Related Research Articles

An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been part of a continent. Oceanic islands can be formed from volcanic activity, grow into atolls from coral reefs, and form from sediment along shorelines, creating barrier islands. River islands can also form from sediment and debris in rivers. Artificial islands are those made by humans, including small rocky outcroppings built out of lagoons and large-scale land reclamation projects used for development.

Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area. Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms.

Alvin (DSV-2) is a crewed deep-ocean research submersible owned by the United States Navy and operated by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) of Woods Hole, Massachusetts. The original vehicle was built by General Mills' Electronics Group in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Named to honor the prime mover and creative inspiration for the vehicle, Allyn Vine, Alvin was commissioned on June 5, 1964.

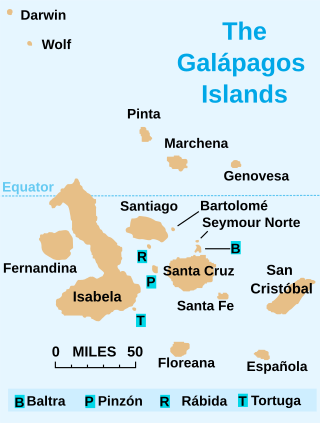
The Galápagos Islands are an archipelago of volcanic islands in the Eastern Pacific, located around the Equator 900 km (560 mi) west of the mainland of South America. They form the Galápagos Province of the Republic of Ecuador, with a population of slightly over 33,000 (2020). The province is divided into the cantons of San Cristóbal, Santa Cruz, and Isabela, the three most populated islands in the chain. The Galápagos are famous for their large number of endemic species, which were studied by Charles Darwin in the 1830s and inspired his theory of evolution by means of natural selection. All of these islands are protected as part of Ecuador's Galápagos National Park and Marine Reserve.

Sylvia Alice Earle is an American marine biologist, oceanographer, explorer, author, and lecturer. She has been a National Geographic Explorer at Large since 1998. Earle was the first female chief scientist of the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and was named by Time Magazine as its first Hero for the Planet in 1998.
Roscoe Lee Browne was an American actor and director. He resisted playing stereotypically black roles, instead performing in several productions with New York City's Shakespeare Festival Theater, Leland Hayward's satirical NBC series That Was the Week That Was, and a poetry performance tour of the United States in addition to his work in television and film. He is perhaps best known for his many guest appearances on TV series from the 1970s and 1980s as well as movies like The Cowboys (1972) with John Wayne.
Isabela Island is the largest of the Galápagos Islands, with an area of 4,586 km2 (1,771 sq mi) and a length of 100 km (62 mi). By itself, it is larger than all the other islands in the chain combined, and it has a little under 2,000 permanent inhabitants. The island straddles the equator.
The Galápagos Islands are located off the west coast of South America straddling the equator. The Galápagos are located at the confluence of several currents including the cold Humboldt Current traveling north from South America and the Panama Current traveling south from Central America make the islands cooler and provide the perfect environment for the unique mix of wildlife that inhabits the islands.

Darwin Island is an isolated northern member of the Galápagos Islands in Ecuador, the uppermost extent of an extinct volcano. It has an area of 1 square kilometer (0.4 sq mi) and reaches 165 meters (541 ft) above sea level. Visits to the island are restricted by the Government of Ecuador, but scuba diving is permitted.

The Galápagos tortoise or Galápagos giant tortoise is a very large species of tortoise in the genus Chelonoidis. The species comprises 15 subspecies. It is the largest living species of tortoise, and can weigh up to 417 kg (919 lb). They are also the largest extant terrestrial cold-blooded animals (ectotherms).

The second voyage of HMS Beagle, from 27 December 1831 to 2 October 1836, was the second survey expedition of HMS Beagle, made under her newest commander, Robert FitzRoy. FitzRoy had thought of the advantages of having someone onboard who could investigate geology, and sought a naturalist to accompany them as a supernumerary. At the age of 22, the graduate Charles Darwin hoped to see the tropics before becoming a parson, and accepted the opportunity. He was greatly influenced by reading Charles Lyell's Principles of Geology during the voyage. By the end of the expedition, Darwin had made his name as a geologist and fossil collector, and the publication of his journal gave him wide renown as a writer.
Understanding is a documentary television series that aired from 1994 to 2004 on TLC. The program covered various things understood from a scientific perspective and was narrated by Jane Curtin, Candice Bergen, and Peter Coyote. It originally aired on TLC and as of 2013 is currently being shown on the Science Channel. The series is presented in a similar fashion to two other programs that also show on the Science Channel, Discover Magazine and Megascience.

The Galápagos rice rat, also known as the Galápagos oryzomys, is a species of rodent that is endemic to the Galápagos Islands.
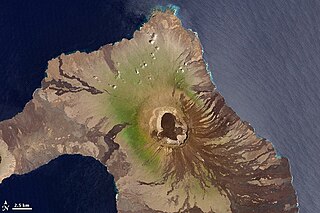
Wolf Volcano, also known as Mount Whiton, is the highest peak in the Galápagos Islands. It is situated on Isabela Island and reaches 1,710 m (5,610 ft). It is a shield volcano with a characteristic upturned soup bowl shape.

Lonesome George was a male Pinta Island tortoise and the last known individual of the subspecies. In his last years, he was known as the rarest creature in the world. George serves as an important symbol for conservation efforts in the Galápagos Islands and throughout the world.
The jaguar catshark, also known as the Galápagos catshark, is a species of shark belonging to the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks, endemic to the Galápagos Islands. The species was first described in 2012. This catshark is about 30 cm (12 in) long when mature, and it is colored blackish-brown with an asymmetrical pattern of light spots.
Cindy Lee Van Dover is the Harvey Smith Professor of Biological Oceanography and chair of the Division of Marine Science and Conservation at Duke University. She is also the director of the Duke University Marine Laboratory. Her primary area of research is oceanography, but she also studies biodiversity, biogeochemistry, conservation biology, ecology, and marine science.

Marine biology is a hybrid subject that combines aspects of organismal function, ecological interaction and the study of marine biodiversity. The earliest studies of marine biology trace back to the Phoenicians and the Greeks who are known as the initial explorers of the oceans and their composition. The first recorded observations on the distribution and habits of marine life were made by Aristotle.

Darwin's Arch was a natural rock arch feature to the south-east of Darwin Island in the Galápagos Archipelago in the Pacific Ocean, and is now a pillar formation. The arch sat on an irregularly shaped, rocky, submerged plateau, nicknamed "the theatre". The arch collapsed into the sea on 17 May 2021 from natural erosion.
OceanX is an ocean exploration initiative founded by Mark Dalio and Ray Dalio, founder of investment firm Bridgewater Associates, an initiative by Dalio Philanthropies. OceanX utilises science, technology and media to explore and engage in public awareness activities and promotion efforts for the oceans and marine conservation efforts. The initiative also has shown to aid and facilitate ocean research for scientists, science institutions, media companies and philanthropy partners.
References
- ↑ Greenberg, Joel (17 August 1996). "'Galapagos: Beyond Darwin' Follows in His Footsteps". Los Angeles Times . Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ↑ Taros, Megan (16 April 2012). "New little shark is a big deal". SF Bay. Retrieved 16 March 2016.