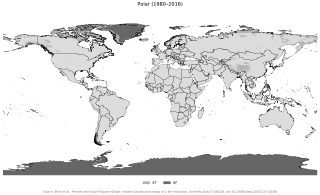
The polar climate regions are characterized by a lack of warm summers but with varying winters. Every month a polar climate has an average temperature of less than 10 °C (50 °F). Regions with a polar climate cover more than 20% of the Earth's area. Most of these regions are far from the equator and near the poles, and in this case, winter days are extremely short and summer days are extremely long. A polar climate consists of cool summers and very cold winters, which results in treeless tundra, glaciers, or a permanent or semi-permanent layer of ice. It is identified with the letter E in the Köppen climate classification.
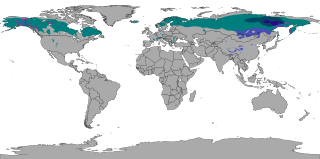
The subarctic climate is a continental climate with long, cold winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50°N to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification Dfc, Dwc, Dsc, Dfd, Dwd and Dsd.

The United Kingdom straddles the higher mid-latitudes between 49° and 61°N on the western seaboard of Europe. Since the UK is always in or close to the path of the polar front jet stream, frequent changes in pressure and unsettled weather are typical. Many types of weather can be experienced in a single day.

The desert climate or arid climate is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert climates are dry and hold little moisture, quickly evaporating the already little rainfall they receive. Covering 14.2% of Earth's land area, hot deserts are the second most common type of climate on Earth after the polar climate.

Formosa is the capital city of the Argentine province of Formosa, on the banks of the Paraguay River, opposite the Paraguayan town of Alberdi, about 1,200 km (746 mi) north from Buenos Aires, on National Route 11. The city has a population of about 234,000 per the 2010 census [INDEC].
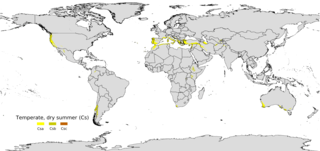
A Mediterranean climate, also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen as Cs, is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes. Such climates typically have dry summers and wet winters, with summer conditions ranging from warm to hot and winter conditions typically being mild to cool. These weather conditions are typically experienced in the majority of Mediterranean-climate regions and countries, but remain highly dependent on proximity to the ocean, altitude and geographical location.

Tahoe City is an unincorporated town in Placer County, California. Tahoe City is located on the shore of Lake Tahoe, at the outlet of the Truckee River.
Central Otago is an area located in the inland part of the Otago region in the South Island of New Zealand. The motto for the area is "A World of Difference".

The climate of Chicago is classified as hot-summer humid continental with hot humid summers and cold, occasionally snowy winters. All four seasons are distinctly represented: Winters are cold and often see snow with below 0 Celsius temperatures and windchills, while summers are warm and humid with temperatures being hotter inland, spring and fall bring bouts of both cool and warm weather and fairly sunny skies. Annual precipitation in Chicago is moderate and relatively evenly distributed, the driest months being January and February and the wettest July and August. Chicago's weather is influenced during all four seasons by the nearby presence of Lake Michigan.

Embarrass is an unincorporated community in Embarrass Township, Saint Louis County, Minnesota, United States.
The climate of Salt Lake City, Utah features cold and snowy winters, hot and dry summers, and modest to light seasonal rainfall. Lying in the Salt Lake Valley, the city is surrounded by mountains and the Great Salt Lake. Under the Köppen climate classification, Salt Lake City has either a Mediterranean climate (Csa) or dry-summer continental climate (Dsa) depending on which variant of the system is used, though it borders on a cold semi-arid climate (BSk) due to the city's relatively low precipitation.

Villa La Angostura is a town located in the Los Lagos Department in the south of the Argentine province of Neuquén, on the northwest shore of the Nahuel Huapi Lake.

The climate of the city of Sydney, Australia is humid subtropical, shifting from mild and cool in winter to warm and hot in the summer, with no extreme seasonal differences as the weather is moderated by proximity to the ocean, although more contrasting temperatures are recorded in the inland western suburbs. Despite the fact that there is no distinct dry or wet season, rainfall peaks in the first few months of the year and is at its lowest just around the middle of the year, though precipitation can be erratic throughout the year. Precipitation varies across the region, with areas adjacent to the coast being the wettest. According to the Bureau of Meteorology, Sydney falls in the temperate climate zone which has warm to hot summers and no dry season. Sydney's plant hardiness zone ranges from zone 11a to 9b throughout the metropolitan area. Under the Holdridge Life Zones classification, eastern Sydney falls in the Subtropical Moist Forest zone and the western suburbs in the Subtropical Dry Forest zone.
The climate of Delhi is an overlap between monsoon-influenced humid subtropical and semi-arid, with high variation between summer and winter temperatures and precipitation. Delhi's version of a humid subtropical climate is markedly different from many other humid subtropical cities such as São Paulo, Houston, and Brisbane in that the city features dust storms and wildfire haze due to its semi-arid climate.
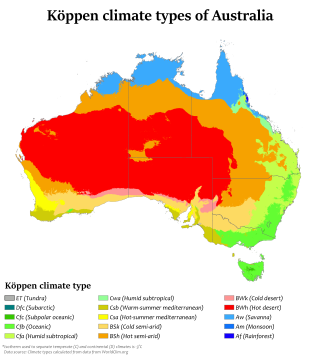
Australia's climate is governed mostly by its size and by the hot, sinking air of the subtropical high pressure belt. This moves north-west and north-east with the seasons. The climate is variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons, thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Australia has a wide variety of climates due to its large geographical size. The largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid. Only the south-east and south-west corners have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate, varying between grasslands and desert. Australia holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, and the highest sunshine duration.

The climate of Italy is the long-term weather pattern in the territory of the Italian Republic. The climate of Italy is influenced by the large body of water of the Mediterranean Seas that surrounds Italy on every side except the north. These seas constitute a reservoir of heat and humidity for Italy. Within the southern temperate zone, they determine a particular climate called Mediterranean climate with local differences due to the geomorphology of the territory, which tends to make its mitigating effects felt, especially in high pressure conditions.

Kosovo is a relatively small country. Because of the climatic position and complicated structure of the relief it has a variety of climate systems.

Estonia lies in the northern part of the temperate climate zone and in the transition zone between maritime and continental climate. Because Estonia is continuously warmed by maritime air influenced by the heat content of the northern Atlantic Ocean, it has a milder climate despite its northern latitude. The Baltic Sea causes differences between the climate of coastal and inland areas. Estonia has four seasons of near-equal length. Average temperatures range from 17.8 °C (64.0 °F) on the Baltic islands to 18.4 °C (65.1 °F) inland in July, the warmest month, and from −1.4 °C (29.5 °F) on the Baltic islands to −5.3 °C (22.5 °F) inland in February, the coldest month.

Maquinchao is a village and municipality in Río Negro Province in Argentina.

The Trewartha climate classification (TCC) or the Köppen–Trewartha climate classification (KTC) is a climate classification system first published by American geographer Glenn Thomas Trewartha in 1966. It is a modified version of the Köppen–Geiger system, created to answer some of its deficiencies. The Trewartha system attempts to redefine the middle latitudes to be closer to vegetation zoning and genetic climate systems.


















