Related Research Articles
Since 1878, there have been two Broadway theatres that have carried the name the Bijou Theatre during their histories.

The Boston Music Hall was a concert hall located on Winter Street in Boston, Massachusetts, with an additional entrance on Hamilton Place.
The Boston Theatre was a theatre in Boston, Massachusetts. It was first built in 1854 and operated as a theatre until 1925. Productions included performances by Thurlow Bergen, Charles A. Bigelow, Edwin Booth, Anna Held, James O'Neill Jennie Kimball, and others.

The Hollis Street Church in Boston, Massachusetts, was a Congregational and Unitarian church. It merged with the South Congregational Society of Boston in 1887.

The Melodeon was a concert hall and performance space in 19th-century Boston, Massachusetts, located on Washington Street, near West Street. Musical concerts, lectures, sermons, conferences, visual displays, and popular entertainments occurred there.

Frost & Adams (est.1869) was an artists' supply firm in Boston, Massachusetts, located in Cornhill, on the current site of Boston City Hall and City Hall Plaza. It began in 1869 when artist Francis Seth Frost and retailer E.H. Adams bought the business of Matthew J. Whipple. By the 1880s Frost & Adams were "the chief dealers in artists' materials in New England."
Beethoven Hall (1874-1878) was an auditorium in Boston, Massachusetts, that hosted musical performances and other entertainments in the 1870s. It sat on Washington Street, near Boylston Street, in today's Boston Theater District/Chinatown neighborhood. The architect was William Washburn, who had also designed the first National Theatre and the second Tremont Temple.

The Park Theatre (est.1879) was a playhouse in Boston, Massachusetts, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It later became the State cinema. Located on Washington Street, near Boylston Street, the building existed until 1990.

The Globe Theatre (est.1871) was a playhouse in Boston, Massachusetts, in the 19th century. It was located at 598 Washington Street, near the corner of Essex Street. Arthur Cheney oversaw the Globe until 1876. From 1871-1873 it occupied the former theatre of John H. Selwyn. After a fire in May 1873, the Globe re-opened on the same site in December 1874. Architect Benjamin F. Dwight designed the new building. From 1877-1893 John Stetson served as proprietor; some regarded him as "a theatrical producer with a reputation for illiteracy in his day such as Samuel Goldwyn has achieved" in the 1960s. The theatre burned down in January 1894.

The Columbia Theatre or Loew's New Columbia Theatre in Boston, Massachusetts, was a playhouse and cinema located in the South End at No. 978 Washington Street. Charles Frohman, Isaac Baker Rich and William Harris oversaw the theatre until 1895. Owners included J.J. Grace of New York and Loews. Staff included Harry Farren, Saul Hamilburg and Philip Shea. The Columbia existed until its demolition in 1957.

B.F. Keith's Theatre (1894–1928) in Boston, Massachusetts, was a vaudeville playhouse run by B.F. Keith. It sat across from Boston Common in the city's theatre district, with an entrance on Tremont Street and another on Washington Street. Personnel included Keith, E.F. Albee and H.E. Gustin. Virgilio Tojetti painted some of the interior decorations. In 1939, the theater was converted to a movie theater named the Normandie.
The Grand Opera House (est.1888) of Boston, Massachusetts, was a theatre in the South End. Architect George Snell designed the 2,600-seat building on Washington Street. Managers and proprietors included Proctor & Mansfield, A.H. Dexter, George W. Magee, and Stair & Wilbur. Performances included Glyn's Three Weeks.

