Related Research Articles

Adenylate cyclase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase . It catalyzes the following reaction:

Hemoglobin is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transport of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin in the blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs to the other tissues of the body, where it releases the oxygen to enable aerobic respiration which powers the animal's metabolism. A healthy human has 12 to 20 grams of hemoglobin in every 100 mL of blood. Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein, a chromoprotein, and globulin.

A hemeprotein, or heme protein, is a protein that contains a heme prosthetic group. They are a very large class of metalloproteins. The heme group confers functionality, which can include oxygen carrying, oxygen reduction, electron transfer, and other processes. Heme is bound to the protein either covalently or noncovalently or both.

Heme, or haem, is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecular component of hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. It is composed of four pyrrole rings with 2 vinyl and 2 propionic acid side chains. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver.

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large proportion of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins contain zinc-binding protein domains although there may be up to 3000 human zinc metalloproteins.
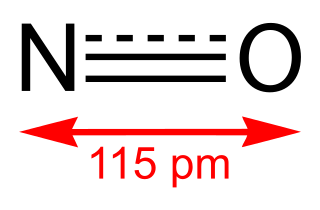
Nitric oxide is a colorless gas with the formula NO. It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula. Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding.

Guanylate cyclase is a lyase enzyme that converts guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and pyrophosphate:
Carboxyhemoglobin is a stable complex of carbon monoxide and hemoglobin (Hb) that forms in red blood cells upon contact with carbon monoxide. Carboxyhemoglobin is often mistaken for the compound formed by the combination of carbon dioxide (carboxyl) and hemoglobin, which is actually carbaminohemoglobin. Carboxyhemoglobin terminology emerged when carbon monoxide was known by its historic name, "carbonic oxide", and evolved through Germanic and British English etymological influences; the preferred IUPAC nomenclature is carbonylhemoglobin.

Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) are a family of enzymes catalyzing the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule. It helps modulate vascular tone, insulin secretion, airway tone, and peristalsis, and is involved in angiogenesis and neural development. It may function as a retrograde neurotransmitter. Nitric oxide is mediated in mammals by the calcium-calmodulin controlled isoenzymes eNOS and nNOS. The inducible isoform, iNOS, involved in immune response, binds calmodulin at physiologically relevant concentrations, and produces NO as an immune defense mechanism, as NO is a free radical with an unpaired electron. It is the proximate cause of septic shock and may function in autoimmune disease.
Bioinorganic chemistry is a field that examines the role of metals in biology. Bioinorganic chemistry includes the study of both natural phenomena such as the behavior of metalloproteins as well as artificially introduced metals, including those that are non-essential, in medicine and toxicology. Many biological processes such as respiration depend upon molecules that fall within the realm of inorganic chemistry. The discipline also includes the study of inorganic models or mimics that imitate the behaviour of metalloproteins.

Heme oxygenase, or haem oxygenase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the degradation of heme to produce biliverdin, ferrous iron, and carbon monoxide.
Gasotransmitters is a class of neurotransmitters. The molecules are distinguished from other bioactive endogenous gaseous signaling molecules based on a need to meet distinct characterization criteria. Currently, only nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide are accepted as gasotransmitters. According to in vitro models, gasotransmitters, like other gaseous signaling molecules, may bind to gasoreceptors and trigger signaling in the cells.

Soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) is one of the gasoreceptors for nitric oxide, NO. It is soluble, i.e. completely intracellular. Most notably, this enzyme is involved in vasodilation. In humans, it is encoded by the genes GUCY1A2, GUCY1A3, GUCY1B2 and GUCY1B3.

Nitric oxide dioxygenase (EC 1.14.12.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of nitric oxide (NO) to nitrate (NO−
3) . The net reaction for the reaction catalyzed by nitric oxide dioxygenase is shown below:

Guanylate cyclase soluble subunit beta-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GUCY1B3 gene.
Biological functions of nitric oxide are roles that nitric oxide plays within biology.
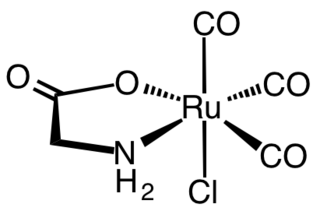
Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs) are chemical compounds designed to release controlled amounts of carbon monoxide (CO). CORMs are being developed as potential therapeutic agents to locally deliver CO to cells and tissues, thus overcoming limitations of CO gas inhalation protocols.
Gaseous signaling molecules are gaseous molecules that are either synthesized internally (endogenously) in the organism, tissue or cell or are received by the organism, tissue or cell from outside and that are used to transmit chemical signals which induce certain physiological or biochemical changes in the organism, tissue or cell. The term is applied to, for example, oxygen, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxide, hydrogen cyanide, ammonia, methane, hydrogen, ethylene, etc.
Hydrogen sulfide is produced in small amounts by some cells of the mammalian body and has a number of biological signaling functions. Only two other such gases are currently known: nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO).

Jonathan Solomon Stamler is an English-born American physician and scientist. He is known for his discovery of protein S-nitrosylation, the addition of a nitric oxide (NO) group to cysteine residues in proteins, as a ubiquitous cellular signal to regulate enzymatic activity and other key protein functions in bacteria, plants and animals, and particularly in transporting NO on cysteines in hemoglobin as the third gas in the respiratory cycle.
References
- 1 2 Chang C (January 2016). "Q&A: How do plants respond to ethylene and what is its importance?". BMC Biology. 14: 7. doi: 10.1186/s12915-016-0230-0 . PMC 4730734 . PMID 26819080.
- 1 2 Farhana A, Saini V, Kumar A, Lancaster JR, Steyn AJ (November 2012). "Environmental heme-based sensor proteins: implications for understanding bacterial pathogenesis". Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 17 (9): 1232–1245. doi:10.1089/ars.2012.4613. PMC 3430476 . PMID 22494151.
- ↑ Taabazuing CY, Hangasky JA, Knapp MJ (April 2014). "Oxygen sensing strategies in mammals and bacteria". Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry. 133: 63–72. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2013.12.010. PMC 4097052 . PMID 24468676.