibungo Prefecture in the southeast. They provided unprecedented 24-hour emergency health services and regular out and in-patient care. As the operation in Rwanda grew, AHA decided to extend their presence to other countries in Africa. By the end of 1995, AHA had moved to Uganda, Angola and began operations in Ethiopia. By the end of 1999, the framework that was implemented in Eastern and Central Africa by AHA had now been transferred to offices in Western Africa.
Kissi Tongi Chiefdom is a chiefdom in Kailahun District of Sierra Leone with a population of 30,455. Its largest town is Koindu, but its headquarters is in Kangama. The major industry in Kissi Tongi Chiefdom is farming. The population of Kissi Tongi Chiefdom is largely from the Kissi ethnic group.
The Southwestern Mande languages are a branch of the Mande languages spoken in Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Liberia. There are around 2.8 million speakers, chiefly in Sierra Leone, due to Mende, the language with the most overall speakers. The Southwestern Mande languages are distantly related to the historic Manding languages, but are mutually unintelligble.