Selwyn's Theatre (1867–1870) of Boston, Massachusetts, was established by British-born actor John H. Selwyn. Architect Benjamin F. Dwight designed the building. Personnel included Dexter H. Follet, Arthur Cheney, H.A. M'Glenen, Charles R. Thorne Jr., and Charles Koppitz. In 1871 Selwyn's was renamed the "Globe Theatre."
Theatre Comique (1865–1869) of Boston, Massachusetts, was located at no. 240 Washington Street. Personnel included Jason Wentworth, William H. Crisp, James S. Maffitt, George Maffitt, B.F. Lowell, Wm. H. Daly, orchestra leader Aug. Muller, and maitre de ballet Signor Constantine. Among the performances: slack rope and acrobatics by Martini Chiriski and the Levantine Brothers; Mlle. Augusta, danseuse; "Aladdin" with Kate Pennoyer and W.H. Bartholomew; dancing by Betty Regl; Snow Brothers ; Morlacchi Ballet Troupe; Wilson Brothers ; Ada Harland; and Jarrett & Palmer's "Forty Thieves." It occupied the building formerly known as Andrews Hall, Barnum's Aquarial Gardens, and the Boston Aquarial and Zoological Gardens. In 1869 the theatre was renamed the "Adelphi Theatre."
Gordon's Olympia Theatre in Boston, Massachusetts, was established by Nathan H. Gordon of Olympia Theatres, Inc. Architect Clarence Blackall designed the building at no.658 Washington Street, near Boylston Street in the theatre district. It later became the Pilgrim Theater. The building was demolished in 1996.
The RKO Boston Theatre was a movie theatre in Boston, Massachusetts, located at 616 Washington Street, near Essex Street in the Boston Theater District. It opened as the Keith-Albee Boston Theatre on October 5, 1925.
The Fenway Theatre (1915–1972) of Boston, Massachusetts, was a cinema and concert hall in the Back Bay, located at no.136 Massachusetts Avenue at Boylston Street. Architect Thomas W. Lamb designed the building; its interior was "marble and velvet." The auditorium sat 1,600. In the early 1970s Aerosmith used the theatre for rehearsals. In 1972 the Berklee College of Music bought the property; the remodeled Berklee Performance Center opened in 1976 and continues today.
The Beacon Theatre was a cinema on Tremont Street in Boston, Massachusetts built in 1910 and closed in 1948. Jacob Lourie established it. Architect Clarence Blackall designed the building, with its 500-seat auditorium which a contemporary critic described as "showy." It had a staff of 26 in 1910. In 1948 the "refurbished" building became the Beacon Hill Theater. The building existed until 1970.
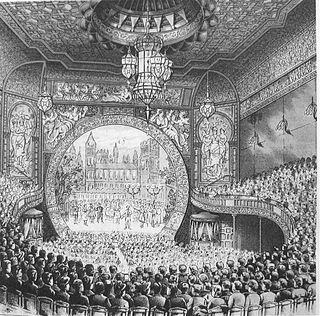
The Bijou Theatre (1882–1943) in Boston, Massachusetts, occupied the second floor of 545 Washington Street near today's Theatre District. Architect George Wetherell designed the space, described by a contemporary reviewer as "dainty." Proprietors included Edward Hastings, George Tyler, and B.F. Keith. Around the 1900s, it featured a "staircase of heavy glass under which flowed an illuminated waterfall." The Bijou "closed 31 December 1943 and was razed in 1951." The building's facade still exists. It is currently a pending Boston Landmark by the Boston Landmarks Commission.
The Gaiety Theatre (1908–1949) or Gayety Theatre of Boston, Massachusetts, was located at no.661 Washington Street near Boylston Street in today's Boston Theater District. It featured burlesque, vaudeville and cinema. Performers included Clark and McCullough, Solly Ward, and Lena Daley; producers included Charles H. Waldron, Earl Carroll, and E.M. Loew. In 1949 it became the "Publix Theatre." The building existed until its razing in 2005.
References
- ↑ Boston Almanac. 1879-1882
- ↑ Boston Daily Globe, Feb. 20, 1881
- ↑ Donald C. King (2005), The Theatres of Boston: a Stage and Screen History, Jefferson, N.C: McFarland & Co., ISBN 0-7864-1910-5, OL 3392044M, 0786419105
- ↑ King's Handbook of Boston, 4th ed. Cambridge, Massachusetts: M. King, 1881
- ↑ Boston Athenaeum. Theater History Archived 2021-04-14 at the Wayback Machine . Bijou Theatre (1882- 1952), 545 Washington Street. Retrieved 2012-03-16
Coordinates: 42°21′15.52″N71°3′44.26″W / 42.3543111°N 71.0622944°W