
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi GCVO was an Italian inventor, electrical engineer, and politician, known for his creation of a practical radio wave–based wireless telegraph system. This led to Marconi's being credited as the inventor of radio, and he shared the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy". His work laid the foundation for the development of radio, television, and all modern wireless communication systems.
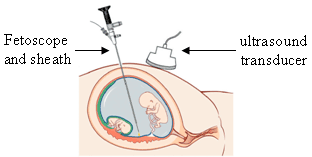
An endoscope is an inspection instrument composed of image sensor, optical lens, light source and mechanical device, which is used to look deep into the body by way of openings such as the mouth or anus. A typical endoscope applies several modern technologies including optics, ergonomics, precision mechanics, electronics, and software engineering. With an endoscope, it is possible to observe lesions that cannot be detected by X-ray, making it useful in medical diagnosis. Endoscopes use tubes which are only a few millimeters thick to transfer illumination in one direction and high-resolution images in real time in the other direction, resulting in minimally invasive surgeries. It is used to examine the internal organs like the throat or esophagus. Specialized instruments are named after their target organ. Examples include the cystoscope (bladder), nephroscope (kidney), bronchoscope (bronchus), arthroscope (joints) and colonoscope (colon), and laparoscope. They can be used to examine visually and diagnose, or assist in surgery such as an arthroscopy.

Paul Baran was an American-Jewish engineer who was a pioneer in the development of computer networks. He was one of the two independent inventors of packet switching, which is today the dominant basis for data communications in computer networks worldwide, and went on to start several companies and develop other technologies that are an essential part of modern digital communication.

Steven J. Sasson is an American electrical engineer and the inventor of the self-contained (portable) digital camera. He joined Kodak shortly after his graduation from engineering school and retired from Kodak in 2009.

In the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, encapsulation refers to a range of dosage forms—techniques used to enclose medicines—in a relatively stable shell known as a capsule, allowing them to, for example, be taken orally or be used as suppositories. The two main types of capsules are:
Enteroscopy is the procedure of using an endoscope for the direct visualization of the small bowel. Etymologically, the word could potentially refer to any bowel endoscopy, but idiomatically it is conventionally restricted to small bowel endoscopy, in distinction from colonoscopy, which is large bowel endoscopy. Various types of enteroscopy exist, as follows:

Martin Cooper is an American engineer. He is a pioneer in the wireless communications industry, especially in radio spectrum management, with eleven patents in the field.

Capsule endoscopy is a medical procedure used to record internal images of the gastrointestinal tract for use in disease diagnosis. Newer developments are also able to take biopsies and release medication at specific locations of the entire gastrointestinal tract. Unlike the more widely used endoscope, capsule endoscopy provides the ability to see the middle portion of the small intestine. It can be applied to the detection of various gastrointestinal cancers, digestive diseases, ulcers, unexplained bleedings, and general abdominal pains. After a patient swallows the capsule, it passes along the gastrointestinal tract, taking a number of images per second which are transmitted wirelessly to an array of receivers connected to a portable recording device carried by the patient. General advantages of capsule endoscopy over standard endoscopy include the minimally invasive procedure setup, ability to visualize more of the gastrointestinal tract, and lower cost of the procedure.
Eric R. Fossum is an Emmy award-winning American engineer and professor, who co-developed some of the active pixel image sensor with intra-pixel charge transfer, with the help of other scientists from the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. He is currently a professor at Thayer School of Engineering in Dartmouth College.
Wireless Home Digital Interface (WHDI) is a consumer electronic specification for a wireless HDTV connectivity throughout the home.

Yossi Gross is an Israeli inventor and entrepreneur. He is a founding partner of Rainbow Medical, an operational investment company, established to launch companies based on the technological ideas and inventions of Gross. Yossi Gross is the founder of multiple medical device companies based on his various inventions in active implantables, neurostimulation, signal processing, nanotechnology, and drug delivery. Gross's various companies have developed or are currently developing treatments for diabetes, gastroenterology, stroke, ophthalmology, asthma, congestive heart failure, and urology. Gross has over 800 filed patents. Companies based on his inventions collectively garnered over $1B dollars in acquisitions.

Given Imaging is an Israeli medical technology company that manufactures and markets diagnostic products for the visualization and detection of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Until March 2014, it was dual-listed on both the NASDAQ and the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange, where it was a component of the TA-100 Index and the TA BlueTech Index. In March 2014 it was acquired by Covidien and became a private company. In 2015 Covidien was purchased by Medtronic.

Start-up Nation: The Story of Israel's Economic Miracle is a 2009 book by Dan Senor and Saul Singer about the economy of Israel. It examines how Israel, a 60-year-old nation with a population of 7.1 million, was able to reach such economic growth that "at the start of 2009, some 63 Israeli companies were listed on the NASDAQ, more than those of any other foreign country."
Blair S. Lewis, M.D., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.G., is an American board-certified gastroenterologist and Clinical Professor of Medicine at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine. Lewis is a specialist in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy and was the primary investigator for the first clinical trial of capsule endoscopy for the small intestine and also the first clinical trial of capsule endoscopy for the colon.

Ramesh Raskar is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology associate professor and head of the MIT Media Lab's Camera Culture research group. Previously he worked as a senior research scientist at Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) during 2002 to 2008. He holds 132 patents in computer vision, computational health, sensors and imaging. He received the $500K Lemelson–MIT Prize in 2016. The prize money will be used for launching REDX.io, a group platform for co-innovation in Artificial Intelligence. He is well known for inventing EyeNetra, EyeCatra and EyeSelfie, Femto-photography and his TED talk for cameras to see around corners.
Philip Augustine, an Indian gastroenterologist, specialist in gastrointestinal endoscopy and a hospital administrator from Ernakulam, Kerala. He founded the Lakeshore Hospital and Research Centre in 2003. In 2010, the Government of India honoured him with the Padma Shri, for his services to the fields of medicine.
Architectural endoscopy or architectural envisioning is used to photograph and film models of new buildings' exterior and interior in the planning stage. An architectural model of a new building in a 1:500 scale is thus correctly visualized from the perspective of a pedestrian walking by in the street. An endoscope connected to a video camera allows for the creation of walkthroughs, allowing the architect to develop the first draft further, and the public to share and critique the architect's vision of proposed buildings and cities.
A digital pill is a pharmaceutical dosage form that contains an ingestible sensor inside of a pill. The sensor begins transmitting medical data after it is consumed. The technology that makes up the pill, as well as the data transmitted by the pill's sensor, are considered to be part of digital medicine. The purpose of the sensor is to determine whether the person is taking their medication or not.

Roy Iddan is an Israeli screenwriter and television actor. Winner of the Awards of the Israeli Television Academy for 2020.










