Waddesdon Manor is a country house in the village of Waddesdon, in Buckinghamshire, England. Owned by the National Trust and managed by the Rothschild Foundation, it is one of the National Trust's most visited properties, with over 463,000 visitors in 2019.

The Wallace Collection is a museum in London occupying Hertford House in Manchester Square, the former townhouse of the Seymour family, Marquesses of Hertford. It is named after Sir Richard Wallace, who built the extensive collection, along with the Marquesses of Hertford, in the 18th and 19th centuries. The collection features fine and decorative arts from the 15th to the 19th centuries with important holdings of French 18th-century paintings, furniture, arms and armour, porcelain and Old Master paintings arranged into 25 galleries. It is open to the public and entry is free.

The Vincennes porcelain manufactory was established in 1740 in the disused royal Château de Vincennes, in Vincennes, east of Paris, which was from the start the main market for its wares.

Chinese export porcelain includes a wide range of Chinese porcelain that was made (almost) exclusively for export to Europe and later to North America between the 16th and the 20th century. Whether wares made for non-Western markets are covered by the term depends on context. Chinese ceramics made mainly for export go back to the Tang dynasty if not earlier, though initially they may not be regarded as porcelain.

Chelsea porcelain is the porcelain made by the Chelsea porcelain manufactory, the first important porcelain manufactory in England, established around 1743–45, and operating independently until 1770, when it was merged with Derby porcelain. It made soft-paste porcelain throughout its history, though there were several changes in the "body" material and glaze used. Its wares were aimed at a luxury market, and its site in Chelsea, London, was close to the fashionable Ranelagh Gardens pleasure ground, opened in 1742.

The Manufacture nationale de Sèvres is one of the principal European porcelain factories. It is located in Sèvres, Hauts-de-Seine, France. It is the continuation of Vincennes porcelain, founded in 1740, which moved to Sèvres in 1756. It has been owned by the French crown or government since 1759, and has always maintained the highest standards of quality. Almost immediately, it replaced Meissen porcelain as the standard-setter among European porcelain factories, retaining this position until at least the 19th century.

The Museum of Royal Worcester is a ceramics museum located in the Royal Worcester porcelain factory's former site in Worcester, England.

The Van Tilburg Collection is an art collection at the University of Pretoria that comprises 17th and 18th century furniture, paintings, Delft ceramics and other works of art, and includes the largest South African collection of Chinese ceramic objects. The oriental ceramic collection comprises 1699 pieces of earthenware, stoneware and porcelain dating from about 2000 BC until the early twentieth century.

A tea set or tea service is a collection of matching teaware and related utensils used in the preparation and serving of tea. The traditional components of a tea set may vary between societies and cultures.

Mintons was a major company in Staffordshire pottery, "Europe's leading ceramic factory during the Victorian era", an independent business from 1793 to 1968. It was a leader in ceramic design, working in a number of different ceramic bodies, decorative techniques, and "a glorious pot-pourri of styles - Rococo shapes with Oriental motifs, Classical shapes with Medieval designs and Art Nouveau borders were among the many wonderful concoctions". As well as pottery vessels and sculptures, the firm was a leading manufacturer of tiles and other architectural ceramics, producing work for both the Houses of Parliament and United States Capitol.

Louis-Simon Boizot (1743–1809) was a French sculptor whose models for biscuit figures for Sèvres porcelain are better-known than his large-scale sculptures.

Pierre-Philippe Thomire (1751–1843) a French sculptor, was the most prominent bronzier, or producer of ornamental patinated and gilt-bronze objects and furniture mounts of the First French Empire. His fashionable neoclassical and Empire style furnishing bronzes established the highest standard in refined finish in the craft that the French called that of the fondeur-ciseleur, "founder-finisher". In his pre-Revolutionary training, Thomire appeared first as a ciseleur, in the division of duties that went into the production, for example, of a set of gilt-bronze wall-lights delivered for Marie-Antoinette's card-room, her Salon des Jeux at Compiègne: under the general supervision of Hauré, the wax and wooden model was carved by Martin, cast by Forestier, and chased by Thomire, as Pierre Verlet was able to show over fifty years ago.

