
The transport system in Rwanda centres primarily around the road network. Paved roads lie between the capital, Kigali, and most other major cities and towns in the country. Rwanda is also linked by road with other countries in the African Great Lakes, via which the majority of the country's imports and exports are made.
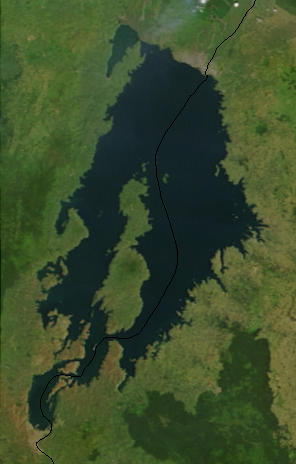
Lake Kivu is one of the African Great Lakes. It lies on the border between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Rwanda, and is in the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift. Lake Kivu empties into the Ruzizi River, which flows southwards into Lake Tanganyika. In 1894, German explorer and officer Gustav Adolf von Götzen was the first European to discover the lake.

Kibuye is a city in Karongi District, and the headquarters of the Western Province in Rwanda.

Gisenyi, historically rendered as Kisenyi, is the second largest city in Rwanda, located in the Rubavu district in Rwanda's Western Province. Gisenyi is contiguous with Goma, the city across the border in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Tourism in Rwanda is the largest source of foreign exchange earnings in Rwanda. It was projected to grow at a rate of 25% every year from 2013–2018. The sector is the biggest contributor to the national export strategy. Total revenue generated from the sector in 2014 alone was USD 305 million.

Bralirwa, also known by its French name Brasseries et Limonaderies du Rwanda, is the largest brewer and soft beverage company in Rwanda. Its shares of stock are listed on the Rwanda Stock Exchange, where they trade under the symbol:BLRW. As of December 2017, the company's total assets were valued at RWF:127.73 billion, with shareholders' equity of RWF:35.7 billion.
The Rusumo Hydroelectric Power Station, also known as the Rusumo Power Station, is a hydropower plant under construction, with initial planned capacity installation of 80 megawatts (110,000 hp) when completed. The project will involve the construction of a dam, with run of river design. A more expensive 90 megawatts (120,000 hp) reservoir design was considered before being abandoned in favor of an 80 MW project with a smaller environmental impact and an estimated cost of US$300 million compared to US$400 million for the bigger project. The World Bank announced on 6 August 2013 that it had approved loans totaling US$340 million towards the US$468.60 million needed for the project. In November 2013, the African Development Bank approved a loan of US$113 million towards completion of the project.
Nyabarongo I Hydroelectric Power Station is a 28 megawatts (38,000 hp) hydroelectric power station in Rwanda.

Silas Stanislaus Bernard Lwakabamba or simply SilasLwakabamba, is a Tanzanian engineer, academic and politician. Since May 2021, he has been serving as the Regional Managing Director of Coventry University African Hub, based in Kigali, Rwanda. Lwakabamba holds a PhD in Mechanical Engineering from University of Leeds in England since 1975. Since 1997, he served as the founding Rector of Rwanda’s Kigali Institute of Science and Technology. In 2006, he was appointed Rector of National University of Rwanda until 2013. Lwakabamba served as Rwanda's Minister of Infrastructure between February 2013 and July 2014, he also served as Rwanda's Minister of Education since July 2014 until June 2015.
The geology of Rwanda comprises Mesoproterozoic metasediments, largely quartzites, sandstones, and shales of the Burundian Supergroup which are locally intruded by granite. There are four types of granite in the Kibaran Belt. In eastern Rwanda are the “older granites” along with granitic-gneisses and migmatites of Palaeoproterozoic age. In the northwest and southwest are Neogene volcanics, ranging in age from Cenozoic to recent. Some of the volcanoes in the area are highly alkaline. Alluvium and lake sediments of Quaternary age occur in parts of the Western Rift and along rivers and lakes.

Energy use in Rwanda is undergoing rapid change at the beginning of the 21st century.
KivuWatt Power Station is a 26 MW (35,000 hp) methane gas-fired thermal power plant in Rwanda.
Rwamagana Solar Power Station is an 8.5MW solar power plant in Rwanda, the fourth-largest economy in the East African Community.
Symbion Thermal Power Station is a 56 megawatts (75,000 hp) methane gas-fired thermal power plant located at the Cape of Busororo near the town of Nyamyumba in Rubavu District, in the Western Province of Rwanda.
Gishoma Thermal Power Station is a 15 MW (20,000 hp), peat-fired thermal power plant, under construction in Gishoma, Rusizi District, in the Western Province of Rwanda.
Kibuye Power Plant 1, also Kibuye Thermal Power Station 1 (KP1), is a 3.6 megawatts (4,800 hp) methane gas-fired thermal power plant in Rwanda.
The Rwanda Standard Gauge Railway is a standard gauge railway (SGR) system, under development, linking the country to the neighboring countries of Tanzania and Uganda. It is intended to ease the transfer of goods between the Indian Ocean ports of Dar es Salaam and Mombasa, and the Rwandan capital Kigali. The system is expected to link, in the future, to Rwanda's two other neighbors, Burundi and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, as part of the East African Railway Master Plan. With no previously existing railway network, Rwanda is developing its railway system from scratch. The project is dependent on the construction of the Tanzanian and Ugandan SGR lines to the Rwandan border, which have not been completed as of October 2023.
Butaro Hospital Cancer Center, or Butaro Cancer Centre of Excellence, is a public, specialized, tertiary care medical facility owned by the Rwanda Ministry of Health.
Ruzizi IV Hydroelectric Power Station, is a proposed hydro-power plant, with planned capacity installation of 287 megawatts (385,000 hp) when completed.







