
Hormizd IV was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 579 to 590. He was the son and successor of Khosrow I and his mother was a Khazar princess.

Peroz I was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II, he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III, eventually seizing the throne after a two-year struggle. His reign was marked by war and famine. Early in his reign, he successfully quelled a rebellion in Caucasian Albania in the west, and put an end to the Kidarites in the east, briefly expanding Sasanian rule into Tokharistan, where he issued gold coins with his likeness at Balkh. Simultaneously, Iran was suffering from a seven-year famine. He soon clashed with the former subjects of the Kidarites, the Hephthalites, who possibly had previously helped him to gain his throne. He was defeated and captured twice by the Hephthalites and lost his recently acquired possessions.

Yazdegerd III was the last Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 632 to 651. His father was Shahriyar and his grandfather was Khosrow II.

Bahram IV, was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 388 to 399. He was likely the son and successor of Shapur III.

Bahram V, also known as Bahram Gur, was the Sasanian King of Kings (shahanshah) from 420 to 438.

Gundeshapur was the intellectual centre of the Sassanid Empire and the home of the Academy of Gundeshapur, founded by Sassanid Emperor Shapur I. Gundeshapur was home to a teaching hospital and had a library and a centre of higher learning. It has been identified with extensive ruins south of Shahabad, a village 14 km south-east of Dezful, to the road for Shushtar, in the present-day province of Khuzestan, southwest Iran.

Sakastan was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, that lay within the kust of Nemroz. The province bordered Kirman in the west, Spahan in the north west, Kushanshahr in the north east, and Turan in the south east. The governor of the province held the title of marzban. The governor also held the title of "Sakanshah" until the title was abolished in ca. 459/60.

Mazun was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, which corresponded to modern-day Bahrain, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, and the northern half of Oman. The province served as a Sasanian outpost and played an important role in the Sasanian efforts to gain control over the Indian Ocean trade, and to establish their dominance in the wealthy regions of Hadramaut and Yemen.

The Sasanian Empire or Sassanid Empire, also the Second Persian Empire, and officially known as Ērānšahr, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th to 8th centuries. Named after the House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651, making it the second longest-lived Persian imperial dynasty after the Arsacids of the Parthian Empire.

Sistān, also known as Sakastān and Sijistan, is a historical region in present-day south-eastern Iran, south-western Afghanistan and extending across the borders of south-western Pakistan. Mostly corresponding to the then Achaemenid region of Drangiana and extending southwards of the Helmand River not far off from the city of Alexandria in Arachosia. Largely desert, the region is bisected by the Helmand River, the largest river in Afghanistan, which empties into the Hamun Lake that forms part of the border between Iran and Afghanistan.

Beth Garmai, is a historical region around the city of Kirkuk in northern Iraq. It is located at southeast of the Little Zab, southwest of the mountains of Shahrazor, northeast of the Tigris and Hamrin Mountains, although sometimes including parts of southwest of Hamrin Mountains, and northwest of the Sirwan River.

Kushanshahr was a province of the Sasanian Empire comprising the region between Kabul Valley and Peshawar Valley. The Kushanshar territory centered on Tukharistan, and covered the area from Tirmidh to Peshawar. The establishment of Sasanian rule in Kushanshar permitted the control of Central Asian trade routes. The Kushano-Sasanids were in charge of the area. They issued coinage which was following the Kushan standard, due to the traditional importance of trade links with India.

Meshan was a province of the Sasanian Empire. It consisted of the Parthian vassal kingdom of Characene and reached north along the Shatt al-Arab river and then the lower Tigris to Madhar and possibly further. Its inhabitants included Babylonians, Arabs, Iranians, and even some Indians and Malays. The province was very fertile, the best place for barley according to Strabo, and contained many date palms. It was also an important trading province along the Persian Gulf.

Padishkhwārgar was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, which almost corresponded to the present-day provinces of Mazandaran and Gilan. The province bordered Adurbadagan and Balasagan in the west, Gurgan in the east, and Spahan in south. The main cities of the province were Amol and Chalus.
The Daylamites or Dailamites were an Iranian people inhabiting the Daylam—the mountainous regions of northern Iran on the southwest coast of the Caspian Sea, now comprising the southeastern half of Gilan Province.

The Church of the East or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian Church, is one of three major branches of Nicene Eastern Christianity that arose from the Christological controversies of the 5th and 6th centuries, alongside the Miaphisite churches and the Chalcedonian Church.

Spahan, also known as Parthau was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, that lay within central Iran, almost corresponding to the present-day Isfahan Province in Iran.

Sasanian Egypt refers to the brief rule of Egypt and parts of Libya by the Sasanian Empire, following the Sasanian conquest of Egypt. It lasted from 618 to 628, until the Sasanian general Shahrbaraz made an alliance with the Roman Byzantine emperor Heraclius to have control over Egypt returned to him.

Harev, was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, that lay within the kust of Khorasan. The province bordered Kushanshahr in the west, Abarshahr in the east, Marv in the north, and Sakastan in the south.
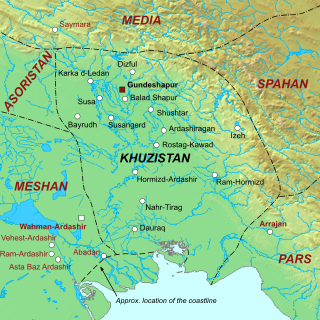
Khuzistan or Huzistan was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, which almost corresponded to the present-day province of Khuzestan. Its capital was Gundeshapur. During the late Sasanian era, the province was included in the southern quadrant (kust) of Nemroz.



