Greenwich armour is the plate armour in a distinctively English style produced by the Royal Almain Armoury founded by Henry VIII in 1511 in Greenwich near London, which continued until the English Civil War. The armoury was formed by imported master armourers hired by Henry VIII, initially including some from Italy and Flanders, as well as the Germans who dominated during most of the 16th century. The most notable head armourer of the Greenwich workshop was Jacob Halder, who was master workman of the armoury from 1576 to 1607. This was the peak period of the armoury's production and it coincided with the elaborately gilded and sometimes coloured decorated styles of late Tudor England.

The city of Nevers, Nièvre, now in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in central France, was a centre for manufacturing faience, or tin-glazed earthenware pottery, between around 1580 and the early 19th century. Production of Nevers faience then gradually died down to a single factory, before a revival in the 1880s. In 2017, there were still two potteries making it in the city, after a third had closed. However the quality and prestige of the wares has gradually declined, from a fashionable luxury product for the court, to a traditional regional speciality using styles derived from the past.

French porcelain has a history spanning a period from the 17th century to the present. The French were heavily involved in the early European efforts to discover the secrets of making the hard-paste porcelain known from Chinese and Japanese export porcelain. They succeeded in developing soft-paste porcelain, but Meissen porcelain was the first to make true hard-paste, around 1710, and the French took over 50 years to catch up with Meissen and the other German factories.
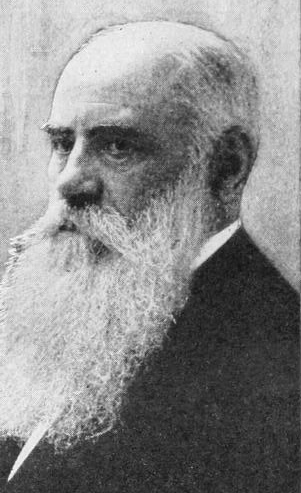
Taxile Maximin Doat (1851–1939) was a French potter who is primarily known for his experimentation with high-fired porcelain and stoneware using the pâte-sur-pâte technique. His book on these techniques Grand Feu Ceramics was published in 1905 and helped spread his discoveries internationally. His influence is apparent in the types of glazes and approaches used in studio pottery in the twentieth century.

Pot pourri à vaisseau or pot pourri en navire is the shape used for a number of pot-pourri vases in the form of masted ships, first produced between the late 1750s to the early 1760s by the Sèvres manufactory near Paris. The colours and details of the painted decoration vary between examples, as is typical of Sèvres porcelain, and one example is on a later gilt wood stand. The openwork lid lifts off to allow refilling of the pot-pourri. The shape was eventually produced in two or three versions, at slightly different sizes. It was first designed in 1757, probably by Jean-Claude Duplessis, the artistic director of the factory. The first surviving finished example dates to 1759. Another name for them is vaisseau à mat.

A toilet service is a set of objects for use at the dressing table. The term is usually reserved for large luxury sets from the 17th to 19th centuries, with toilet set or vanity set used for later or simpler sets. Historically, services were made in metal, ceramics, and other materials, for both men and women, though male versions were generally much smaller. The rich had services in gold, silver, or silver-gilt. The contents vary, but typically include a mirror, one or more small ewers and basins, two candlesticks, and an assortment of bowls, boxes, caskets, and other containers. One or more brushes and a pin-cushion, often as a top to a box, are often included. The sets usually came with a custom-made travelling case, and some services were especially designed for travelling.

Dihl and Guérhard porcelain was made by the Duc d'Angoulême's porcelain factory, a hard-paste porcelain factory in Paris, active from February 25, 1781 until 1828. It was founded by Christophe Dihl (1752-1830) and Antoine Guérhard (d.1793), together with Louise-Françoise-Madeleine Croizé (1751-1831), then married to Guérhard, but married to Dihl from 1797. Dihl was a chemist, and the factory experimented with new colours and finishes.

In European porcelain, a cabinet cup is an unusually richly decorated cup, normally with a saucer, that did not form part of a tea service but was sold singly to give as a present or to collectors. They were expected to be displayed in a glass-fronted china cabinet rather than put to regular use. The heyday of the cabinet cup was the second half of the 18th century and the first decades of the 19th century; they worked well in the showy Empire style then in fashion. A more general term, also covering plates and other shapes, is cabinet piece.