Gerard Piel was the publisher of the new Scientific American magazine starting in 1948. He wrote for magazines, including The Nation, and published books on science for the general public. In 1990, Piel was presented with the In Praise of Reason award by the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry (CSICOP).
William McGinnis is an American molecular biologist who is a professor of biology at the University of California San Diego. At UC San Diego he has also served as the Chairman of the Department of Biology from July 1998 to June 1999, as Associate Dean of the Division of Natural Sciences from July 1, 1999 to June 2000, and as Interim Dean of the newly established Division of Biological Sciences from July 1, 2000 to February 1, 2001. McGinnis was appointed Dean of the Divisional Biological Sciences on July 1, 2013.
Glayde D. Whitney was an American behavioral geneticist and psychologist. He was professor at Florida State University. Beyond his work into the genetics of sensory system function in mice, in his later life he supported David Duke as well as research into race and intelligence and eugenics.

Synaptosomal-Associated Protein, 25kDa (SNAP-25) is a Target Soluble NSF (N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor) Attachment Protein Receptor (t-SNARE) protein encoded by the SNAP25 gene found on chromosome 20p12.2 in humans. SNAP-25 is a component of the trans-SNARE complex, which accounts for membrane fusion specificity and directly executes fusion by forming a tight complex that brings the synaptic vesicle and plasma membranes together.

NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NLRP3 gene located on the long arm of chromosome 1.
Karen K. Hsiao Ashe is a professor at the Department of Neurology and Neuroscience at the University of Minnesota (UMN) Medical School, where she holds the Edmund Wallace and Anne Marie Tulloch Chairs in Neurology and Neuroscience. She is the founding director of the N. Bud Grossman Center for Memory Research and Care, and her specific research interest is memory loss resulting from Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Her research has included the development of an animal model of Alzheimer's.

Plakoglobin, also known as junction plakoglobin or gamma-catenin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JUP gene. Plakoglobin is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to β-catenin. Plakoglobin is a cytoplasmic component of desmosomes and adherens junctions structures located within intercalated discs of cardiac muscle that function to anchor sarcomeres and join adjacent cells in cardiac muscle. Mutations in plakoglobin are associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia.

Presenilins are a family of related multi-pass transmembrane proteins which constitute the catalytic subunits of the gamma-secretase intramembrane protease protein complex. They were first identified in screens for mutations causing early onset forms of familial Alzheimer's disease by Peter St George-Hyslop. Vertebrates have two presenilin genes, called PSEN1 that codes for presenilin 1 (PS-1) and PSEN2 that codes for presenilin 2 (PS-2). Both genes show conservation between species, with little difference between rat and human presenilins. The nematode worm C. elegans has two genes that resemble the presenilins and appear to be functionally similar, sel-12 and hop-1.

C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2 or CD192 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR2 gene. CCR2 is a CC chemokine receptor.
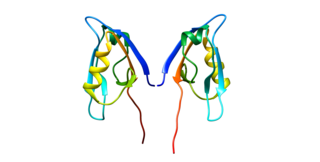
Interleukin 8 receptor, beta is a chemokine receptor. IL8RB is also known as CXCR2, and CXCR2 is now the IUPHAR Committee on Receptor Nomenclature and Drug classification-recommended name.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit alpha (CAMKIIα), a.k.a.Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha, is one subunit of CamKII, a protein kinase (i.e., an enzyme which phosphorylates proteins) that in humans is encoded by the CAMK2A gene.

G-protein coupled receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family of transmembrane receptors and is involved in signal transduction.

G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase subfamily of the Ser/Thr protein kinases, and is most highly similar to GRK4 and GRK6. The protein phosphorylates the activated forms of G protein-coupled receptors to regulate their signaling.

Gail Roberta Martin is an American biologist. She is professor emerita in the Department of Anatomy, University of California, San Francisco. She is known for her pioneering work on the isolation of pluripotent stem cells from normal embryos, for which she coined the term 'embryonic stem cells'. She is widely recognized for her work on the function of fibroblast growth factors and their negative regulators in vertebrate organogenesis. She and her colleagues made contributions to gene targeting technology.
George Musser is a contributing editor for Scientific American magazine in New York and the author of The Complete Idiot’s Guide to String Theory and of Spooky Action at a Distance.
Bruce Martin Russett was an American political scientist who was most well-known for his work on the democratic peace. He was Dean Acheson Professor of Political Science and Professor in International and Area Studies, MacMillan Center, Yale University, and edited the Journal of Conflict Resolution from 1972 to 2009.

PR domain zinc finger protein 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRDM9 gene. PRDM9 is responsible for positioning recombination hotspots during meiosis by binding a DNA sequence motif encoded in its zinc finger domain. PRDM9 is the only speciation gene found so far in mammals, and is one of the fastest evolving genes in the genome.

(Thomas) Michael Dexter FRS is a British haematologist and director of the Wellcome Trust, from 1998 to 2003.
Li-Huei Tsai is an American neuroscientist and the director of the Picower Institute for Learning and Memory in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.

YoungSoo Kim is a South Korean chemist. Kim is an associate professor in Department of Pharmacy at Yonsei University.












