Related Research Articles

The First Punic War was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated.
Hamilcar Barca or Barcas was a Carthaginian general and statesman, leader of the Barcid family, and father of Hannibal, Hasdrubal and Mago. He was also father-in-law to Hasdrubal the Fair.

The siege of Carthage was the main engagement of the Third Punic War fought between Carthage and Rome. It consisted of the nearly-three-year siege of the Carthaginian capital, Carthage. In 149 BC, a large Roman army landed at Utica in North Africa. The Carthaginians hoped to appease the Romans, but despite the Carthaginians surrendering all of their weapons, the Romans pressed on to besiege the city of Carthage. The Roman campaign suffered repeated setbacks through 149 BC, only alleviated by Scipio Aemilianus, a middle-ranking officer, distinguishing himself several times. A new Roman commander took over in 148 BC, and fared equally badly. At the annual election of Roman magistrates in early 147 BC, the public support for Scipio was so great that the usual age restrictions were lifted to allow him to be appointed commander in Africa.
Xanthippusof Lacedaemon, or of Carthage, was a Spartan mercenary general employed by Carthage during the First Punic War. He led the Carthaginian army to considerable success against the Roman Republic during the course of the war, training the army to a professional standard before defeating the Romans at the Battle of Tunis, where Carthaginian forces routed the Roman expeditionary force and captured the Roman consul Marcus Atilius Regulus in 255 BC.

The Battle of the Lipari Islands or Battle of Lipara was a naval encounter fought in 260 BC during the First Punic War. A squadron of 20 Carthaginian ships commanded by Boödes surprised 17 Roman ships under the senior consul for the year Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio in Lipara Harbour. The inexperienced Romans made a poor showing, with all 17 of their ships captured, along with their commander.

The Battle of Cape Ecnomus or Eknomos was a naval battle, fought off southern Sicily, in 256 BC, between the fleets of Carthage and the Roman Republic, during the First Punic War. The Carthaginian fleet was commanded by Hanno and Hamilcar; the Roman fleet jointly by the consuls for the year, Marcus Atilius Regulus and Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus. It resulted in a clear victory for the Romans.
The naval Battle of Drepana took place in 249 BC during the First Punic War near Drepana in western Sicily, between a Carthaginian fleet under Adherbal and a Roman fleet commanded by Publius Claudius Pulcher.
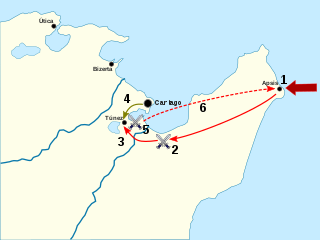
The Battle of the Bagradas River, also known as the Battle of Tunis, was a victory by a Carthaginian army led by Xanthippus over a Roman army led by Marcus Atilius Regulus in the spring of 255 BC, nine years into the First Punic War. The previous year, the newly constructed Roman navy established naval superiority over Carthage. The Romans used this advantage to invade Carthage's homeland, which roughly aligned with modern-day Tunisia in North Africa. After landing on the Cape Bon Peninsula and conducting a successful campaign, the fleet returned to Sicily, leaving Regulus with 15,500 men to hold the lodgement in Africa over the winter.
The Battle of Panormus was fought in Sicily in 250 BC during the First Punic War between a Roman army led by Lucius Caecilius Metellus and a Carthaginian force led by Hasdrubal, son of Hanno. The Roman force of two Roman and two allied legions defending the city of Panormus defeated the much larger Carthaginian army of 30,000 men and between 60 and 142 war elephants.
The Treaty of Lutatius was the agreement between Carthage and Rome of 241 BC, that ended the First Punic War after 23 years of conflict. Most of the fighting during the war took place on, or in the waters around, the island of Sicily and in 241 BC a Carthaginian fleet was defeated by a Roman fleet commanded by Gaius Lutatius Catulus while attempting to lift the blockade of its last, beleaguered, strongholds there. Accepting defeat, the Carthaginian Senate ordered their army commander on Sicily, Hamilcar Barca, to negotiate a peace treaty with the Romans, on whatever terms he could negotiate. Hamilcar refused, claiming the surrender was unnecessary, and the negotiation of the peace terms was left to Gisco, the commander of Lilybaeum, as the next most senior Carthaginian on the island. A draft treaty was rapidly agreed upon, but when it was referred to Rome for ratification it was rejected.
Hanno, whose full name was in Phoenician 𐤇𐤍𐤀 𐤁𐤍 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋 Hna Ben Hanibal) or Hanno son of Hannibal, was, according to Diodorus Siculus, a Carthaginian general during the First Punic War.

