
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. It is the world's third largest island country with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

The Papuan languages are the non-Austronesian and non-Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan peoples as distinct from Austronesian-speaking Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892.

Lae is the capital of Morobe Province and is the second-largest city in Papua New Guinea. It is located near the delta of the Markham River and at the start of the Highlands Highway, which is the main land transport corridor between the Highlands region and the coast. Lae is the largest cargo port of the country and is the industrial hub of Papua New Guinea. The city is known as the Garden City and home of the University of Technology.
Religion in Papua New Guinea is predominantly Christian, with traditional animism and ancestor worship often occurring less openly as another layer underneath or more openly side by side Christianity. The courts, government, and general society uphold a constitutional right to freedom of speech, thought, and belief. There is no state religion, although the government openly partners with several Christian groups to provide services, and churches participate in local government bodies.
Mailu, or Magi (Magɨ), is a Papuan language of Papua New Guinea.
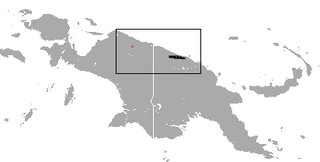
The golden-mantled tree-kangaroo is a species of tree-kangaroo endemic to the Northern New Guinea montane rain forests ecoregion of the island.
The eastern white-eared giant rat is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found only in Papua New Guinea.
Rothschild's woolly rat is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found on the island of New Guinea: both in the West Papua region of Indonesia and Papua New Guinea.

The white-striped dorcopsis or greater forest wallaby is a species of marsupial in the family Macropodidae. It is found in the northern part of West Papua, Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. It is a common species in suitable tropical forest habitat and the IUCN lists its conservation status as being of "Least concern".

Macleay's dorcopsis, also known as the Papuan dorcopsis or the Papuan forest wallaby, is a species of marsupial in the family Macropodidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea, where its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. Being little threatened by habitat destruction, the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated it as being of "least concern".
The Papua New Guinea Post-Courier is a newspaper based in Konedobu, Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea.

The monarchy of Papua New Guinea is a system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of Papua New Guinea. The current monarch, since 16 September 1975, is Queen Elizabeth II. Although the person of the sovereign is equally shared with 14 other independent countries within the Commonwealth of Nations, each country's monarchy is separate and legally distinct. As a result, the current monarch is officially titled the Queen of Papua New Guinea and, in this capacity, she and other members of the Royal Family undertake public and private functions domestically and abroad as representatives of the Papua New Guinean state. However, the Queen is the only member of the Royal Family with any constitutional role. The Queen lives predominantly in the United Kingdom and, while several powers are the sovereign's alone, most of the royal governmental and ceremonial duties in Papua New Guinea are carried out by the Queen's representative, the governor-general.

The Kainantu–Goroka language are a family of Papuan languages established by Arthur Capell in 1948 under the name East Highlands. They formed the core of Stephen Wurm's 1960 East New Guinea Highlands family, and are one of the larger branches of Trans–New Guinea in the 2005 classification of Malcolm Ross.

The Engan, or more precisely Enga – Southern Highland languages are a small family of Papuan languages of the highlands of Papua New Guinea. The two branches of the family are rather distantly related, but were connected by Franklin and Voorhoeve (1973).

The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul, Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, Meganesia, or Papualand to distinguish it from the country of Australia, consists of the landmasses located next to Wallacea. The name "Sahul" takes its name from the Sahul Shelf, which is part of the continental shelf of the Australian continent. The continent includes mainland Australia, Tasmania, the island of New Guinea, the Aru Islands, the Ashmore and Cartier Islands, most of the Coral Sea Islands, and some other offshore continental islands. Situated in the geographical region of Oceania, Australia is the smallest of the seven traditional continents.
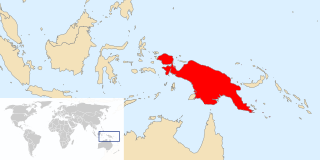
New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, and with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi), the largest island in the Southern Hemisphere. Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, it is separated by the 150 km wide Torres Strait from Australia. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua and West Papua. The largest cities on the island are Jayapura and Port Moresby.
Telefol is a language spoken by the Telefol people in Papua New Guinea, notable for possessing a base-27 numeral system.

Mpur, is a language isolate spoken in and around Mpur and Amberbaken Districts in Tambrauw Regency of the Bird's Head Peninsula, New Guinea. It is not closely related to any other language, and though Ross (2005) tentatively assigned it to the West Papuan languages, based on similarities in pronouns, Palmer (2018), Ethnologue, and Glottolog list it as a language isolate.

Dowsett is a suburb of Lae in the Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea.

The Tua River is a tributary of the Purari River of Papua New Guinea. It originates in the Eastern Highlands Province and flows through the highlands of the Simbu Province, where it joins the Pio River, giving rise to the Purari.














