Related Research Articles
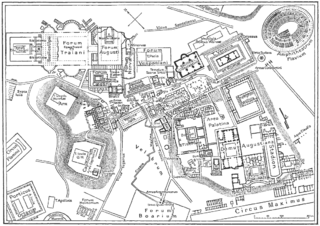
Vicus Tuscus was an ancient street in the city of Rome, running southwest out of the Roman Forum between the Basilica Julia and the Temple of Castor and Pollux towards the Forum Boarium and Circus Maximus via the west side of the Palatine Hill and Velabrum.
Titus Larcius was a Roman general and statesman during the early Republic, who served twice as consul and became the first Roman dictator.

The gens Aquillia or Aquilia was a plebeian family of great antiquity at ancient Rome. Two of the Aquillii are mentioned among the Roman nobles who conspired to bring back the Tarquins, and a member of the house, Gaius Aquillius Tuscus, was consul in 487 BC.

The gens Cloelia, originally Cluilia, and occasionally written Clouilia or Cloulia, was a patrician family at ancient Rome. The gens was prominent throughout the period of the Republic. The first of the Cloelii to hold the consulship was Quintus Cloelius Siculus, in 498 BC.
Lucius Aebutius Helva was a politician and general of the Roman Republic. He was consul in 463 BC with Publius Servilius Priscus, but died of the plague during his term.
The gens Menenia was a very ancient and illustrious patrician house at ancient Rome from the earliest days of the Roman Republic to the first half of the fourth century BC. The first of the family to obtain the consulship was Agrippa Menenius Lanatus in 503 BC. The gens eventually drifted into obscurity, although its members were still living in the first century BC.
The gens Lartia, also spelled Larcia, or rarely Largia, was a patrician family at ancient Rome, whose members earned great distinction at the beginning of the Republic. Spurius Larcius was one of the two companions of Horatius, who defended the Pons Sublicius against Lars Porsena in 508 BC. A few years later, Titus Larcius became the first Roman dictator. However, the gens all but vanishes from history after this period. A family of the same name existed in the late Republic and under the early Empire, but their relationship to the earlier Lartii is unknown.
Spurius Larcius was one of the leading men of the early Roman Republic, of which he was twice consul. However, his greatest fame was won as one of the defenders of the Sublician bridge against the army of Lars Porsena, the King of Clusium.
The gens Verginia or Virginia was a prominent family at ancient Rome, which from an early period was divided into patrician and plebeian branches. The gens was of great antiquity, and frequently filled the highest honors of the state during the early years of the Republic. The first of the family who obtained the consulship was Opiter Verginius Tricostus in 502 BC, the seventh year of the Republic. The plebeian members of the family were also numbered amongst the early tribunes of the people.
The war between Clusium and Aricia was a military conflict in central Italy that took place around 508 BC.

The gens Sicinia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens occur throughout the history of the Republic, but only one of them obtained the consulship, Titus Sicinius Sabinus in 487 BC. Throughout the long Conflict of the Orders, the Sicinii were celebrated for their efforts on behalf of the plebeians.
The Roman conquest of the Hernici, an ancient Italic people, took place during the 4th century BC. For most of the 5th century BC, the Roman Republic had been allied with the other Latin states and the Hernici to successfully fend off the Aequi and the Volsci. In the early 4th century BC, this alliance fell apart. A war fought between Rome and the Hernici in the years 366 - 358 BC ended in Roman victory and the submission of the Hernici. Rome also defeated a rebellion by some Hernician cities in 307 - 306 BC. The rebellious Hernici were incorporated directly into the Roman Republic, while those who had stayed loyal retained their autonomy and nominal independence. In the course of the following century, the Hernici became indistinguishable from their Latin and Roman neighbours and disappeared as a separate people.
Titus Sicinius (Sabinus?) or Siccius was a Roman Republican politician during the beginning of the 5th century BC. He served as Consul of Rome in 487 BC, serving together with Gaius Aquillius Tuscus.
Quintus Fabius Vibulanus was an aristocrat of the Early Roman republic. He was the first of three brothers to hold the consulate, in both 485 and 482 BC.
Marcus Fabius Vibulanus was consul of the Roman republic in 483 and 480 BC.
Titus Veturius Geminus Cicurinus was a Roman politician of the 5th century BC, consul in 462 BC and maybe decemvir in 451 BC.
Gaius Horatius Pulvillus was a Roman politician during the 5th century BC, and was consul in 477 and 457 BC.
Spurius Furius Medullinus Fusus was a Roman politician in the 5th century BC, and was consul in 464 BC, and consul suffect in 453 BC.
The gens Metilia was a minor family at ancient Rome. Although they occur throughout Roman history, and several were tribunes of the plebs, beginning in the fifth century BC, none of the Metilii attained the higher offices of the Roman state until imperial times, when several of them became consul.
Titus Verginius Tricostus Caeliomontanus was consul of the Roman Republic in 448 BC with Lars Herminius Aquilinus. Little is known about his life.
References
- ↑ T.R.S. Broughton, The Magistrates of the Roman Republic (American Philological Association, 1952, 1986), vol. 1, pp. 19–20.
- ↑ Ampolo, "Gli Aquilii del V. Secolo a.C. e il Problema di Fasti Consolari piu antichi nell'Anno 487 BC", PdP, 30 (1975), pp. 410-6; cited in Gary Forsythe, A Critical History of Early Rome (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2006), p. 164