Hanno was a Carthaginian general, prominent in the events leading to the start of the First Punic War.
The siege of Lilybaeum lasted for nine years, from 250 to 241 BC, as the Roman army laid siege to the Carthaginian-held Sicilian city of Lilybaeum during the First Punic War. Rome and Carthage had been at war since 264 BC, fighting mostly on the island of Sicily or in the waters around it, and the Romans were slowly pushing the Carthaginians back. By 250 BC, the Carthaginians held only the cities of Lilybaeum and Drepana; these were well-fortified and situated on the west coast, where they could be supplied and reinforced by sea without the Romans being able to use their superior army to interfere.
Titus Otacilius Crassus was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the two consuls of 261 BCE, serving with Lucius Valerius Flaccus. During his consulship, he and his consular colleague Flaccus fought against the Carthaginians on Sicily as part of the ongoing First Punic War. Before sailing to Sicily they strengthened the coastal defences of Italy against attacks by Hannibal Gisco, a Carthaginian admiral sent to raid the Tyrrhenian coast. The consuls besieged Mytistraton, but were eventually driven off by Hamilcar, the new commander of Carthage's Sicilian army, who defeated them at Thermae near Palermo. They returned to Italy were they started building Rome's first warfleet, created after Carthaginian example. In 260, the fleet was ready and would be used by Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Asina, one of the two consuls of that year.
The Roman withdrawal from Africa was the attempt by the Roman Republic in 255 BC to rescue the survivors of their defeated expeditionary force to Carthaginian Africa during the First Punic War. A large fleet commanded by Servius Fulvius Paetinus Nobilior and Marcus Aemilius Paullus successfully evacuated the survivors after defeating an intercepting Carthaginian fleet, but was struck by a storm while returning, losing most of its ships.
Gnaeus Cornelius Blasio was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the two consuls of 257 BCE, serving with Gaius Atilius Regelus. Blasio was considered a princeps of the Senate. He was consul during the First Punic War against Carthage. During his consulship he commanded the Republic's land forces on Sicily, while his fellow consul Regelus led the fleet. He did not achieve any stunning victories, but focused on consolidating Rome's power on the island.
Marcus Aemilius Paullus was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the consuls of 255 BCE, serving with Servius Fulvius Paetinius Nobilior. As consul Paullus led the Republic's forces in the ongoing First Punic War against Carthage; he and Paetinus led a Roman fleet of 350 warships to Africa to rescue the remnants of the army of proconsul Marcus Atilius Regelus, who had been defeated in the Battle of the Bagradas River earlier that year. Onroute they defeated a Carthaginian fleet of 200 warships in the Battle of Cape Hermaeum.
Servius Fulvius Paetinius Nobilior was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the two consuls of 255 BCE, serving with Marcus Aemilius Paullus. He was consul during the First Punic War against Carthage. Paetinus and his consular colleague led a Roman fleet of 350 warships to Africa to rescue the remnants of the army of proconsul Marcus Atilius Regelus, who had been defeated at the Battle of the Bagradas River during their consulship. En route they defeated a Carthaginian fleet of 200 warships in the Battle of Cape Hermaeum.
Gnaeus Servilius Caepio was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the two consuls of 253 BCE, serving with Gaius Sempronius Blaesus. He was consul during the First Punic War against Carthage. During his consulship Servilius Caepio commanded Rome's land forces on Sicily, while his consular colleague led a fleet to Africa.
Publius Servilius Geminus was a Roman statesman and general during the middle era of the Roman Republic. He was one of the two consuls of 252 BCE, serving with Gaius Aurelius Cotta. They fought against the Carthaginians in the ongoing First Punic War; Geminus and Cotta were very successful; they took several Carthaginian strongholds on Sicily. In 248 he obtained the consulship a second time, together with his former colleague, Aurelius Cotta, and again fought in Sicily against the Carthaginians.
References
- ↑ Jona Lendering, De Vergeten Oorlog, p. 99; Adrian Goldsworthy, The Fall of Carthage, pp 116–117; Polybius, The Histories , 1.39.1–6; Diodorus, Bibliotheca historica , 23.19.1; Zonaras, 8, fr.14.
- ↑ Jona Lendering, De Vergeten Oorlog, p. 99; Adrian Goldsworthy, The Fall of Carthage, p. 117; Diodorus, Bibliotheca historica , 23.19.1; Zonaras, 8, fr.14.